| [1] |
PAIK JM, GOLABI P, YOUNOSSI Y, et al. Changes in the global burden of chronic liver diseases from 2012 to 2017: The growing impact of NAFLD[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 5): 1605- 1616. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31173. |
| [2] |
NOUREDDIN M, VIPANI A, BRESEE C, et al. NASH leading cause of liver transplant in women: Updated analysis of indications for liver transplant and ethnic and gender variances[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2018, 113( 11): 1649- 1659. DOI: 10.1038/s41395-018-0088-6. |
| [3] |
LI J, ZOU BY, YEO YH, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4( 5): 389- 398. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1. |
| [4] |
YOUNOSSI Z, ANSTEE QM, MARIETTI M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15( 1): 11- 20. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109. |
| [5] |
SHEKA AC, ADEYI O, THOMPSON J, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323( 12): 1175- 1183. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.2298. |
| [6] |
ZHAO YC, GAO LC, JIANG CL, et al. The transcription factor zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 alleviates NASH by transcriptional activation of phosphatase and tensin homolog[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 75( 4): 939- 954. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32165. |
| [7] |
LENG YR, ZHANG MH, LUO JG, et al. Pathogenesis of NASH and promising natural products[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2021, 19( 1): 12- 27. DOI: 10.1016/S1875-5364(21)60002-X. |
| [8] |
FRIEDMAN SL, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI BA, RINELLA M, et al. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24( 7): 908- 922. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9. |
| [9] |
SUTTI S, ALBANO E. Adaptive immunity: An emerging player in the progression of NAFLD[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17( 2): 81- 92. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0210-2. |
| [10] |
PROKHNEVSKA N, CARDENAS MA, VALANPARAMBIL RM, et al. CD8 + T cell activation in cancer comprises an initial activation phase in lymph nodes followed by effector differentiation within the tumor[J]. Immunity, 2023, 56( 1): 107- 124.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.12.002. |
| [11] |
SUN QL, CAI DL, LIU DF, et al. BCL6 promotes a stem-like CD8 + T cell program in cancer via antagonizing BLIMP1[J]. Sci Immunol, 2023, 8( 88): eadh1306. DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adh1306. |
| [12] |
SUN LN, SU YH, JIAO AJ, et al. T cells in health and disease[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8( 1): 235. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01471-y. |
| [13] |
BAI L, XIN YJ, DUAN DY, et al. Advances in macrophage function and its anti-inflammatory and proresolving activity and role in periodontitis development[J]. West China J Stomatol, 2017, 35( 4): 427- 432. DOI: 10.7518/hxkq.2017.04.016. |
| [14] |
AICHELE P, NEUMANN-HAEFELIN C, EHL S, et al. Immunopathology caused by impaired CD8 + T-cell responses[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2022, 52( 9): 1390- 1395. DOI: 10.1002/eji.202149528. |
| [15] |
RITTER AT, SHTENGEL G, XU CS, et al. ESCRT-mediated membrane repair protects tumor-derived cells against T cell attack[J]. Science, 2022, 376( 6591): 377- 382. DOI: 10.1126/science.abl3855. |
| [16] |
ZHAO WJ, ZHU Y, LU ZX. Radix tetrastigme polysaccharide promotes antitumor immune response in lewis lung cancer mice[J]. Chin J Lung Cancer, 2023, 26( 8): 559- 571. DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.106.16. |
| [17] |
GLUKHOVA XA, TRIZNA JA, PROUSSAKOVA OV, et al. Impairment of Fas-ligand-caveolin-1 interaction inhibits Fas-ligand translocation to rafts and Fas-ligand-induced cell death[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9( 2): 73. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-017-0109-1. |
| [18] |
WILSON NS, DIXIT V, ASHKENAZI A. Death receptor signal transducers: Nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks[J]. Nat Immunol, 2009, 10( 4): 348- 355. DOI: 10.1038/ni.1714. |
| [19] |
POBEZINSKAYA YL, LIU ZG. The role of TRADD in death receptor signaling[J]. Cell Cycle, 2012, 11( 5): 871- 876. DOI: 10.4161/cc.11.5.19300. |
| [20] |
HOLBROOK J, LARA-REYNA S, JAROSZ-GRIFFITHS H, et al. Tumour necrosis factor signalling in health and disease[J]. F1000Res, 2019, 8: F1000 Faculty Rev-111. DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.17023.1. |
| [21] |
CHADWICK W, MAGNUS T, MARTIN B, et al. Targeting TNF-alpha receptors for neurotherapeutics[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2008, 31( 10): 504- 511. DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.07.005. |
| [22] |
HAMMERICH L, TACKE F. Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20( 10): 633- 646. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-023-00807-x. |
| [23] |
DUAN HX, JING L, XIANG JQ, et al. CD146 associates with Gp130 to control a macrophage pro-inflammatory program that regulates the metabolic response to obesity[J]. Adv Sci, 2022, 9( 13): e2103719. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202103719. |
| [24] |
NISHIMURA S, MANABE I, NAGASAKI M, et al. CD8 + effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity[J]. Nat Med, 2009, 15( 8): 914- 920. DOI: 10.1038/nm.1964. |
| [25] |
DUFFAUT C, GALITZKY J, LAFONTAN M, et al. Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009, 384( 4): 482- 485. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.002. |
| [26] |
KIRAN S, KUMAR V, MURPHY EA, et al. High fat diet-induced CD8 + T cells in adipose tissue mediate macrophages to sustain low-grade chronic inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 680944. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680944. |
| [27] |
RUF B, GRETEN TF, KORANGY F. Innate lymphoid cells and innate-like T cells in cancer- at the crossroads of innate and adaptive immunity[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23( 6): 351- 371. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-023-00562-w. |
| [28] |
MARICIC I, MARRERO I, EGUCHI A, et al. Differential activation of hepatic invariant NKT cell subsets plays a key role in progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201( 10): 3017- 3035. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800614. |
| [29] |
BHATTACHARJEE J, KIRBY M, SOFTIC S, et al. Hepatic natural killer T-cell and CD8 + T-cell signatures in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2017, 1( 4): 299- 310. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1041. |
| [30] |
DENG T, LYON CJ, MINZE LJ, et al. Class II major histocompatibility complex plays an essential role in obesity-induced adipose inflammation[J]. Cell Metab, 2013, 17( 3): 411- 422. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.02.009. |
| [31] |
FERNANDEZ-RUIZ D, NG WY, HOLZ LE, et al. Liver-resident memory CD8 + T cells form a front-line defense against malaria liver-stage infection[J]. Immunity, 2019, 51( 4): 780. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.09.019. |
| [32] |
TOPHAM DJ, REILLY EC. Tissue-resident memory CD8 + T cells: From phenotype to function[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 515. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00515. |
| [33] |
KHAN O, GILES JR, MCDONALD S, et al. TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8 + T cell exhaustion[J]. Nature, 2019, 571( 7764): 211- 218. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1325-x. |
| [34] |
ALFEI F, KANEV K, HOFMANN M, et al. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection[J]. Nature, 2019, 571( 7764): 265- 269. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1326-9. |
| [35] |
LEONARD WJ, LIN JX, O’SHEA JJ. The γ c family of cytokines: Basic biology to therapeutic ramifications[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50( 4): 832- 850. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.028. |
| [36] |
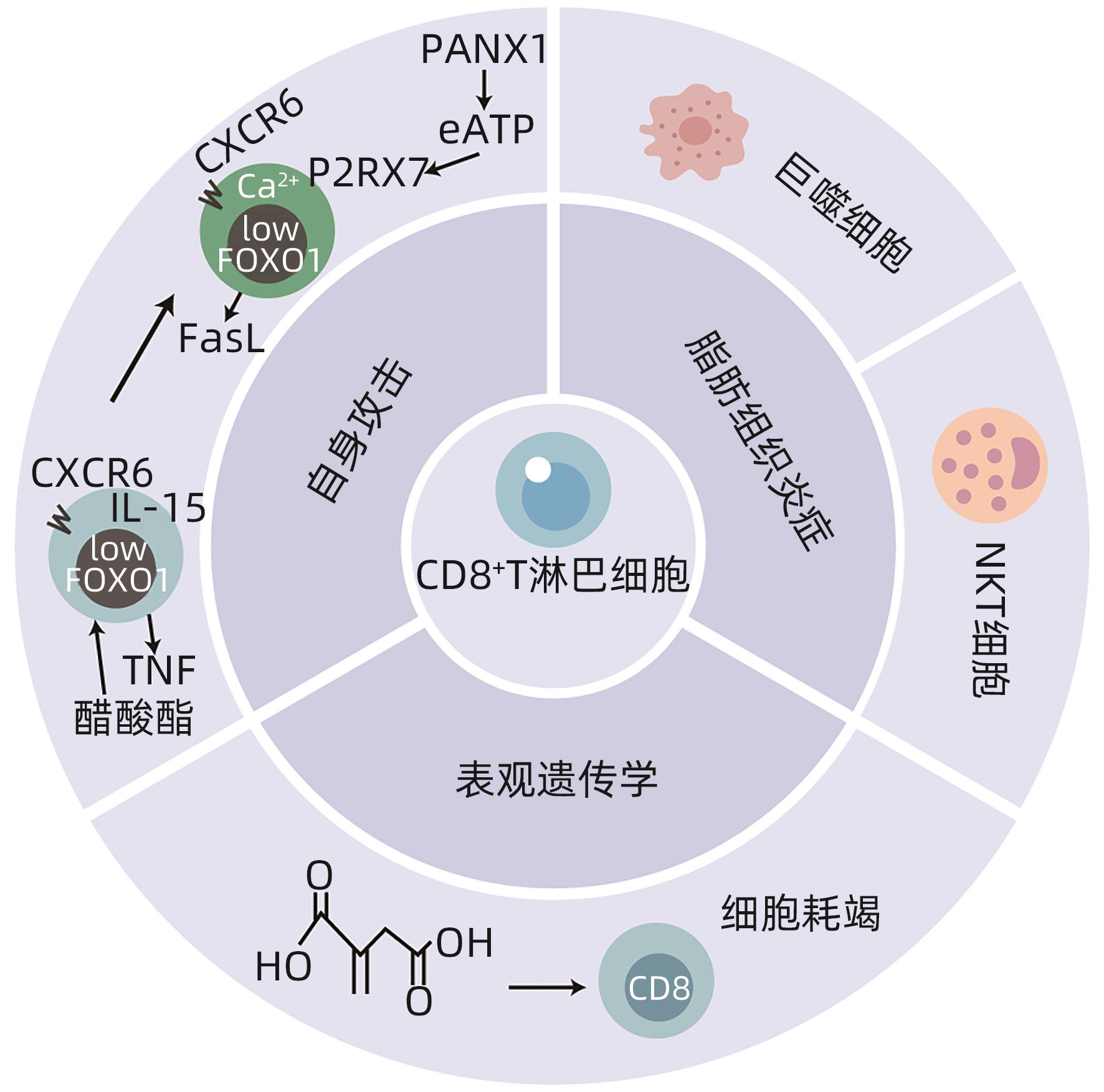
DUDEK M, PFISTER D, DONAKONDA S, et al. Auto-aggressive CXCR6 + CD8 T cells cause liver immune pathology in NASH[J]. Nature, 2021, 592( 7854): 444- 449. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03233-8. |
| [37] |
LINDEN J, KOCH-NOLTE F, DAHL G. Purine release, metabolism, and signaling in the inflammatory response[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2019, 37: 325- 347. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052406. |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
LUO CY, HAJKOVA P, ECKER JR. Dynamic DNA methylation: In the right place at the right time[J]. Science, 2018, 361( 6409): 1336- 1340. DOI: 10.1126/science.aat6806. |
| [40] |
PANG BR, SUI SY, WANG Q, et al. Upregulation of DLEU1 expression by epigenetic modification promotes tumorigenesis in human cancer[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234( 10): 17420- 17432. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28364. |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
STEPANOV AI, BESEDOVSKAIA ZV, MOSHAREVA MA, et al. Studying chromatin epigenetics with fluorescence microscopy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 16): 8988. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23168988. |
| [43] |
KIMURA M, IGUCHI T, IWASAWA K, et al. En masse organoid phenotyping informs metabolic-associated genetic susceptibility to NASH[J]. Cell, 2022, 185( 22): 4216- 4232. e 16. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.031. |
| [44] |
FORD BR, POHOLEK AC. Regulation and immunotherapeutic targeting of the epigenome in exhausted CD8 T cell responses[J]. J Immunol, 2023, 210( 7): 869- 879. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200681. |
| [45] |
ZHAO HY, TENG D, YANG LF, et al. Myeloid-derived itaconate suppresses cytotoxic CD8 + T cells and promotes tumour growth[J]. Nat Metab, 2022, 4( 12): 1660- 1673. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00676-9. |
| [46] |
GLOBIG AM, ZHAO S, ROGINSKY J, et al. The β 1-adrenergic receptor links sympathetic nerves to T cell exhaustion[J]. Nature, 2023, 622( 7982): 383- 392. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06568-6. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: