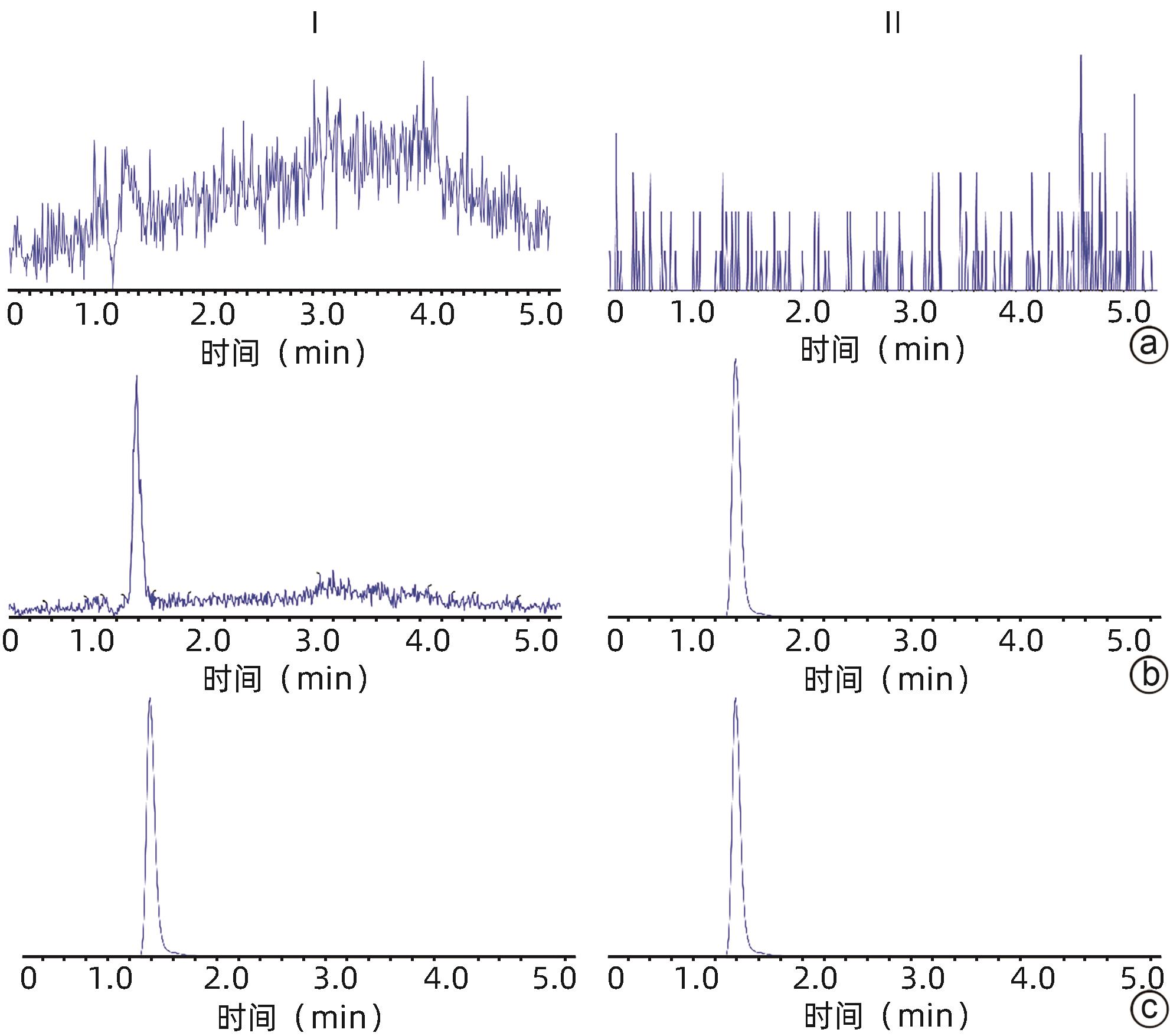
| [1] |
LI JJ, YANG HH, HUO G. Analysis of clinical features,cell morphology and prognostic factors in patients with primary liver cancer[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2024, 23( 6): 566- 570. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2024.06.002. |
| [2] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. |
| [3] |
LI J, ZHANG YJ, XIA JL. Interpretation of NCCN clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma, version 1.2023[J]. J Pract Oncol, 2023, 38( 5): 408- 415. DOI: 10.13267/j.cnki.syzlzz.2023.064. |
| [4] |
XU HC, WANG FL, XIE LH. Current status and perspectives in clinical treatment of intermediate and advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2024, 40( 1): 103- 107. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2024.01.024. |
| [5] |
AL-SALAMA ZT, SYED YY, SCOTT LJ. Lenvatinib: A review in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Drugs, 2019, 79( 6): 665- 674. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-019-01116-x. |
| [6] |
ZHAO Y, ZHANG YN, WANG KT, et al. Lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma: From preclinical mechanisms to anti-cancer therapy[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2020, 1874( 1): 188391. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188391. |
| [7] |
LI JM, WANG XQ, NING C, et al. Influences of ABC transporter and CYP3A4/5 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib in Chinese healthy subjects[J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 76( 8): 1125- 1133. DOI: 10.1007/s00228-020-02879-z. |
| [8] |
OZEKI T, NAGAHAMA M, FUJITA K, et al. Influence of CYP3A4/5 and ABC transporter polymorphisms on lenvatinib plasma trough concentrations in Japanese patients with thyroid cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 5404. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41820-y. |
| [9] |
YANG XR, SUN HC, XIE Q, et al. Chinese expert guidance on overall application of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 2): 167- 180. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20230201-00035. |
| [10] |
FOGLI S, GIANFILIPPO G, CUCCHIARA F, et al. Clinical pharmacology and drug-drug interactions of lenvatinib in thyroid cancer[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2021, 163: 103366. DOI: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103366. |
| [11] |
KIM BH, YU SJ, KANG W, et al. Expert consensus on the management of adverse events in patients receiving lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37( 3): 428- 439. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15727. |
| [12] |
WALIANY S, SAINANI KL, PARK LS, et al. Increase in blood pressure associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting vascular endothelial growth factor[J]. JACC CardioOncol, 2019, 1( 1): 24- 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2019.08.012. |
| [13] |
CHEN SJ, KUANG ZM, YUAN H, et al. Advances in research on interactions between amlodipine and other drugs[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 19( 6): 701- 706.
陈沈珏, 匡泽民, 袁洪, 等. 氨氯地平与其他药物的相互作用研究进展[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2014, 19( 6): 701- 706.
|
| [14] |
ZHU YL, WANG F, LI Q, et al. Amlodipine metabolism in human liver microsomes and roles of CYP3A4/5 in the dihydropyridine dehydrogenation[J]. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014, 42( 2): 245- 249. DOI: 10.1124/dmd.113.055400. |
| [15] |
NAIK KN, JHAJHARIA K, CHAUDHARY R, et al. Multidrug resistance 1 gene polymorphism in amlodipine-induced gingival enlargement[J]. J Indian Soc Periodontol, 2015, 19( 2): 239- 241. DOI: 10.4103/0972-124X.145837. |
| [16] |
DARVARI R, BOROUJERDI M. Concentration dependency of modulatory effect of amlodipine on P-glycoprotein efflux activity of doxorubicin: A comparison with tamoxifen[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2004, 56( 8): 985- 991. DOI: 10.1211/0022357043941. |
| [17] |
TAKARA K, MATSUBARA M, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Differential effects of calcium antagonists on ABCG2/BCRP-mediated drug resistance and transport in SN-38-resistant HeLa cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2012, 5( 3): 603- 609. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2011.734. |
| [18] |
ZHOU YN, ZHANG BK, LI J, et al. Effect of amlodipine on the pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in rats[J]. Xenobiotica, 2013, 43( 8): 699- 704. DOI: 10.3109/00498254.2012.756992. |
| [19] |
KUZUYA T, KOBAYASHI T, MORIYAMA N, et al. Amlodipine, but not MDR1 polymorphisms, alters the pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine A in Japanese kidney transplant recipients[J]. Transplantation, 2003, 76( 5): 865- 868. DOI: 10.1097/01.TP.0000084873.20157.67. |
| [20] |
CUI YJ, LI Y, FAN LJ, et al. UPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of Lenvatinib in rat plasma and its application to drug-drug interaction studies[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2021, 206: 114360. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2021.114360. |
| [21] |
CUI YJ, LI Y, GUO CH, et al. Pharmacokinetic interactions between canagliflozin and sorafenib or lenvatinib in rats[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27( 17): 5419. DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175419. |
| [22] |
CUI YJ, MA YL, LI Y, et al. Influence of schisantherin A on the pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib in rats and its potential mechanism[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 13( 2): 802- 811. DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-174. |
| [23] |
CUI YJ, LI Y, LI X, et al. A simple UPLC/MS-MS method for simultaneous determination of lenvatinib and telmisartan in rat plasma, and its application to pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction study[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27( 4): 1291. DOI: 10.3390/molecules27041291. |
| [24] |
|



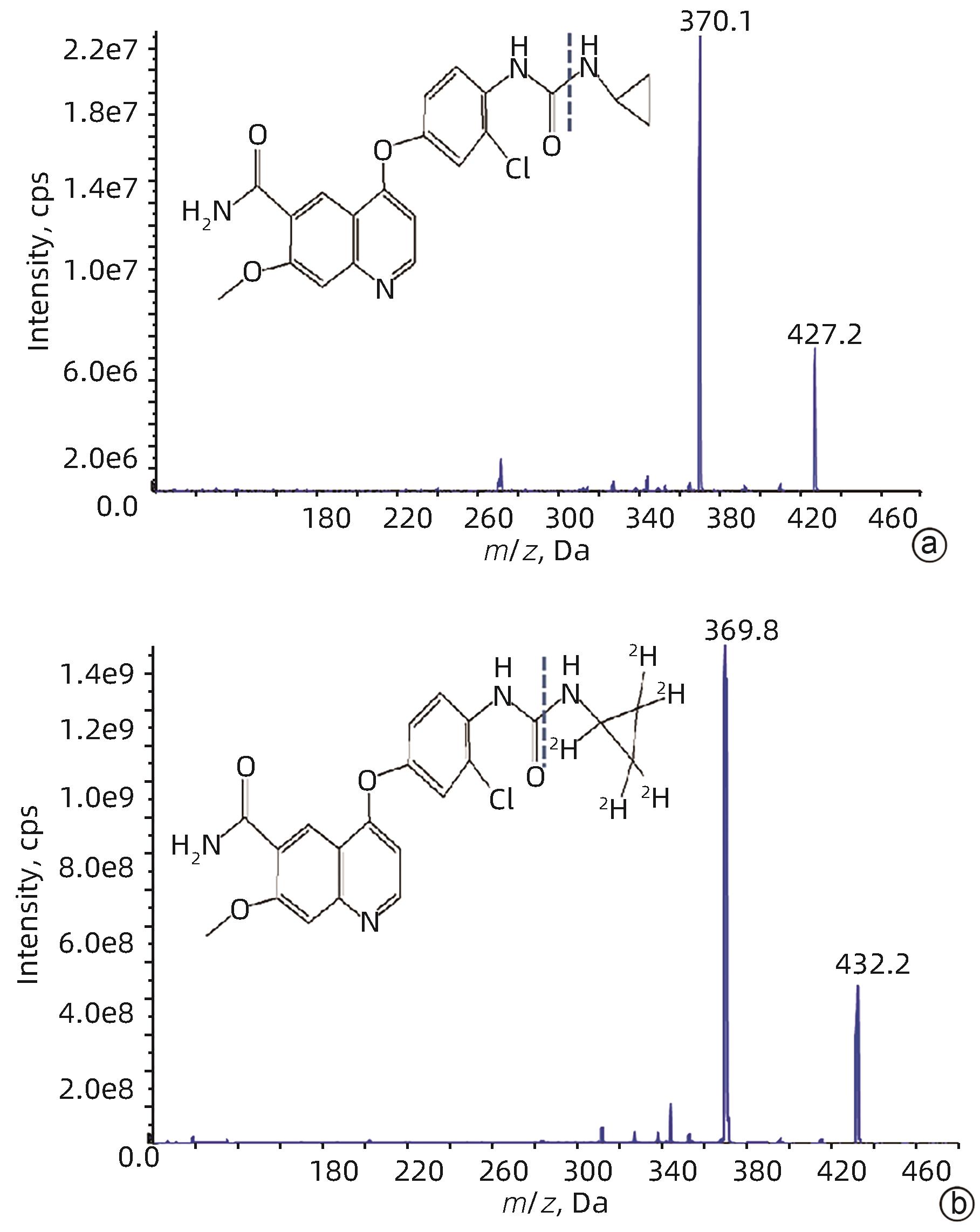




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: