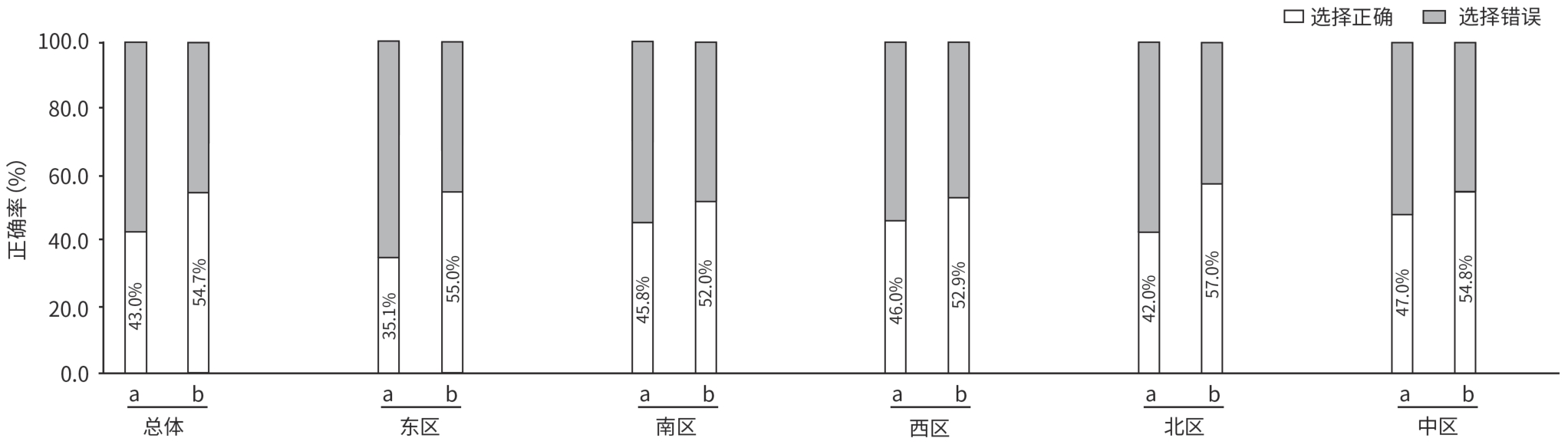
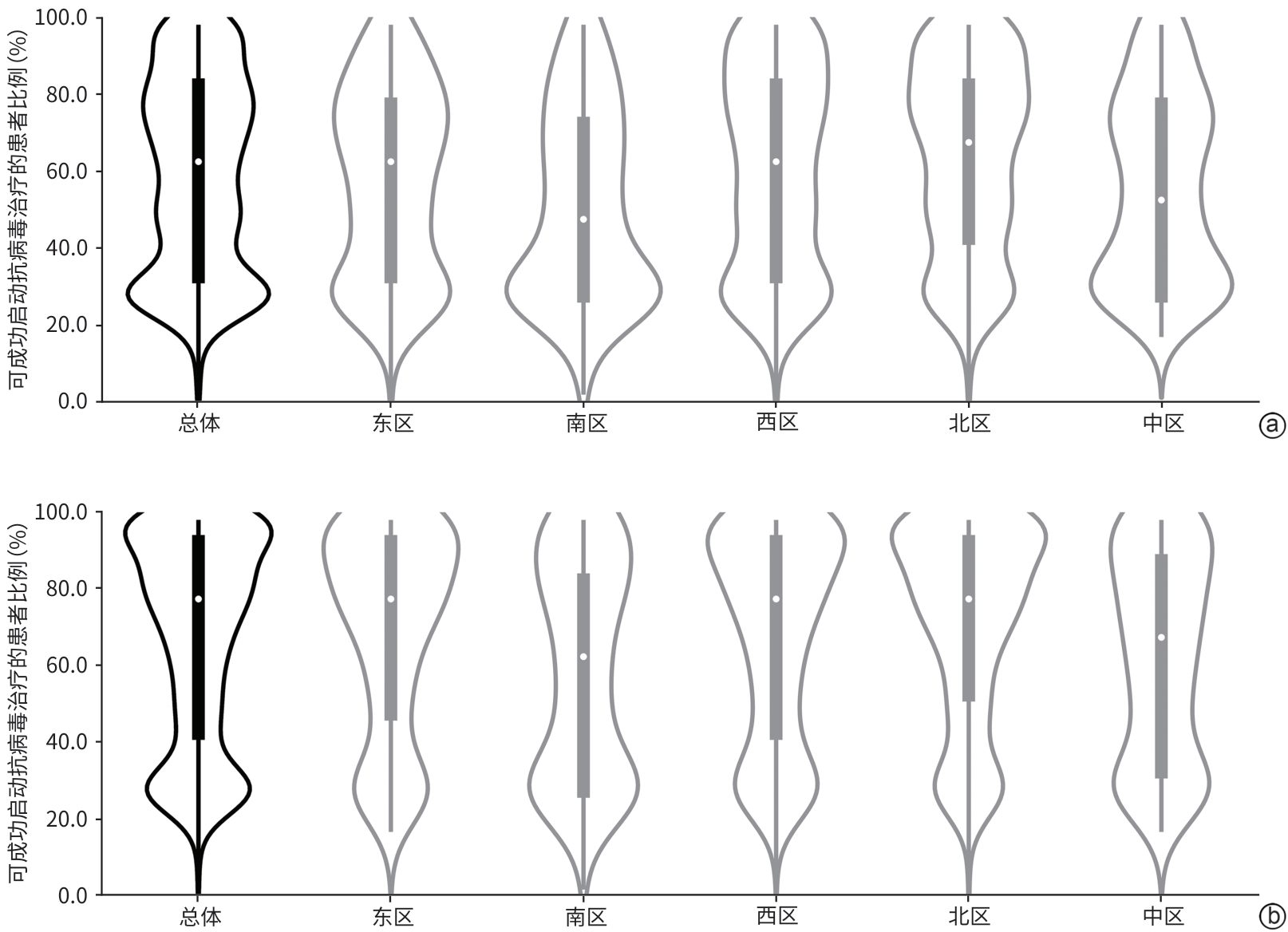
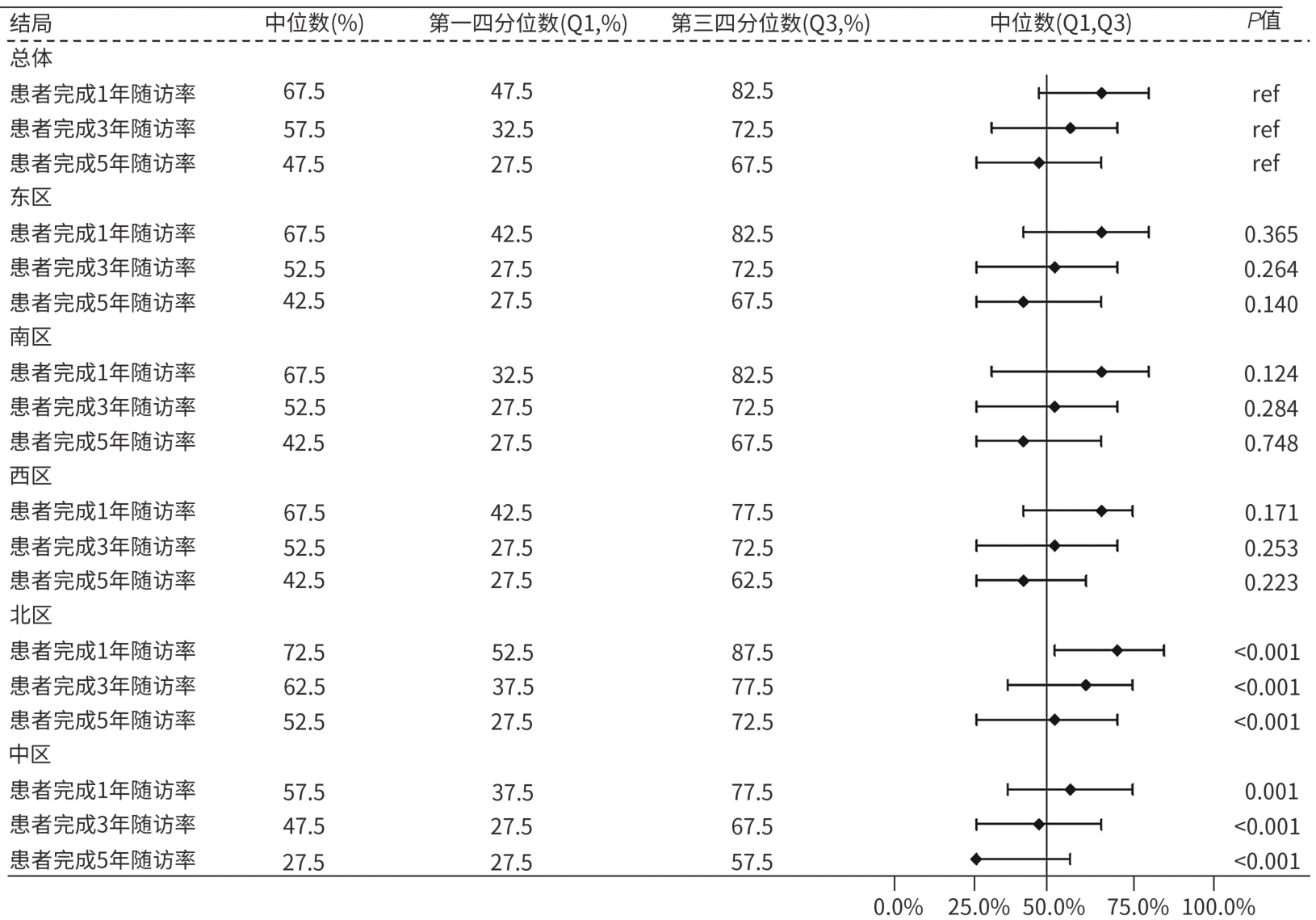
| [1] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2023, 41( 1): 3- 28. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20230220-00050. |
| [2] |
XIE YD, FENG B, RAO HY. Interpretation of guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 7): 1553- 1559. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.07.007. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [5] |
HUANG Y. Age and family history are both not required for initiation of antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 4): 426- 428. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220320-00127. |
| [6] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67( 2): 370- 398. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.021. |
| [7] |
TERRAULT NA, LOK ASF, MCMAHON BJ, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67( 4): 1560- 1599. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29800. |
| [8] |
GANE EJ, CHARLTON MR, MOHAMED R, et al. Asian consensus recommendations on optimizing the diagnosis and initiation of treatment of hepatitis B virus infection in resource-limited settings[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2020, 27( 5): 466- 475. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13244. |
| [9] |
Drafting Committee for Hepatitis Management Guidelines, the Japan Society of Hepatology. Japan society of hepatology guidelines for the management of hepatitis B virus infection: 2019 update[J]. Hepatol Res, 2020, 50( 8): 892- 923. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13504. |
| [10] |
LUBEL JS, STRASSER SI, THOMPSON AJ, et al. Australian consensus recommendations for the management of hepatitis B[J]. Med J Aust, 2022, 216( 9): 478- 486. DOI: 10.5694/mja2.51430. |
| [11] |
REN S, WANG WJ, LU JF, et al. Effect of the change in antiviral therapy indication on identifying significant liver injury among chronic hepatitis B virus infections in the grey zone[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1035923. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035923. |
| [12] |
CHOI GH, KIM GA, CHOI J, et al. High risk of clinical events in untreated HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with high viral load and no significant ALT elevation[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50( 2): 215- 226. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15311. |
| [13] |
ZHANG SH, WANG C, LIU B, et al. Cost-effectiveness of expanded antiviral treatment for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in China: An economic evaluation[J]. Lancet Reg Health West Pac, 2023, 35: 100738. DOI: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100738. |
| [14] |
SHAN S, ZHAO XY, JIA JD. Comprehensive approach to controlling chronic hepatitis B in China[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2024, 30( 2): 135- 143. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0412. |
| [15] |
School of Population Medicine and Public Health, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College; School of Public Health, Peking University; Department of Management on Infectious Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, et al. Expert consensus on the key technologies for a multi‑point trigger intelligent surveillance and early warning system for infectious diseases[J]. Natl Med J China, 2024, 104( 32): 2995- 3009. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20240612-01317. |
| [16] |
|








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: