| [1] |
DEVARBHAVI H, ASRANI SK, ARAB JP, et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 2): 516- 537. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017. |
| [2] |
TERRAULT NA, FRANCOZ C, BERENGUER M, et al. Liver transplantation 2023: Status report, current and future challenges[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21( 8): 2150- 2166. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.005. |
| [3] |
YADAV P, SINGH SK, RAJPUT S, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cells in regeneration of liver in chronic liver diseases: Current perspectives and future challenges[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2024, 253: 108563. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108563. |
| [4] |
SANI F, SANI M, MOAYEDFARD Z, et al. Potential advantages of genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of acute and chronic liver diseases[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14( 1): 138. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03364-x. |
| [5] |
TAHA EA, LEE J, HOTTA A. Delivery of CRISPR-Cas tools for in vivo genome editing therapy: Trends and challenges[J]. J Control Release, 2022, 342: 345- 361. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.01.013. |
| [6] |
JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337( 6096): 816- 821. DOI: 10.1126/science.1225829. |
| [7] |
CUSHMAN-VOKOUN A, SCHMIDT RJ, HIEMENZ MC, et al. A primer on gene editing[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2023. DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0410-CP.[ Epub ahead of print] |
| [8] |
ADLAT S, VÁZQUEZ SALGADO AM, LEE M, et al. Emerging and potential use of CRISPR in human liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2023. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000578.[ Online ahead of print] |
| [9] |
LONGHURST HJ, LINDSAY K, PETERSEN RS, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 in vivo gene editing of KLKB1 for hereditary angioedema[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390( 5): 432- 441. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309149. |
| [10] |
PIERCE EA, ALEMAN TS, JAYASUNDERA KT, et al. Gene editing for CEP290-associated retinal degeneration[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390( 21): 1972- 1984. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309915. |
| [11] |
FERRARI S, VALERI E, CONTI A, et al. Genetic engineering meets hematopoietic stem cell biology for next-generation gene therapy[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30( 5): 549- 570. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.04.014. |
| [12] |
CHANCELLOR D, BARRETT D, NGUYEN-JATKOE L, et al. The state of cell and gene therapy in 2023[J]. Mol Ther, 2023, 31( 12): 3376- 3388. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.11.001. |
| [13] |
ISHII T, ETO K. Fetal stem cell transplantation: Past, present, and future[J]. World J Stem Cells, 2014, 6( 4): 404- 420. DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i4.404. |
| [14] |
KLOPP AH, GUPTA A, SPAETH E, et al. Concise review: Dissecting a discrepancy in the literature: Do mesenchymal stem cells support or suppress tumor growth?[J]. Stem Cells, 2011, 29( 1): 11- 19. DOI: 10.1002/stem.559. |
| [15] |
KIMBREL EA, LANZA R. Next-generation stem cells: Ushering in a new era of cell-based therapies[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020, 19( 7): 463- 479. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-020-0064-x. |
| [16] |
HAMANN A, PANNIER AK. Innovative nonviral gene delivery strategies for engineering human mesenchymal stem cell phenotypes toward clinical applications[J]. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 2022, 78: 102819. DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2022.102819. |
| [17] |
MENG X, ZHENG MJ, YU M, et al. Transplantation of CRISPRa system engineered IL10-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of myocardial infarction in diabetic mice[J]. J Biol Eng, 2019, 13: 49. DOI: 10.1186/s13036-019-0163-6. |
| [18] |
LI J, TAO T, XU J, et al. HIF-1α attenuates neuronal apoptosis by upregulating EPO expression following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat MCAO model[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2020, 45( 4): 1027- 1036. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4480. |
| [19] |
WANG XY, WANG HZ, LU JH, et al. Erythropoietin-modified mesenchymal stem cells enhance anti-fibrosis efficacy in mouse liver fibrosis model[J]. Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2020, 17( 5): 683- 693. DOI: 10.1007/s13770-020-00276-2. |
| [20] |
SHAHROR RA, LINARES GR, WANG Y, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing fibroblast growth factor 21 facilitates cognitive recovery and enhances neurogenesis in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury[J]. J Neurotrauma, 2020, 37( 1): 14- 26. DOI: 10.1089/neu.2019.6422. |
| [21] |
HUAI Q, ZHU C, ZHANG X, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells armored by FGF21 ameliorate alcohol-induced liver injury through modulating polarization of macrophages[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2024, 8( 4): e0410. DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000410. |
| [22] |
BYUN CS, HWANG S, WOO SH, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppress growth of Huh7 hepatocellular carcinoma cells via interferon(IFN)-β-mediated JAK/STAT1 pathway in vitro[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2020, 17( 5): 609- 619. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.41354. |
| [23] |
VIGO T, LA ROCCA C, FAICCHIA D, et al. IFNβ enhances mesenchymal stromal(Stem) cells immunomodulatory function through STAT1-3 activation and mTOR-associated promotion of glucose metabolism[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10( 2): 85. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1336-4. |
| [24] |
HWANG S, EOM YW, KANG SH, et al. IFN-β overexpressing adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells mitigate alcohol-induced liver damage and gut permeability[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 15): 8509. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158509. |
| [25] |
MORRIS AB, FARLEY CR, PINELLI DF, et al. Signaling through the inhibitory Fc receptor FcγRIIB induces CD8 + T cell apoptosis to limit T cell immunity[J]. Immunity, 2020, 52( 1): 136- 150. e 6. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.006. |
| [26] |
JI WB, WANG WW, LI PY, et al. sFgl2 gene-modified MSCs regulate the differentiation of CD4 + T cells in the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14( 1): 316. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03550-x. |
| [27] |
PUCHE JE, SAIMAN Y, FRIEDMAN SL. Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis[J]. Compr Physiol, 2013, 3( 4): 1473- 1492. DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c120035. |
| [28] |
FAN WG, LIU TH, CHEN W, et al. ECM1 prevents activation of transforming growth factor β, hepatic stellate cells, and fibrogenesis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 157( 5): 1352- 1367. e 13. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.036. |
| [29] |
LIU Q, LV CQ, HUANG QQ, et al. ECM1 modified HF-MSCs targeting HSC attenuate liver cirrhosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8( 1): 51. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-00846-4. |
| [30] |
DOOLEY S, HAMZAVI J, BREITKOPF K, et al. Smad7 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis in rats[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 125( 1): 178- 191. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00666-8. |
| [31] |
SU DN, WU SP, XU SZ. Mesenchymal stem cell-based Smad7 gene therapy for experimental liver cirrhosis[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11( 1): 395. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-01911-4. |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
BAI YP, LUO Y, LIU SJ, et al. PRL-1 protein promotes ERK1/2 and RhoA protein activation through a non-canonical interaction with the Src homology 3 domain of p115 Rho GTPase-activating protein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286( 49): 42316- 42324. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286302. |
| [34] |
KIM JY, CHOI JH, JUN JH, et al. Enhanced PRL-1 expression in placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates hepatic function via mitochondrial dynamics in a cirrhotic rat model[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11( 1): 512. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-02029-3. |
| [35] |
ZAGOURA D, TROHATOU O, MAKRIDAKIS M, et al. Functional secretome analysis reveals Annexin-A1 as important paracrine factor derived from fetal mesenchymal stem cells in hepatic regeneration[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 45: 542- 552. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.009. |
| [36] |
CHEN HO, TANG SG, LIAO JM, et al. VEGF 165 gene-modified human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells protect against acute liver failure in rats[J]. J Gene Med, 2021, 23( 10): e3369. DOI: 10.1002/jgm.3369. |
| [37] |
XU RX, NI BB, WANG L, et al. CCR2-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells targeting damaged liver enhance recovery of acute liver failure[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13( 1): 55. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02729-y. |
| [38] |
KONG DF, XU HM, CHEN M, et al. Co-encapsulation of HNF4α overexpressing UMSCs and human primary hepatocytes ameliorates mouse acute liver failure[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11( 1): 449. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-01962-7. |
| [39] |
FERNÁNDEZ M, SEMELA D, BRUIX J, et al. Angiogenesis in liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 50( 3): 604- 620. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.011. |
| [40] |
RUMGAY H, ARNOLD M, FERLAY J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 6): 1598- 1606. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021. |
| [41] |
YAMAGUCHI R, YANO H, IEMURA A, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 1998, 28( 1): 68- 77. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510280111. |
| [42] |
KRISHNAN B, TORTI FM, GALLAGHER PE, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) reduces proliferation and angiogenesis of human prostate cancer xenografts with a decrease in angiogenic factors and an increase in sFlt-1[J]. Prostate, 2013, 73( 1): 60- 70. DOI: 10.1002/pros.22540. |
| [43] |
LI GL, MIAO F, ZHU JH, et al. Anti-angiogenesis gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma via systemic injection of mesenchymal stem cells engineered to secrete soluble Flt-1[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16( 5): 5799- 5806. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7310. |
| [44] |
WU N, ZHANG YL, WANG HT, et al. Overexpression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in human mesenchymal stem cells suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma development through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway downregulation[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2016, 17( 5): 558- 565. DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1177675. |
| [45] |
WANG XL, HE Y, MACKOWIAK B, et al. microRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases[J]. Gut, 2021, 70( 4): 784- 795. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322526. |
| [46] |
KISSELEVA T, BRENNER D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18( 3): 151- 166. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00372-7. |
| [47] |
CHEN W, YANG AT, JIA JD, et al. Lysyl oxidase(LOX) family members: Rationale and their potential as therapeutic targets for liver fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 2): 729- 741. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31236. |
| [48] |
WANG YJ, CHEN YF, YANG FJ, et al. miR-4465-modified mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles inhibit liver fibrosis development via targeting LOXL2 expression[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2024, 25( 7): 594- 604. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2300305. |
| [49] |
LIU YJ, WANG JY, YANG RX, et al. GP73-mediated secretion of AFP and GP73 promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Oncogenesis, 2021, 10( 10): 69. DOI: 10.1038/s41389-021-00358-3. |
| [50] |
HOU X, YANG L, JIANG XH, et al. Role of microRNA-141-3p in the progression and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 128: 331- 339. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.144. |
| [51] |
GAI XC, TANG BF, LIU FM, et al. miR-27a is negatively regulated by mTOR and inhibits liver cancer cell invasion via targeting GP73[J]. Basic Clin Med, 2017, 37( 7): 1015- 1020. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6325.2017.07.022.
|
| [52] |
BONGOLO CC, THOKERUNGA E, YAN Q, et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-27a-3p overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the progression of liver cancer through suppression of Golgi membrane protein 1[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2022, 2022: 9748714. DOI: 10.1155/2022/9748714. |
| [53] |
GIORDANO S, COLUMBANO A. microRNAs: New tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma?[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57( 2): 840- 847. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26095. |
| [54] |
CALLEGARI E, D’ABUNDO L, GUERRIERO P, et al. miR-199a-3p modulates MTOR and PAK4 pathways and inhibits tumor growth in a hepatocellular carcinoma transgenic mouse model[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2018, 11: 485- 493. DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.04.002. |
| [55] |
LOU GH, CHEN L, XIA CX, et al. miR-199a-modified exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatocellular carcinoma chemosensitivity through mTOR pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39( 1): 4. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1512-5. |



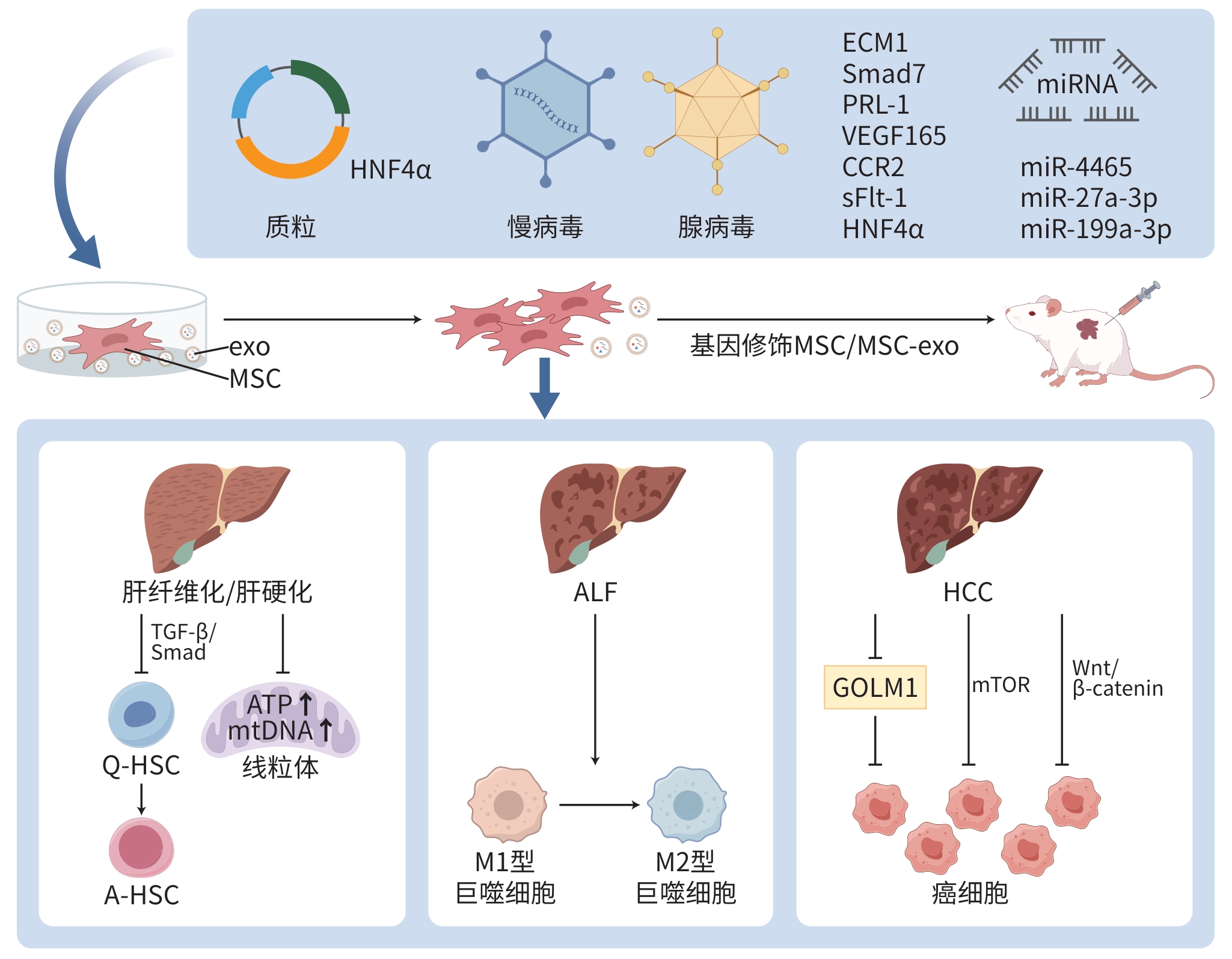




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: