| [1] |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
KITAHARA CM, BERRINGTON de GONZÁLEZ A, FREEDMAN ND, et al. Total cholesterol and cancer risk in a large prospective study in Korea[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(12): 1592-1598. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.5200 |
| [4] |
GAO XH, ZHANG SS, CHEN H, et al. Systemic hepatic-damage index for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection[J]. Front Physiol, 2017, 8: 480. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00480 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China (2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(2): 277-292. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
COSTENTIN CE, MOURAD A, LAHMEK P, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma is diagnosed at a later stage in alcoholic patients: Results of a prospective, nationwide study[J]. Cancer, 2018, 124(9): 1964-1972. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.31215 |
| [9] |
GEORGILA K, VYRLA D, DRAKOS E. Apolipoprotein A-Ⅰ (ApoA-Ⅰ), immunity, inflammation and cancer[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2019, 11(8): 1097. DOI: 10.3390/cancers11081097 |
| [10] |
YE J, LUO Q Y, WANG X P, et al. Serum apolipoprotein A-Ⅰ combined with C-reactive protein serves as a novel prognostic stratification system for colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 9265-9276. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S215599 |
| [11] |
TATEMATSU S, FRANCIS SA, NATARAJAN P, et al. Endothelial lipase is a critical determinant of high-density lipoprotein-stimulated sphingosine 1-phosphate-dependent signaling in vascular endothelium[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2013, 33(8): 1788-1794. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301300 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
TRIEB M, RAINER F, STADLBAUER V, et al. HDL-related biomarkers are robust predictors of survival in patients with chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(1): 113-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.01.026 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
FUJII S, KOGA S, SHONO T, et al. Serum apoprotein A-Ⅰ and A-Ⅱ levels in liver diseases and cholestasis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 1981, 115(3): 321-331. DOI: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90245-X |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
BEEGHLY-FADIEL A, KHANKARI NK, DELAHANTY RJ, et al. A Mendelian randomization analysis of circulating lipid traits and breast cancer risk[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2020, 49(4): 1117-1131. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyz242 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
SCHAIRER C, LAURENT CA, MOY LM, et al. Obesity and related conditions and risk of inflammatory breast cancer: A nested case-control study[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2020, 183(2): 467-478. DOI: 10.1007/s10549-020-05785-1 |
| [21] |
QU F, CHEN R, PENG Y, et al. Assessment of the predictive role of serum lipid profiles in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. J Breast Cancer, 2020, 23(3): 246-258. DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2020.23.e32 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
YU JF. Analysis of abnormal levels of blood lipid and homocysteine in patients with different types of malignant tumors[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Medical University), 2017. (in Chinese)
余敬福. 不同类型恶性肿瘤患者血脂、同型半胱氨酸水平异常分析[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2017.
|
| [24] |
ZOU Y, WU L, YANG Y, et al. Serum lipid levels correlate to the progression of gastric cancer with neuroendocrine immunophenotypes: A multicenter retrospective study[J]. Transl Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 100925. DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100925 |
| [25] |
BRANTLEY KD, RIIS AH, ERICHSEN R, et al. The association of serum lipid levels with colorectal cancer recurrence[J]. Cancer Epidemiol, 2020, 66: 101725. DOI: 10.1016/j.canep.2020.101725 |
| [26] |
YUAN B, FU J, YU WL, et al. Prognostic value of serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with gallbladder cancer[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2019, 111(11): 839-845. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31595756 |
| [27] |
SAITO N, SAIRENCHI T, IRIE F, et al. Low serum LDL cholesterol levels are associated with elevated mortality from liver cancer in Japan: The Ibaraki Prefectural health study[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 2013, 229(3): 203-211. DOI: 10.1620/tjem.229.203 |
| [28] |
ZHAN CL. Serum makers of lipid metabolism as a new prognostic factor in cancer: A meta-analysis[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2019. (in Chinese)
湛长丽. 血清脂代谢标志物作为恶性肿瘤预后预测因子的Meta分析[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2019.
|
| [29] |
JIANG SS, WENG DS, JIANG L, et al. The clinical significance of preoperative serum cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2016, 7(6): 626-632. DOI: 10.7150/jca.13837 |
| [30] |
CARR BI, GIANNELLI G, GUERRA V, et al. Plasma cholesterol and lipoprotein levels in relation to tumor aggressiveness and survival in HCC patients[J]. Int J Biol Markers, 2018, 33(4): 423-431. DOI: 10.1177/1724600818776838 |
| [31] |
ZHONG GC, HUANG SQ, PENG Y, et al. HDL-C is associated with mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer in a J-shaped dose-response fashion: A pooled analysis of 37 prospective cohort studies[J]. Eur J Prev Cardiol, 2020, 27(11): 1187-1203. DOI: 10.1177/2047487320914756 |



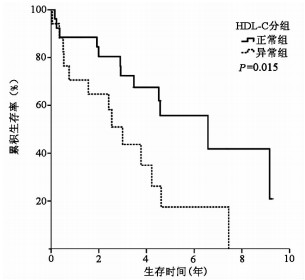




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: