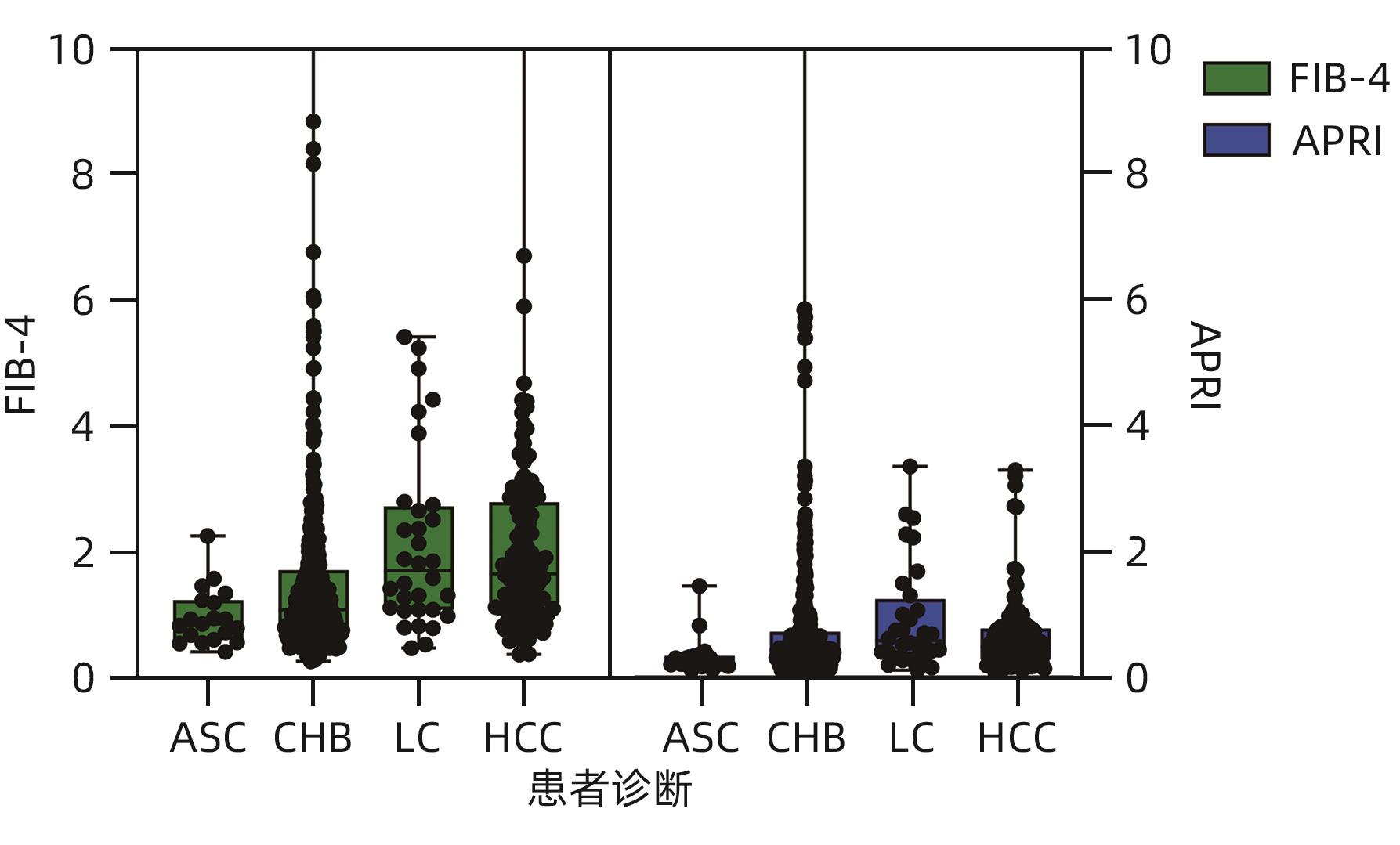
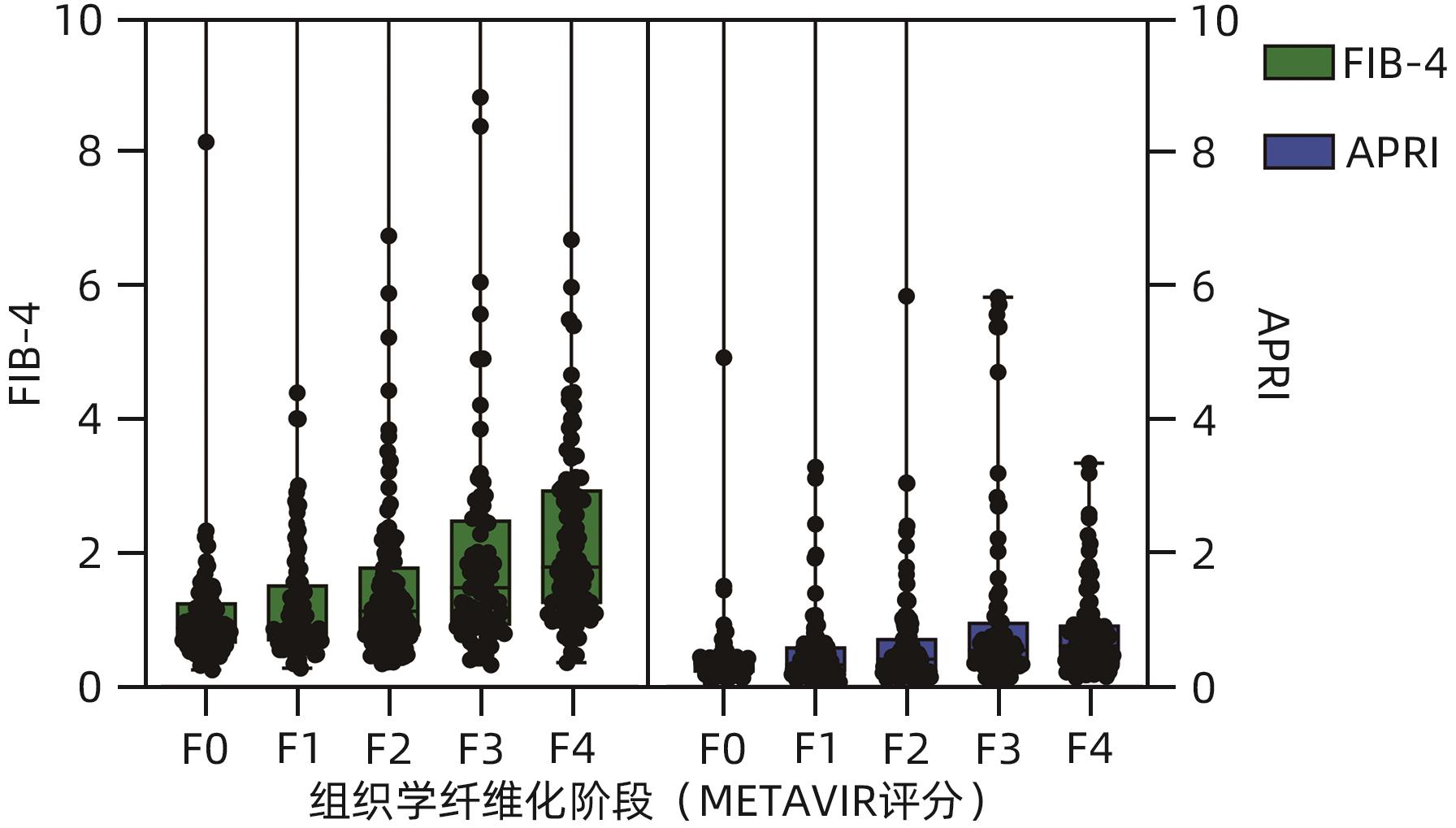
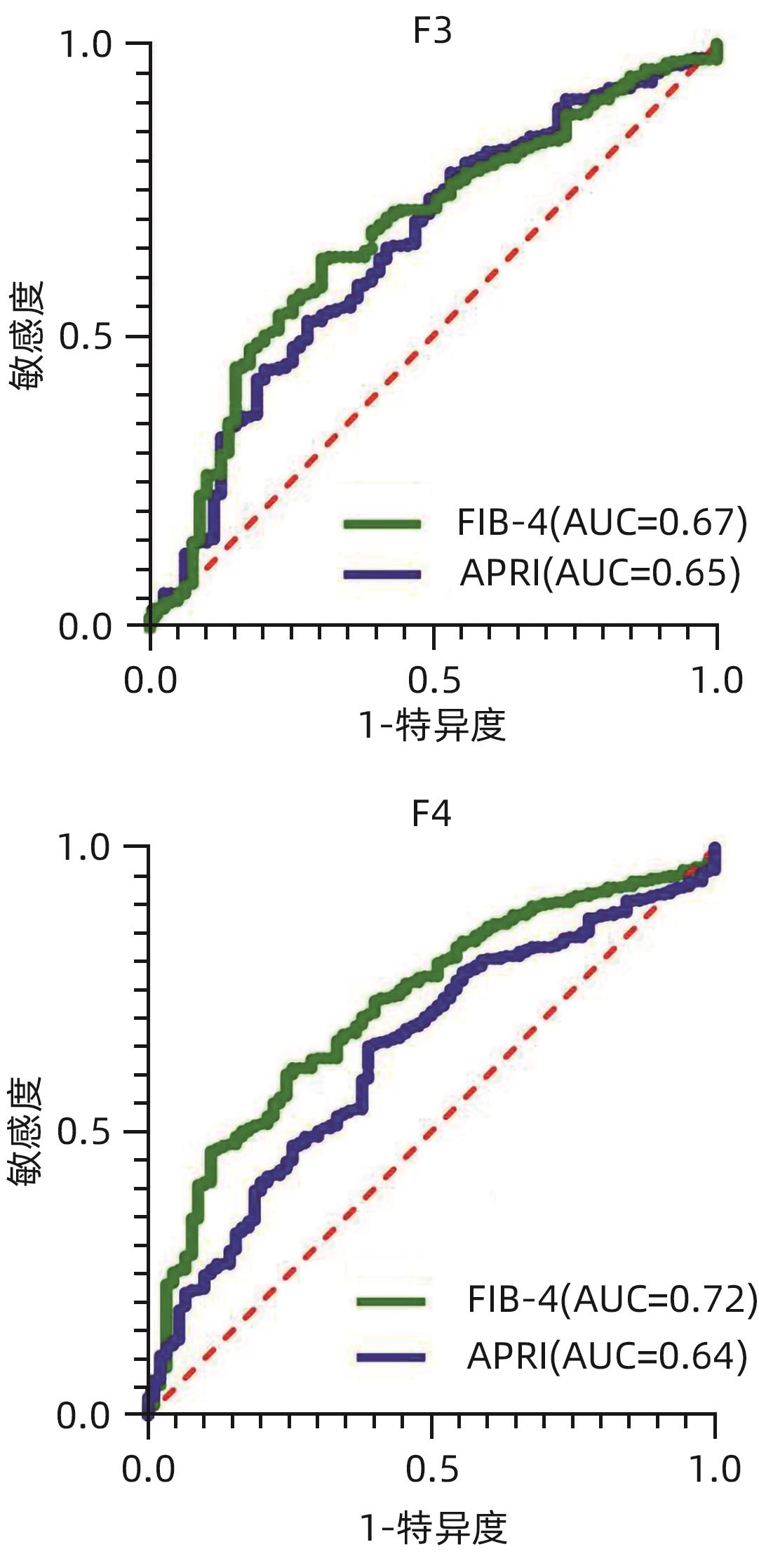
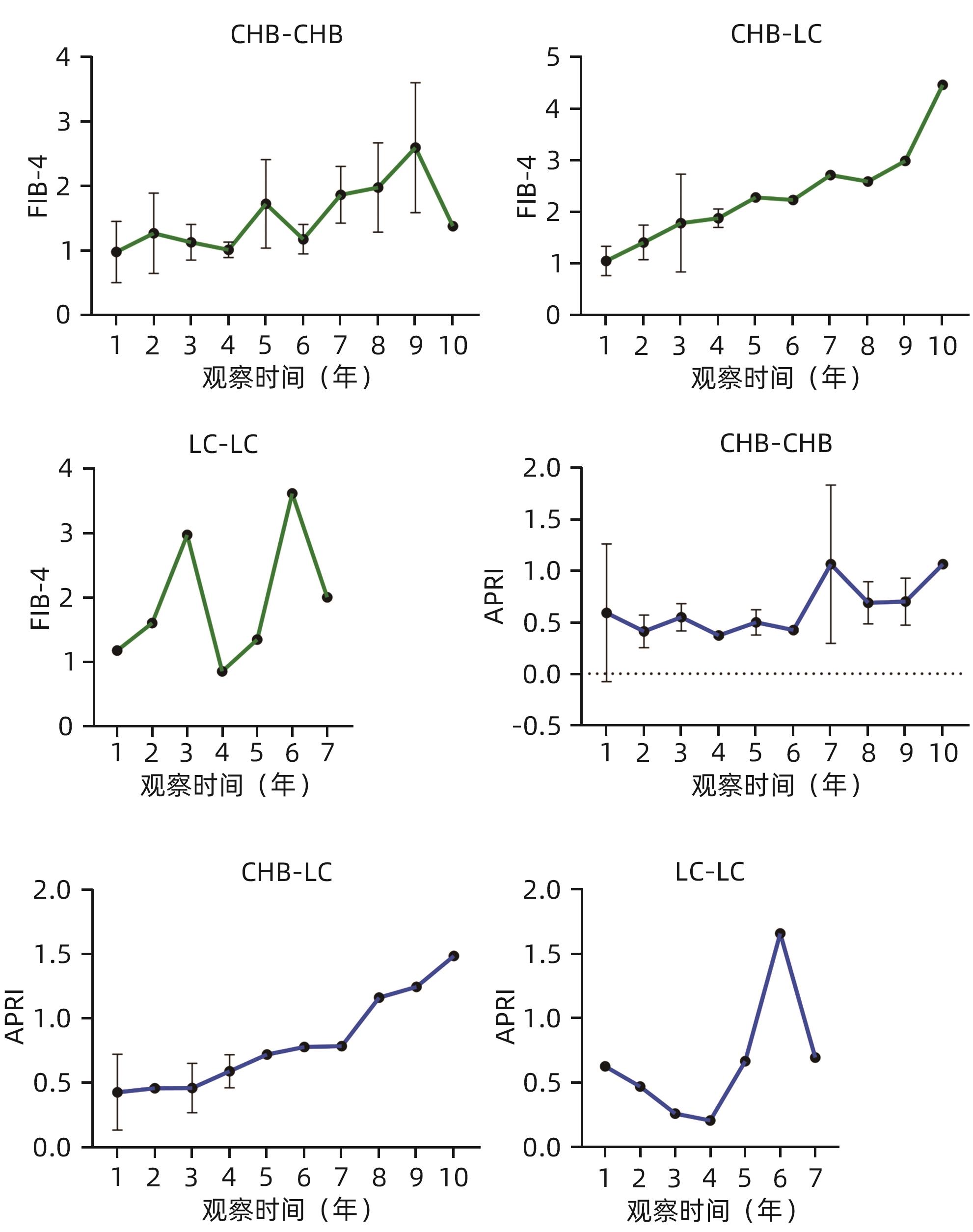
| [1] |
ROEHLEN N, CROUCHET E, BAUMERT TF. Liver fibrosis: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 4): 875. DOI: 10.3390/cells9040875. |
| [2] |
SETO WK, LO YR, PAWLOTSKY JM, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392( 10161): 2313- 2324. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31865-8. |
| [3] |
KUMARI B, KUMAR R, SHARMA S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of FIB-4 and FIB-5 scores as compared to fibroscan for assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cureus, 2021, 13( 8): e17622. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.17622. |
| [4] |
DAY JW, ROSENBERG WM. The enhanced liver fibrosis(ELF) test in diagnosis and management of liver fibrosis[J]. Br J Hosp Med(Lond), 2018, 79( 12): 694- 699. DOI: 10.12968/hmed.2018.79.12.694. |
| [5] |
SINGH S, MUIR AJ, DIETERICH DT, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the role of elastography in chronic liver diseases[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152( 6): 1544- 1577. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.016. |
| [6] |
ITAKURA J, KUROSAKI M, SETOYAMA H, et al. Applicability of APRI and FIB-4 as a transition indicator of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2021, 56( 5): 470- 478. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-021-01782-3. |
| [7] |
SHAH AG, LYDECKER A, MURRAY K, et al. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2009, 7( 10): 1104- 1112. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.05.033. |
| [8] |
RASMUSSEN DN, THIELE M, JOHANSEN S, et al. Prognostic performance of 7 biomarkers compared to liver biopsy in early alcohol-related liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 5): 1017- 1025. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.037. |
| [9] |
LU M, LI J, ZHANG T, et al. Serum biomarkers indicate long-term reduction in liver fibrosis in patients with sustained virological response to treatment for HCV infection[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 14( 7): 1044- 1055. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.01.009. |
| [10] |
SCHMID P, BREGENZER A, HUBER M, et al. Progression of liver fibrosis in HIV/HCV co-infection: a comparison between non-invasive assessment methods and liver biopsy[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10( 9): e0138838. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138838. |
| [11] |
GORDON SC, LAMERATO LE, RUPP LB, et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection and development of hepatocellular carcinoma in a US population[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 12( 5): 885- 893. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.062. |
| [12] |
LI J, GORDON SC, RUPP LB, et al. Long-term progression of viral load and serum markers of fibrosis among treated and untreated patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 32( 6): 1250- 1257. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13667. |
| [13] |
LI Q, REN X, LU C, et al. Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 for noninvasive assessment of significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in HBeAg-negative CHB patients with ALT ≤2 ULN: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2017, 96( 12): e6336. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006336. |
| [14] |
XIAO G, YANG J, YAN L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systemic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 1): 292- 302. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27382. |
| [15] |
GRAF C, MONDORF A, KNOP V, et al. Evaluation of point shear wave elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for longitudinal fibrosis assessment in patients with HBeAg-negative hbv infection[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8( 12): 2101. DOI: 10.3390/jcm8122101. |
| [16] |
SANAI FM, FARAH T, ALBELADI K, et al. Diminished accuracy of biomarkers of fibrosis in low replicative chronic hepatitis B[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2017, 17( 1): 101. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-017-0658-x. |
| [17] |
AMERNIA B, MOOSAVY SH, BANOOKH F, et al. FIB-4, APRI, and AST/ALT ratio compared to FibroScan for the assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Bandar Abbas, Iran[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21( 1): 453. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-02038-3. |
| [18] |
SHIHA G, SEIF S, ELDESOKY A, et al. A simple bedside blood test(Fibrofast; FIB-5) is superior to FIB-4 index for the differentiation between non-significant and significant fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11( 3): 286- 291. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9796-z. |
| [19] |
GRAUPERA I, THIELE M, SERRA-BURRIEL M, et al. Low accuracy of FIB-4 and NAFLD fibrosis scores for screening for liver fibrosis in the population[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20( 11): 2567- 2576. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.034. |
| [20] |
HAYMART MR, MILLER DC, HAWLEY ST. Active surveillance for low-risk cancers-a viable solution to overtreatment?[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377( 3): 203- 206. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMp1703787. |
| [21] |
JOHANSSON M, JØRGENSEN KJ, BRODERSEN J. The benefits of screening-and its harms[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388( 10044): 563- 564. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31219-3. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: