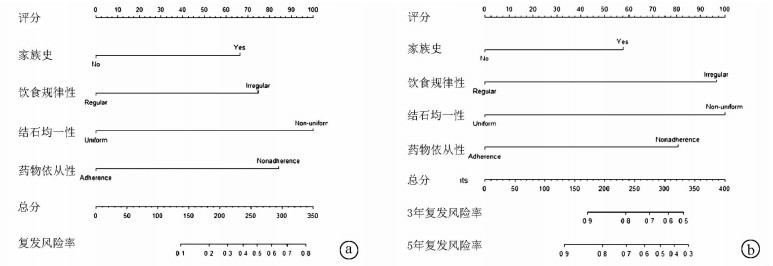
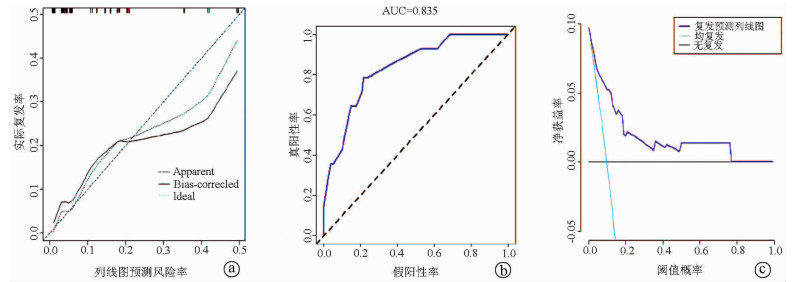
| [1] |
HE XY, SHI J. Consensus opinion on medical treatment of chronic cholecystitis and cholecystolithiasis in China (2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(6): 1231-1236. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.01.002 |
| [2] |
KERLAN RK, LABERGE JM, RING EJ. Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy: Preliminary experience[J]. J Radiology, 1985, 157(3): 653-656. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.157.3.4059554 |
| [3] |
CHESLYN-CURTIS S, RUSSELL RCG. Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy[J]. BMJ Clin Res, 1990, 301(6747): 339-340.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
TAN YY, ZHAO G, WANG D, et al. A new strategy of minimally invasive surgery for cholecystolithiasis: Calculi removal and gallbladder preservation[J]. Dig Surg, 2013, 30(4-6): 466-471. DOI: 10.1159/000357823 |
| [6] |
GAO DK, WEI SH, LI W, et al. Totally laparoscopic gallbladder-preserving surgery: A minimally invasive and favorable approach for cholelithiasis[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 9(2): 395-398. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.2107 |
| [7] |
SAUERBREI W, ROYSTON P, BINDER H. Selection of important variables and determination of functional form for continuous predictors in multivariable model building[J]. Stat Med, 2007, 26(30): 5512-5528. DOI: 10.1002/sim.3148 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
KIDD AC, MCGETTRICK M, TSIM S, et al. Survival prediction in mesothelioma using a scalable Lasso regression model: Instructions for use and initial performance using clinical predictors[J]. BMJ Open Respir Res, 2018, 5(1): e000240. DOI: 10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000240 |
| [10] |
BALACHANDRAN VP, GONEN M, SMITH JJ, et al. Nomograms in oncology: More than meets the eye[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(4): e173-e180. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71116-7 |
| [11] |
IASONOS A, SCHRAG D, RAJ GV, et al. How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2008, 26(8): 1364-1370. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.9791 |
| [12] |
KRAMER AA, ZIMMERMAN JE. Assessing the calibration of mortality benchmarks in critical care: The Hosmer-Lemeshow test revisited[J]. Crit Care Med, 2007, 35(9): 2052-2056. DOI: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000275267.64078.B0 |
| [13] |
PENCINA MJ, D'AGOSTINO RB. Overall C as a measure of discrimination in survival analysis: Model specific population value and confidence interval estimation[J]. Stat Med, 2004, 23(13): 2109-2123. DOI: 10.1002/sim.1802 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Science Foundation in China, 2016, 24(4): 35.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
WEI L, CHAMPMAN S, LI X, et al. Beliefs about medicines and non-adherence in patients with stroke, diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study in China[J]. BMJ Open, 2017, 7(10): e017293. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017293 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
CONDAT B, ZANDITENAS D, BARBU V, et al. Prevalence of low phospholipid-associated cholelithiasis in young female patients[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2013, 45(11): 915-919. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.04.002 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|



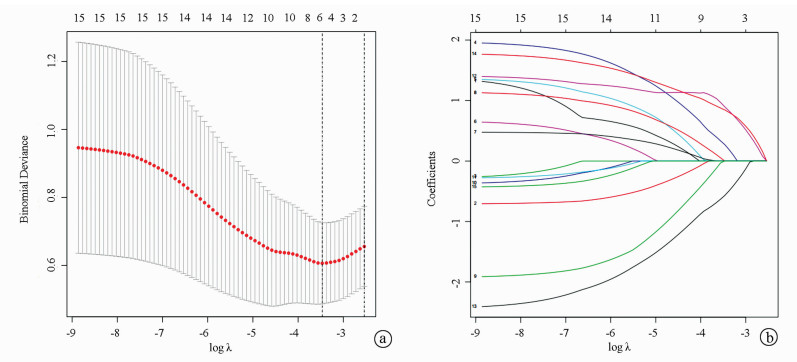




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: