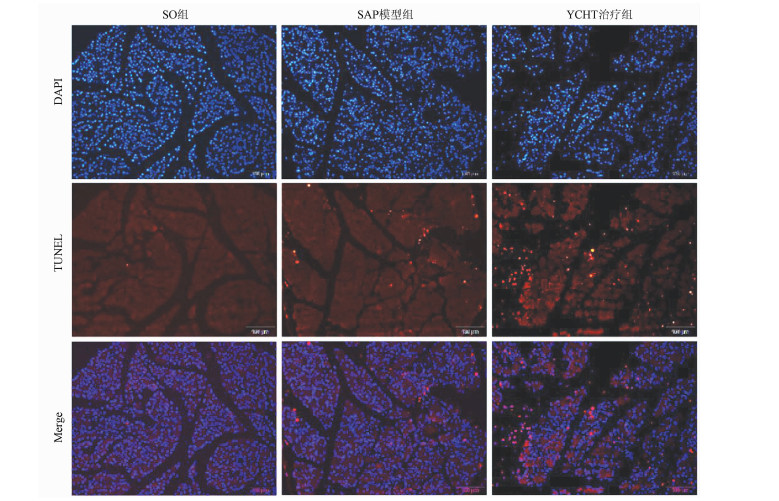
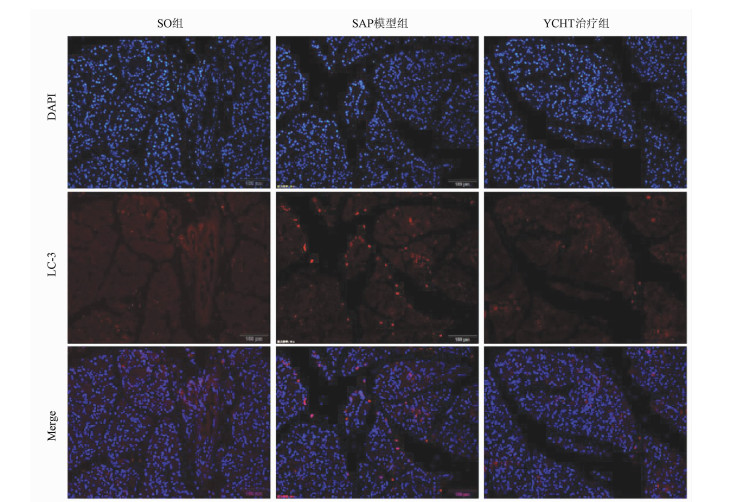
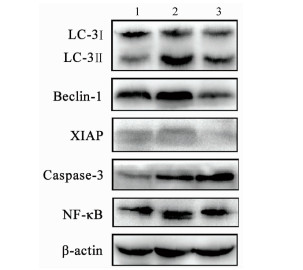
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
XIANG H, ZHANG Q, QI B, et al. Chinese herbal medicines attenuate acute pancreatitis: Pharmacological activities and mechanisms[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 216. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00216 |
| [3] |
SENDLER M, WEISS FU, GOLCHERT J, et al. Cathepsin B-mediated activation of trypsinogen in endocytosing macrophages increases severity of pancreatitis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(3): 704-718.e10. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.018 |
| [4] |
LIU Y, CHEN XD, YU J, et al. Deletion Of XIAP reduces the severity of acute pancreatitis via regulation of cell death and nuclear factor-κB activity[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(3): e2685. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.70 |
| [5] |
LEVINE B. Cell biology: Autophagy and cancer[J]. Nature, 2007, 446(7137): 745-747. DOI: 10.1038/446745a |
| [6] |
SU Z, YANG Z, XU Y, et al. MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(11): 8474-8490. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3523 |
| [7] |
LI Y, JIANG J, LIU W, et al. microRNA-378 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis in skeletal muscle[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115(46): e10849-e10858. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1803377115 |
| [8] |
ZHOU W, XU J, WANG C, et al. miR-23b-3p regulates apoptosis and autophagy via suppressing SIRT1 in lens epithelial cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(12): 19635-19646. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.29270 |
| [9] |
QUINN JJ, CHANG HY. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2016, 17(1): 47-62. DOI: 10.1038/nrg.2015.10 |
| [10] |
TIAN Q, LIU F, XU Z, et al. Evaluation of the chemical consistency of Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang prepared by combined and separated decoction methods using high-performance liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry coupled with multivariate statistical analysis[J]. J Sep Sci, 2019, 42(9): 1664-1675. DOI: 10.1002/jssc.201800961 |
| [11] |
XIANG H, WANG G, QU J, et al. Yin-Chen-Hao Tang attenuates severe acute pancreatitis in rat: An experimental verification of in silico network target prediction[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2016, 7: 378. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00378 |
| [12] |
XIANG H, TAO X, XIA S, et al. Emodin alleviates sodium taurocholate-induced pancreatic acinar cell injury via MicroRNA-30a-5p-mediated inhibition of high-temperature requirement a/transforming growth factor beta 1 inflammatory signaling[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 1488. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01488 |
| [13] |
LEE PJ, PAPACHRISTOU GI. New insights into acute pancreatitis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(8): 479-496. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0158-2 |
| [14] |
HAHM KB, KIM JH, YOU BM, et al. Induction of apoptosis with an extract of Artemisia asiatica attenuates the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats[J]. Pancreas, 1998, 17(2): 153-157. DOI: 10.1097/00006676-199808000-00007 |
| [15] |
IWAHASHI K, HIKITA H, MAKINO Y, et al. Autophagy impairment in pancreatic acinar cells causes zymogen granule accumulation and pancreatitis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 503(4): 2576-2582. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.018 |
| [16] |
GUKOVSKAYA AS, PERKINS P, ZANINOVIC V, et al. Mechanisms of cell death after pancreatic duct obstruction in the opossum and the rat[J]. Gastroenterology, 1996, 110(3): 875-884. DOI: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8608898 |
| [17] |
PARZYCH KR, KLIONSKY DJ. An overview of autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2014, 20(3): 460-473. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5371 |
| [18] |
WANG S, DING WX. Does autophagy promote or protect against the pathogenesis of pancreatitis?[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155(4): 1273-1274. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.02.046 |
| [19] |
KONDO Y, KANZAWA T, SAWAYA R, et al. The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to therapy[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2005, 5(9): 726-734. DOI: 10.1038/nrc1692 |
| [20] |
YANG Y, HUANG Q, LUO C, et al. MicroRNAs in acute pancreatitis: From pathogenesis to novel diagnosis and therapy[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(3): 1948-1961. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29212 |
| [21] |
XIANG H, TAO X, XIA S, et al. Targeting MicroRNA function in acute pancreatitis[J]. Front Physiol, 2017, 8: 726. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00726 |
| [22] |
ABREU FB, LIU X, TSONGALIS GJ. miRNA analysis in pancreatic cancer: The Dartmouth experience[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2017, 55(5): 755-762.
|
| [23] |
QUAN X, LI X, YIN Z, et al. p53/miR-30a-5p/ SOX4 feedback loop mediates cellular proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(12): 22884-22895. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28851 |
| [24] |
KIM JW, YOU YH, JUNG S, et al. miRNA-30a-5p-mediated silencing of Beta2/NeuroD expression is an important initial event of glucotoxicity-induced beta cell dysfunction in rodent models[J]. Diabetologia, 2013, 56(4): 847-855. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-012-2812-x |
| [25] |
ZHOU L, JIA S, DING G, et al. Down-regulation of miR-30a-5p is associated with poor prognosis and promotes chemoresistance of gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(21): 5031-5040. DOI: 10.7150/jca.31191 |
| [26] |
YANG X, BAI F, XU Y, et al. Intensified Beclin-1 Mediated by low expression of Mir-30a-5p promotes chemoresistance in human small cell lung cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 43(3): 1126-1139. DOI: 10.1159/000481754 |
| [27] |
XU X, JIN S, MA Y, et al. miR-30a-5p enhances paclitaxel sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer through targeting BCL-2 expression[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2017, 95(8): 861-871. DOI: 10.1007/s00109-017-1539-z |
| [28] |
YAO RW, WANG Y, CHEN LL. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2019, 21(5): 542-551. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-019-0311-8 |



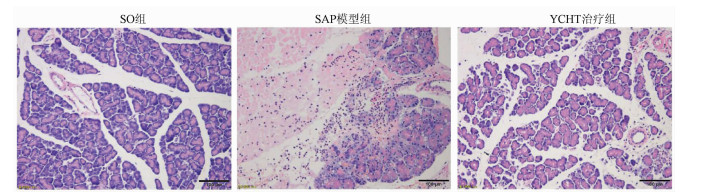




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: