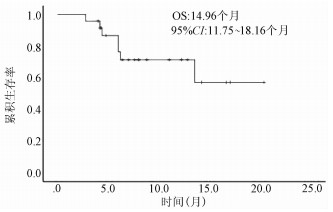
| [1] |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492 |
| [2] |
ZHENG R, QU C, ZHANG S, et al. Liver cancer incidence and mortality in China: Temporal trends and projections to 2030[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2018, 30(6): 571-579. DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.06.01 |
| [3] |
LLOVET JM, MONTAL R, SIA D, et al. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2018, 15(10): 599-616. DOI: 10.1038/s41571-018-0073-4 |
| [4] |
GRETEN TF, PAPENDORF F, BLECK JS, et al. Survival rate in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of 389 patients[J]. Br J Cancer, 2005, 92(10): 1862-1868. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602590 |
| [5] |
KUDO M, FINN RS, QIN S, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10126): 1163-1173. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1 |
| [6] |
TOPALIAN SL, HODI FS, BRAHMER JR, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366(26): 2443-2454. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690 |
| [7] |
EL-KHOUEIRY AB, SANGRO B, YAU T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10088): 2492-2502. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2 |
| [8] |
ZHU AX, FINN RS, EDELINE J, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2018, 19(7): 940-952. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6 |
| [9] |
FUKUMURA D, KLOEPPER J, AMOOZGAR Z, et al. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2018, 15(5): 325-340. DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.29 |
| [10] |
KATO Y, TABATA K, KIMURA T, et al. Lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody combination treatment activates CD8 + T cells through reduction of tumor-associated macrophage and activation of the interferon pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(2): e0212513. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212513 |
| [11] |
FINN RS, IKEDA M, ZHU AX, et al. Phase Ib study of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(26): 2960-2970. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.00808 |
| [12] |
LENCIONI R, LLOVET JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2010, 30(1): 52-60. DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132 |
| [13] |
EISENHAUER EA, THERASSE P, BOGAERTS J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1)[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2009, 45(2): 228-247. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026 |
| [14] |
WANG F, QIN S, SUN X, et al. Reactive cutaneous capillary endothelial proliferation in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with camrelizumab: Data derived from a multicenter phase 2 trial[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 47. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00886-2 |
| [15] |
HOOS A. Development of immuno-oncology drugs-from CTLA4 to PD1 to the next generations[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2016, 15(4): 235-247. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2015.35 |
| [16] |
SHEN H, YANG ES, CONRY M, et al. Predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint blockade and opportunities for combination therapies[J]. Genes Dis, 2019, 6(3): 232-246. DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.06.006 |
| [17] |
FINN RS, RYOO BY, MERLE P, et al. Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A randomized, double-blind, phase Ⅲ trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(3): 193-202. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.01307 |
| [18] |
RIVERA LB, MEYRONET D, HERVIEU V, et al. Intratumoral myeloid cells regulate responsiveness and resistance to antiangiogenic therapy[J]. Cell Rep, 2015, 11(4): 577-591. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.055 |
| [19] |
YASUDA S, SHO M, YAMATO I, et al. Simultaneous blockade of programmed death 1 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2(VEGFR2) induces synergistic anti-tumour effect in vivo[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2013, 172(3): 500-506. DOI: 10.1111/cei.12069 |
| [20] |
KIMURA T, KATO Y, OZAWA Y, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model[J]. Cancer Sci, 2018, 109(12): 3993-4002. DOI: 10.1111/cas.13806 |
| [21] |
CHEN J, HU X, LI Q, et al. Effectiveness and safety of toripalimab, camrelizumab, and sintilimab in a real-world cohort of hepatitis B virus associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(18): 1187. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-6063 |



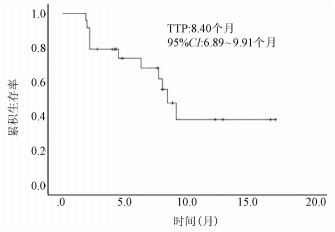




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: