| [1] |
ESLAM M, SANYAL AJ, GEORGE J, et al. MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(7): 1999-2014. e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312 |
| [2] |
IQBAL U, PERUMPAIL BJ, AKHTAR D, et al. The epidemiology, risk profiling and diagnostic challenges of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Medicines (Basel), 2019, 6(1): 41.
|
| [3] |
ATHYROS VG, POLYZOS SA, KOUNTOURAS J, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; new kids on the block[J]. Curr Vasc Pharmacol, 2020, 18(2): 172-181. DOI: 10.2174/1570161117666190405164313 |
| [4] |
YANG Z, FU BS. Research status of liver transplantation in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Ogran Transplantation, 2020, 11(3): 419-423. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2020.03.017 |
| [5] |
ZHOU F, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4): 1119-1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
BULLOCK BP, HELLER RS, HABENER JF. Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor[J]. Endocrinology, 1996, 137(7): 2968-2978. DOI: 10.1210/endo.137.7.8770921 |
| [12] |
RICHARDS P, PARKER HE, ADRIAENSSENS AE, et al. Identification and characterization of GLP-1 receptor-expressing cells using a new transgenic mouse model[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(4): 1224-1233. DOI: 10.2337/db13-1440 |
| [13] |
CANTINI G, MANNUCCI E, LUCONI M. Perspectives in GLP-1 Research: New targets, new receptors[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 27(6): 427-438. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.017 |
| [14] |
XIAO C, BANDSMA RH, DASH S, et al. Exenatide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, acutely inhibits intestinal lipoprotein production in healthy humans[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2012, 32(6): 1513-1519. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.246207 |
| [15] |
HSIEH J, LONGUET C, BAKER CL, et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor is essential for postprandial lipoprotein synthesis and secretion in hamsters and mice[J]. Diabetologia, 2010, 53(3): 552-561. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1611-5 |
| [16] |
SHARMA D, VERMA S, VAIDYA S, et al. Recent updates on GLP-1 agonists: Current advancements & challenges[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 108: 952-962. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.088 |
| [17] |
KHOO J, HSIANG J, TANEJA R, et al. Comparative effects of liraglutide 3 mg vs structured lifestyle modification on body weight, liver fat and liver function in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot randomized trial[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2017, 19(12): 1814-1817. DOI: 10.1111/dom.13007 |
| [18] |
ARMSTRONG MJ, HULL D, GUO K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 decreases lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(2): 399-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.038 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
SHAO N, KUANG HY, HAO M, et al. Benefits of exenatide on obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with elevated liver enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2014, 30(6): 521-529. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.2561 |
| [21] |
ARMSTRONG MJ, GAUNT P, AITHAL GP, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10019): 679-690. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X |
| [22] |
EGUCHI Y, KITAJIMA Y, HYOGO H, et al. Pilot study of liraglutide effects in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with glucose intolerance in Japanese patients (LEAN-J)[J]. Hepatol Res, 2015, 45(3): 269-278. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12351 |
| [23] |
SEKO Y, SUMIDA Y, TANAKA S, et al. Effect of 12-week dulaglutide therapy in Japanese patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Hepatol Res, 2017, 47(11): 1206-1211. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12837 |
| [24] |
RAHMAN K, LIU Y, KUMAR P, et al. C/EBP homologous protein modulates liraglutide-mediated attenuation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Lab Invest, 2016, 96(8): 895-908. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.61 |
| [25] |
LAKOSKI SG, LAGACE TA, COHEN JC, et al. Genetic and metabolic determinants of plasma PCSK9 levels[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2009, 94(7): 2537-2543. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2009-0141 |
| [26] |
YANG SH, LI S, ZHANG Y, et al. Positive correlation of plasma PCSK9 levels with HbA1c in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2016, 32(2): 193-199. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.2712 |
| [27] |
DONG B, SINGH AB, AZHAR S, et al. High-fructose feeding promotes accelerated degradation of hepatic LDL receptor and hypercholesterolemia in hamsters via elevated circulating PCSK9 levels[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2015, 239(2): 364-374. DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.01.013 |
| [28] |
YANG SH, XU RX, CUI CJ, et al. Liraglutide downregulates hepatic LDL receptor and PCSK9 expression in HepG2 cells and db/db mice through a HNF-1a dependent mechanism[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2018, 17(1): 48. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-018-0689-9 |
| [29] |
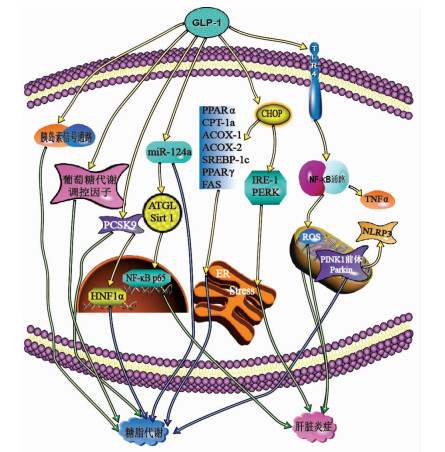
FANG QH, SHEN QL, LI JJ, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-124a attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through upregulation of adipose triglyceride lipase and the effect of liraglutide intervention[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49(7): 743-757. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30861258 |
| [30] |
CHIKKA MR, MCCABE DD, TYRA HM, et al. C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) contributes to suppression of metabolic genes during endoplasmic reticulum stress in the liver[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(6): 4405-4415. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432344 |
| [31] |
SZEGEZDI E, LOGUE SE, GORMAN AM, et al. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis[J]. EMBO Rep, 2006, 7(9): 880-885. DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400779 |
| [32] |
RUTKOWSKI DT, WU J, BACK SH, et al. UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators[J]. Dev Cell, 2008, 15(6): 829-840. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.015 |
| [33] |
YU X, HAO M, LIU Y, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis activation via mitophagy[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 864: 172715. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172715 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
SAAD ZA, KHODEER DM, ZAITONE SA, et al. Exenatide ameliorates experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats via suppression of toll-like receptor 4/NFκB signaling: Comparison to metformin[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 253: 117725. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117725 |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: