| [1] |
GANGOPADHYAY A, IBRAHIM R, THEBERGE K, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and mental illness: Mechanisms linking mood, metabolism and medicines[J]. Front Neurosci, 2022, 16: 1042442. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1042442. |
| [2] |
JICHITU A, BUNGAU S, STANESCU AMA, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular comorbidities: Pathophysiological links, diagnosis, and therapeutic management[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2021, 11( 4): 689. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11040689. |
| [3] |
THOMAS JA, KENDALL BJ, EL-SERAG HB, et al. Hepatocellular and extrahepatic cancer risk in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 9( 2): 159- 169. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00275-3. |
| [4] |
PENG HL, LIU LN, LIU DL, et al. Depression and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Association and potential mechanisms[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2022, 30( 7): 295- 302.
彭海玲, 刘丽妮, 刘德良, 等. 抑郁症和非酒精性脂肪性肝病: 相关性及潜在机制[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2022, 30( 7): 295- 302.
|
| [5] |
TARANTINO G, CITRO V, BALSANO C. Liver-spleen axis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 15( 7): 759- 769. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1914587. |
| [6] |
TARGHER G, LONARDO A, BYRNE CD. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14( 2): 99- 114. DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.173. |
| [7] |
LIU Y, BASTY N, WHITCHER B, et al. Genetic architecture of 11 organ traits derived from abdominal MRI using deep learning[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e65554. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.65554. |
| [8] |
KOGA Y, FUJITA M, NAKAHARA T, et al. Splenic volume in severe sepsis is associated with disease severity and pneumococcal infection[J]. Acute Med Surg, 2016, 3( 4): 339- 344. DOI: 10.1002/ams2.204. |
| [9] |
KHOSHPOURI P, GHADIMI M, REZVANI HABIBABADI R, et al. Cross-sectional imaging in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: Single time-point liver or spleen volume is associated with survival[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2020, 132: 109331. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109331. |
| [10] |
BARREA L, DI SOMMA C, MUSCOGIURI G, et al. Nutrition, inflammation and liver-spleen axis[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2018, 58( 18): 3141- 3158. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1353479. |
| [11] |
TARANTINO G, SCALERA A, FINELLI C. Liver-spleen axis: Intersection between immunity, infections and metabolism[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19( 23): 3534- 3542. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i23.3534. |
| [12] |
ZHANG SY, WAN D, ZHU MC, et al. CD11b +CD43 hi Ly6C lo splenocyte-derived macrophages exacerbate liver fibrosis via spleen-liver axis[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 5): 1612- 1629. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32782. |
| [13] |
ZHANG X, LEI B, YUAN Y, et al. Brain control of humoral immune responses amenable to behavioural modulation[J]. Nature, 2020, 581( 7807): 204- 208. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2235-7. |
| [14] |
QIN XY, CHEN DF, HU YH. Application of Mendeiian randomization in the etioiogicai study[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2006, 27( 7): 630- 633. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn: 0254-6450.2006.07.020.
|
| [15] |
NI JJ, XU Q, YAN SS, et al. Gut microbiota and psychiatric disorders: A two-sample mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 12: 737197. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.737197. |
| [16] |
LONG YW, TANG LH, ZHOU YY, et al. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and cancers: A two-sample Mendelian randomisation study[J]. BMC Med, 2023, 21( 1): 66. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-023-02761-6. |
| [17] |
LIANG H, MU HB, ZHANG FH, et al. Causal relationship between linoleic acid and type 2 diabetes and glycemic traits: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1277153. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1277153. |
| [18] |
Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease Group of the Hepatology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Steatotic Liver Disease Expert Committee of the Chinese Physicians Association. Guide lines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. 中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组, 中国医师协会脂肪性肝病专家委员会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病防治指南(2018年更新版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001- 5256.2018.05.007
|
| [19] |
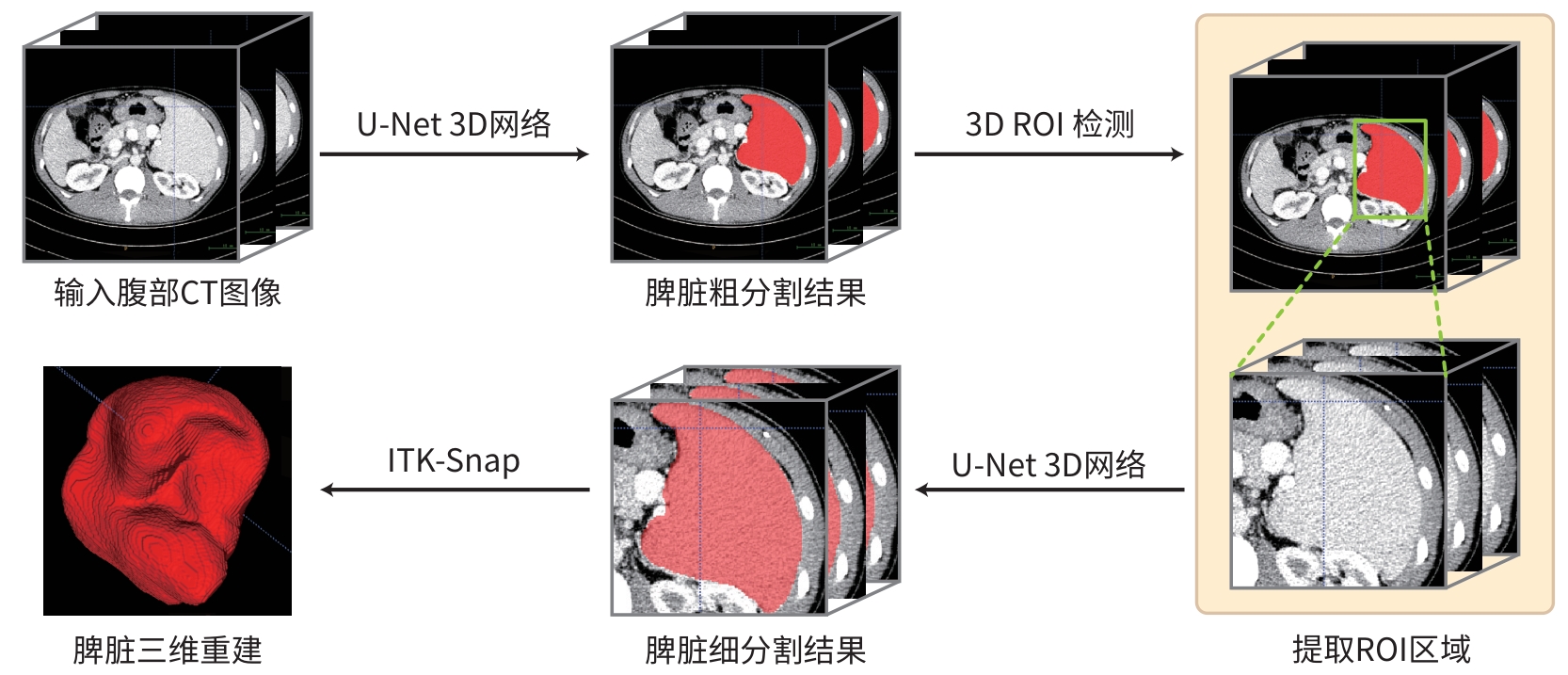
ÇIÇEK Ö, ABDULKADIR A, LIENKAMP SS, et al. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation[C]// Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2016. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 424- 432. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49. |
| [20] |
LI JJ, ZHAO SP, ZHAO D, et al. 2023 Chinese guideline for lipid management[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1190934. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1190934. |
| [21] |
LEE JH, KIM D, KIM HJ, et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2010, 42( 7): 503- 508. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.08.002. |
| [22] |
GHODSIAN N, ABNER E, EMDIN CA, et al. Electronic health record-based genome-wide meta-analysis provides insights on the genetic architecture of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2021, 2( 11): 100437. DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100437. |
| [23] |
POLIMENI L, PASTORI D, BARATTA F, et al. Spleen dimensions are inversely associated with lysosomal acid lipase activity in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2017, 12( 8): 1159- 1165. DOI: 10.1007/s11739-017-1746-1. |
| [24] |
SUZUKI K, KIRIKOSHI H, YONEDA M, et al. Measurement of spleen volume is useful for distinguishing between simple steatosis and early-stage non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2010, 40( 7): 693- 700. DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2010.00643.x. |
| [25] |
TSUSHIMA Y, ENDO K. Spleen enlargement in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver: Correlation between degree of fatty infiltration in liver and size of spleen[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2000, 45( 1): 196- 200. DOI: 10.1023/a:1005446418589. |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
GAO WH, GE KX, XIANG XX. Association of Th17 cells, regulatory T cells, and their imbalance with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 6): 1347- 1350. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.06.046. |
| [28] |
HE BH, WU LY, XIE W, et al. The imbalance of Th17/Treg cells is involved in the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice[J]. BMC Immunol, 2017, 18( 1): 33. DOI: 10.1186/s12865-017-0215-y. |
| [29] |
TARANTINO G, CONCA P, PASANISI F, et al. Could inflammatory markers help diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2009, 21( 5): 504- 511. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283229b40. |
| [30] |
GU XC, MA ZY, FANG J, et al. Obesity enhances antioxidant capacity and reduces cytokine levels of the spleen in mice to resist splenic injury challenged by Escherichia coli[J]. J Immunol Res, 2020, 2020: 5948256. DOI: 10.1155/2020/5948256. |
| [31] |
ZHAO P, JIN H, ZHU JX, et al. Role of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hainan Med J, 2022, 33( 1): 96- 99.
赵鹏, 金海, 朱加兴, 等. 白细胞介素-1β、白细胞介素-6与肿瘤坏死因子-α在非酒精性脂肪性肝病发展过程中的作用[J]. 海南医学, 2022, 33( 1): 96- 99.
|
| [32] |
LEITE ND, MONTES EG, FISHER SV, et al. Splenectomy attenuates obesity and decreases insulin hypersecretion in hypothalamic obese rats[J]. Metabolism, 2015, 64( 9): 1122- 1133. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.05.003. |
| [33] |
KERAMIDA G, DUNFORD A, KAYA G, et al. Hepato-splenic axis: Hepatic and splenic metabolic activities are linked[J]. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2018, 8( 3): 228- 238.
|
| [34] |
WANG ZM, LI NS, WANG B, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats is accelerated by splenic regulation of liver PTEN/AKT[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21( 4): 232- 238. DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.161641. |
| [35] |
LI NS, WANG ZM, LIN JH. Up-regulated expression of PTEN after splenetomy may prevent the progression of liver fibrosis in rats[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2016, 23( 1): 50- 56. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.300. |
| [36] |
MUROTOMI K, TAWARA H, SUTOH M, et al. Iron-accumulating splenocytes may exacerbate non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through the production of proinflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species[J]. Exp Biol Med(Maywood), 2022, 247( 10): 848- 855. DOI: 10.1177/15353702221077218. |
| [37] |
CACCIOTTOLO TM, KUMAR A, GODFREY EM, et al. Spleen size does not correlate with histological stage of liver disease in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21( 2): 535- 537.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.007. |
| [38] |
HAMABE A, UTO H, IMAMURA Y, et al. Impact of cigarette smoking on onset of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease over a 10-year period[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2011, 46( 6): 769- 778. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-011-0376-z. |
| [39] |
CHEN JH, ZHOU H, JIN HW, et al. Role of inflammatory factors in mediating the effect of lipids on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A two-step, multivariable mendelian randomization study[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14( 20): 4434. DOI: 10.3390/nu14204434. |
| [40] |
HU YJ, LIU J, DONG XJ, et al. Clinical study of serum homocysteine and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in euglycemic patients[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22: 4146- 4151. DOI: 10.12659/msm.897924. |
| [41] |
CIGRI E, INAN FC, ER ER, et al. The relationship between lipid profile and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents with obesity[J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2022, 32( 5): 591- 595. DOI: 10.29271/jcpsp.2022.05.591. |
| [42] |
QIU JJ, KUANG MB, YANG RJ, et al. The newly proposed alanine aminotransferase to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio has shown effectiveness in identifying non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1239398. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1239398. |
| [43] |
SUN DQ, LIU WY, WU SJ, et al. Increased levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol within the normal range as a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7( 5): 5728- 5737. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6799. |
| [44] |
WANG S, LIN XH, ZHU CC, et al. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and increased glucose-to-albumin ratio in adults without diabetes[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2024, 14: 1287916. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1287916. |
| [45] |
CHOI SH, OH DJ, KWON KH, et al. A vegetarian diet does not protect against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD): A cross-sectional study between Buddhist priests and the general population[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2015, 26( 4): 336- 343. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2015.0046. |
| [46] |
ZHANG M, CHEN L, ZHAI MD, et al. Analysis of the risk factors for NAFLD in patients with T2DM[J]. Parenter Enter Nutr, 2019, 26( 5): 271- 275. DOI: 10.16151/j.1007-810x.2019.05.004. |
| [47] |
HAN XC, XU PF, ZHOU JM, et al. Fasting C-peptide is a significant indicator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2020, 160: 108027. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108027. |
| [48] |
YIN SM, ZHENG SB, ZHOU H, et al. Age-related changes in serum albumin, globulin and hemoglobin levels in healthy normal populations[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2010, 30( 9): 1201- 1203.
尹曙明, 郑松柏, 周骅, 等. 健康正常人群血清白蛋白、球蛋白、血红蛋白水平的增龄变化[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2010, 30( 9): 1201- 1203.
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: