| [1] |
Pancreas Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Pancreatology; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Digestion. Chinese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Shenyang, 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2706-2711. (in Chinese)
中华医学会消化病学分会胰腺疾病学组, 《中华胰腺病杂志》编委会, 《中华消化杂志》编委会. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2019年, 沈阳)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2706-2711.
|
| [2] |
HE WH, ZHU Y, ZHU Y, et al. Comparison of severity and clinical outcomes between hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis and acute pancreatitis due to other causes[J]. Natl Med J China, 2016, 96(32) : 2569-2572. (in Chinese)
何文华, 祝荫, 朱勇, 等. 高脂血症与其他病因所致急性胰腺炎的病情严重程度及预后比较[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(32): 2569-2572.
|
| [3] |
SCHERER J, SINGH VP, PITCHUMONI CS, et al. Issues in hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: An update[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2014, 48(3): 195-203. DOI: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000436438.60145.5a |
| [4] |
NAWAZ H, KOUTROUMPAKIS E, EASLER J, et al. Elevated serum triglycerides are independently associated with persistent organ failure in acute pancreatitis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2015, 110(10): 1497-1503. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2015.261 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
KOLBER W, KUS'NIERZ-CABALA B, MARAJ M, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio at the early phase of acute pancreatitis correlates with serum urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and interleukin 6 and predicts organ failure[J]. Folia Med Cracov, 2018, 58(4): 57-74.
|
| [7] |
ZHOU CL, ZHANG CH, ZHAO XY, et al. Early prediction of persistent organ failure by serum apolipoprotein A-I and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2018, 476: 139-145. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.11.028 |
| [8] |
BANKS PA, BOLLEN TL, DERVENIS C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. Gut, 2013, 62(1): 102-111. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779 |
| [9] |
VALDIVIELSO P, RAMÍREZ-BUENO A, EWALD N. Current knowledge of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2014, 25(8): 689-694. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.08.008 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
WU C, KE L, TONG Z, et al. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for acute kidney injury in the early phase of acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2014, 43(8): 1312-1316. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000180 |
| [12] |
ZHANG N, ZHANG HY, GUO XH, et al. Changes of etiology in acute pancreatitis in recent 10 years in China: Meta-analysis[J/CD]. Chin J Digest Med Imageol (Electronic Edition), 2016, 6(2): 71-75. (in Chinese)
张娜, 张海燕, 郭晓红, 等. 中国近十年急性胰腺炎病因变化特点的Meta分析[J/CD]. 中华消化病与影像杂志(电子版), 2016, 6(2): 71-75.
|
| [13] |
ZHU Y, PAN X, ZENG H, et al. A study on the etiology, severity, and mortality of 3260 patients with acute pancreatitis according to the revised atlanta classification in Jiangxi, China over an 8-year period[J]. Pancreas, 2017, 46(4): 504-509. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000776 |
| [14] |
CHEN L, YU BP, LIN MJ. The comparison between biliary acute pancreatitis and hypertriglyceridemia induced acute pancreatitis, and the relation between triglyceride and acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 26(7): 749-753. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCBX201707009.htm |
| [15] |
HU QM, NIU CY. Predictive value of combined measurement of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and peripheral blood leukocyte count for severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(8): 1522-1526. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.08.023 |
| [16] |
PINHU L, QIN Y, XIONG B, et al. Overexpression of Fas and FasL is associated with infectious complications and severity of experimental severe acute pancreatitis by promoting apoptosis of lymphocytes[J]. Inflammation, 2014, 37(4): 1202-1212. DOI: 10.1007/s10753-014-9847-8 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
XING ZC, WANG JH, HOU XT. Accumulation and different sources between neutrophils and monocytes in sepsis-related acute lung injury[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis (Electronic Edition, 2014, 8(3): 303-307. (in Chinese)
邢智辰, 王金宏, 侯晓彤. 中性粒细胞和单核细胞在脓毒症相关急性肺损伤聚集和来源差异的研究[J/CD]. 中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版), 2014, 8(3): 303-307.
|
| [20] |
VUILLEUMIER N, DAYER JM, VON ECKARDSTEIN A, et al. Pro- or anti-inflammatory role of apolipoprotein A-1 in high-density lipoproteins?[J]. Swiss Med Wkly, 2013, 143: w13781. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/23740387 |
| [21] |
PENG YS, CHEN YC, TIAN YC, et al. Serum levels of apolipoprotein A-I and high-density lipoprotein can predict organ failure in acute pancreatitis[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19: 88. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-015-0832-x |
| [22] |
ZHOU CL, ZHANG CH, ZHAO XY, et al. Early prediction of persistent organ failure by serum apolipoprotein A-I and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2018, 476: 139-145. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.11.028 |
| [23] |
CASTRO FS, NASCIMENTO AM, COUTINHO IA, et al. Plasmapheresis as a therapeutic approach for hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis[J]. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva, 2012, 24(3): 302-307. DOI: 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300015 |
| [24] |
BASAR R, UZUM AK, CANBAZ B, et al. Therapeutic apheresis for severe hypertriglyceridemia in pregnancy[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2013, 287(5): 839-843. DOI: 10.1007/s00404-013-2786-z |
| [25] |
GAO F, YAN Z, ZHANG J. Association between triglyceride level and the severity of acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(11): 2360-2363. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.11.018 |
| [26] |
|



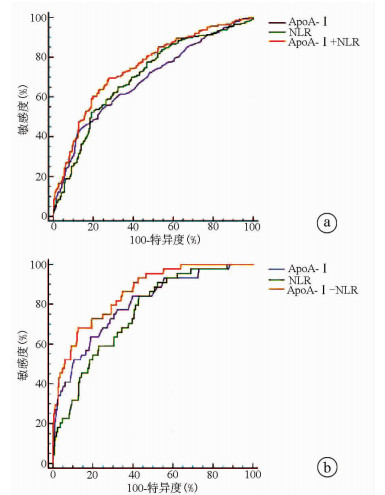




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: