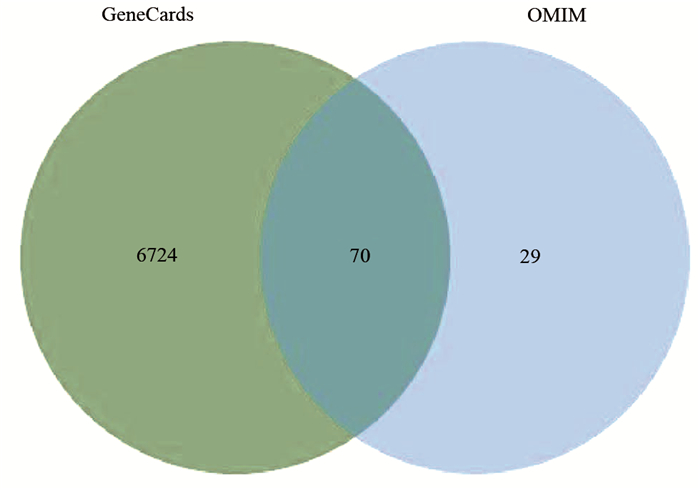
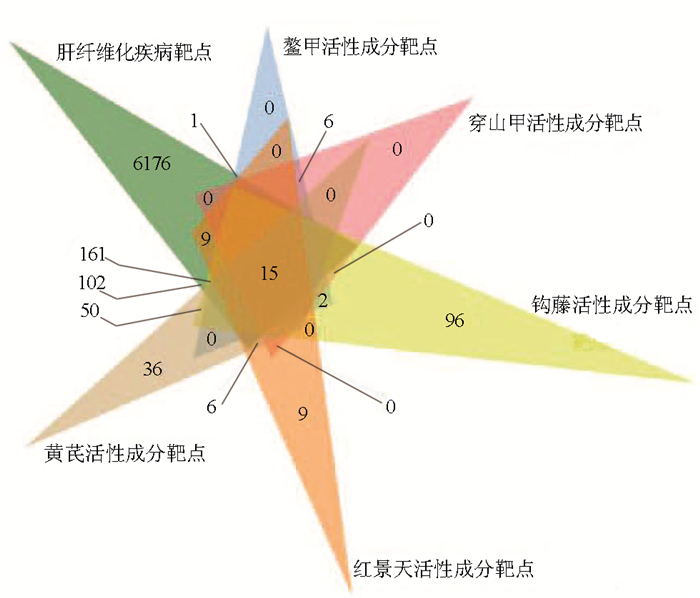
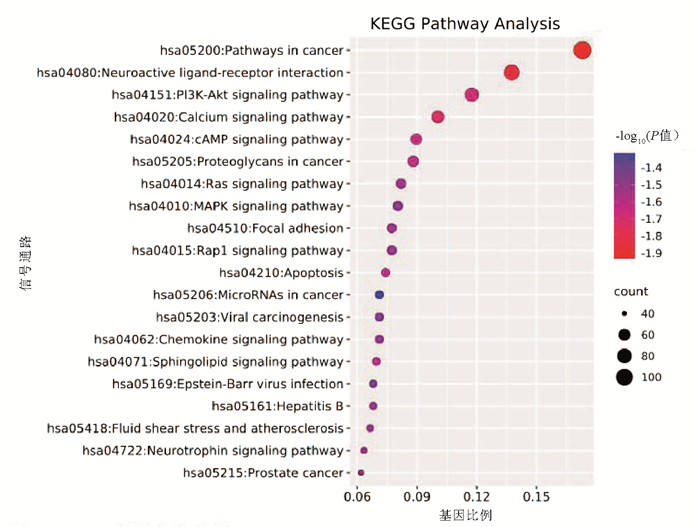
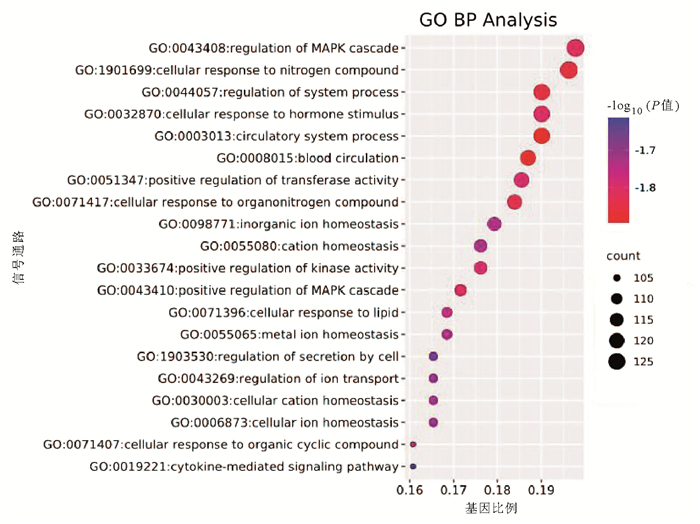
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
WYNN TA, RAMALINGAM TR. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease[J]. Nat Med, 2012, 18(7): 1028-1040. DOI: 10.1038/nm.2807 |
| [3] |
SEKI E, BRENNER DA. Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2015, 22(7): 512-518. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.245 |
| [4] |
TANG CF. Experimental and clinical study on Xiaozheng Huoluo Fang in prevention and treatment of liver arthralgia[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 2016. (in Chinese)
唐成芳. 消癥活络方防治肝痹的实验与临床研究[D]. 长春: 长春中医药大学, 2016.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
XU SY, BIAN RL, CHEN X. Methodology of pharmacological experiment[M]. 3rd Ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2002: 1350-1351. (in Chinese)
徐淑云, 卞如濂, 陈修. 药理实验方法学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2002: 1350-1351.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
NISHIMOTO S, NISHIDA E. MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2[J]. EMBO Rep, 2006, 7(8): 782-786. DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400755 |
| [13] |
CHAO TH, HAYASHI M, TAPPING RI, et al. MEKK3 directly regulates MEK5 activity as part of the big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) signaling pathway[J]. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274(51): 36035-36038. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.51.36035 |
| [14] |
SUN W, KESAVAN K, SCHAEFER BC, et al. MEKK2 associates with the adapter protein Lad/RIBP and regulates the MEK5-BMK1/ERK5 pathway[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(7): 5093-5100. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M003719200 |
| [15] |
ENGLISH JM, VANDERBILT CA, XU S, et al. Isolation of MEK5 and differential expression of alternatively spliced forms[J]. J Biol Chem, 1995, 270(48): 28897-28902. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28897 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
WANG Y, SU B, XIA Z. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activates ERK5 in cortical neurons via a Rap1-MEKK2 signaling cascade[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(47): 35965-35974. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M605503200 |
| [18] |
DORADO F, VELASCO S, ESPARÍS-OGANDO A, et al. The mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk5 mediates human mesangial cell activation[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2008, 23(11): 3403-3411. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfn333 |
| [19] |
RAMSAY AK, MCCRACKEN SR, SOOFI M, et al. ERK5 signalling in prostate cancer promotes an invasive phenotype[J]. Br J Cancer, 2011, 104(4): 664-672. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606062 |
| [20] |
URUSHIHARA M, TAKAMATSU M, SHIMIZU M, et al. ERK5 activation enhances mesangial cell viability and collagen matrix accumulation in rat progressive glomerulonephritis[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2010, 298(1): F167-F176. DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00124.2009 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: