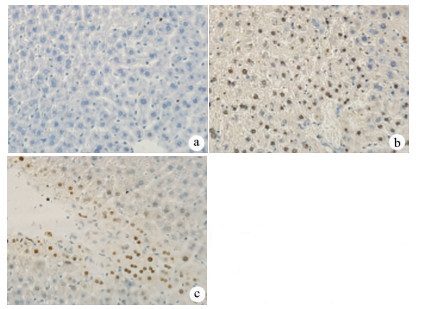
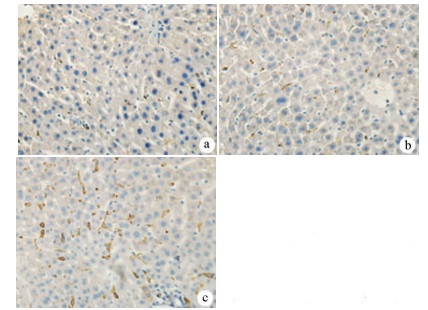
| [1] |
YANG L, WANG W, WANG X, et al. Creg in hepatocytes ameliorates liver ischemia/reper fusion injury in a TAK1-dependent manner in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(1): 294-313. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30203 |
| [2] |
ZHANG S, JIANG S, WANG H, et al. SIRT6 protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy related cell death[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2018, 115: 18-30. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.11.005 |
| [3] |
ZAKI AM, EL-TANBOULY DM, ABDELSALAM RM, et al. Plumbagin ameliorates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: Role of high mobility group box 1 in inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 106: 785-793. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.004 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
HAN JY, FAN JY, HORIE Y, et al. Ameliorating effects of compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia and reperfusion[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2008, 117(2): 280-295. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.09.008 |
| [6] |
ZHOU L, ZUO Z, CHOW MS. Danshen: An overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use[J]. J Clin Pharmacol, 2005, 45(12): 1345-1359. DOI: 10.1177/0091270005282630 |
| [7] |
PARK JH, OK P, CHO JH, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of tanshinone I in neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in the gerbil hippocampus[J]. Neurochem Res, 2014, 39(7): 1300-1312. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-014-1312-4 |
| [8] |
WANG S, JING H, YANG H, et al. Tanshinone I selectively suppresses pro-inflammatory genes expression in activated microglia and prevents nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 164: 247-255. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.042 |
| [9] |
JING X, WEI X, REN M, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Tanshinone I against 6-OHDA- induced oxidative stress in cellular and mouse model of parkinson's disease through upregulating Nrf2[J]. Neurochem Res, 2016, 41(4): 779-786. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-015-1751-6 |
| [10] |
TAO S, ZHENG Y, LAU A, et al. Tanshinone I activates the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response and protects against As(Ⅲ)-induced lung inflammation in vitro and in vivo[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2013, 19(14): 1647-1661. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2012.5117 |
| [11] |
GAO L, QIAN BL, CHEN H, et al. Hic-5 deficiency attenuates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 249: 117517. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117517 |
| [12] |
KONISHI T, LENTSCH AB. Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion: Mechanisms of tissue injury, repair, and regeneration[J]. Gene Expr, 2017, 17(4): 277-287. DOI: 10.3727/105221617X15042750874156 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
LIANG R, NICKKHOLGH A, KERN M, et al. Green tea extract ameliorates reperfusion injury to rat livers after warm ischemia in a dose-dependent manner[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2011, 55(6): 855-863. DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201000643 |
| [15] |
HASSAN-KHABBAR S, COTTART CH, WENDUM D, et al. Postischemic treatment by trans-resveratrol in rat liver ischemia-reperfusion: A possible strategy in liver surgery[J]. Liver Transpl, 2008, 14(4): 451-459. DOI: 10.1002/lt.21405 |
| [16] |
CHENG F, LI Y, FENG L, et al. Effects of tetrandrine on ischemia/reperfusion injury in mouse liver[J]. Transplant Proc, 2008, 40(7): 2163-2166. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.07.082 |
| [17] |
GAO WQ, QIU XF, LI K, et al. Protective effect of Tanshinone I against renal ischemia /reperfusion injury[J]. J Southeast Univ(Med Sci Edi), 2018, 37(3): 372-379. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6264.2018.03.002 |
| [18] |
LI X, WU Y, ZHANG W, et al. Pre-conditioning with tanshinone ⅡA attenuates the ischemia/reperfusion injury caused by liver grafts via regulation of HMGB1 in rat Kupffer cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 89: 1392-1400. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.022 |
| [19] |
QI YY, XIAO L, ZHANG LD, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA pretreatment attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion[J]. Front Biosci (Elite Ed), 2012, 4: 1303-1313.
|
| [20] |
WANG QQ, ZHAO X, CHEN YC, et al. Research advances in mechanisms and intervention of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(6): 1225-1229. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.06.049 |
| [21] |
WANG JY, LI SW, GONG JP, et al. Role of silent information regulator 1 in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(6): 1388-1391. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.047 |
| [22] |
ZHANG H, FORMAN HJ. Glutathione synthesis and its role in redox signaling[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2012, 23(7): 722-728. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.03.017 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
HUANG TT, ZOU Y, CORNIOLA R. Oxidative stress and adult neurogenesis-effects of radiation and superoxide dismutase deficiency[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2012, 23(7): 738-744. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.04.003 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
ATEF Y, EL-FAYOUMI HM, ABDEL-MOTTALEB Y, et al. Quercetin and tin protoporphyrin attenuate hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: Role of HO-1[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 2017, 390(9): 871-881. DOI: 10.1007/s00210-017-1389-9 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
LIU X, LIU J. Tanshinone I induces cell apoptosis by reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and by suppressing p53/DRAM-mediated autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2020, 48(1): 488-497. DOI: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1709862 |
| [29] |
ESTOLANO-COBIÁN A, ALONSO MM, DÍAZ-RUBIO L, et al. Tanshinones and their derivatives: Heterocyclic ring-fused diterpene of biological interest[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2020.[Online ahead of print]
|



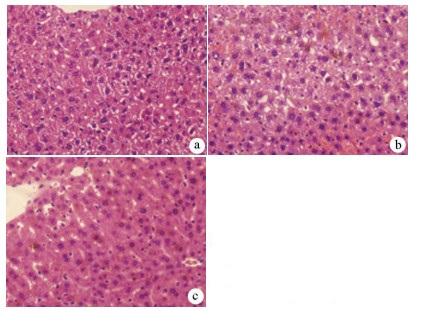




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: