| [1] |
YAMAGIWA S, KAMIMURA H, TAKAMURA M, et al. Autoantibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis: Recent progress in research on the pathogenetic and clinical significance[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(10): 2606-2612. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2606 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
SMEDBY KE, HJALGRIM H, ASKLING J, et al. Autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disorders and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma by subtype[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2006, 98(1): 51-60. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djj004 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
GOLDIN LR, LANDGREN O. Autoimmunity and lymphomagenesis[J]. Int J Cancer, 2009, 124(7): 1497-1502. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24141 |
| [6] |
FLOREANI A, SPINAZZÈ A, CABALLERIA L, et al. Extrahepatic malignancies in primary biliary cirrhosis: A comparative study at two European centers[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2015, 48(2-3): 254-262. DOI: 10.1007/s12016-014-8446-7 |
| [7] |
KANELLOPOULOU T, ALEXOPOULOU A, KONTOPIDOU FN, et al. Development of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in a patient with primary biliary cirrhosis: A case report and review of the literature[J]. Ann Gastroenterol, 2011, 24(2): 125-128. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC3959296/ |
| [8] |
PANJALA C, TALWALKAR JA, LINDOR KD. Risk of lymphoma in primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2007, 5(6): 761-764. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.02.020 |
| [9] |
TIAN H. Rheumatic and skin manifestations associated with autoimmune liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(9): 2021-2026. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.09.041 |
| [10] |
ZHANG W, FENG S, YAN S, et al. Incidence of malignancy in primary Sjogren's syndrome in a Chinese cohort[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2010, 49(3): 571-577. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep404 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
JARDIN F. Development of autoimmunity in lymphoma[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2008, 4(2): 247-266. DOI: 10.1586/1744666X.4.2.247 |
| [13] |
MYERS RP, SWAIN MG, LEE SS, et al. B-cell depletion with rituximab in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis refractory to ursodeoxycholic acid[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2013, 108(6): 933-941. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2013.51 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
TSUDA M, MORITOKI Y, LIAN ZX, et al. Biochemical and immunologic effects of rituximab in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and an incomplete response to ursodeoxycholic acid[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(2): 512-521. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24748 |
| [16] |
KHANNA A, JOPSON L, HOWEL D, et al. Rituximab is ineffective for treatment of fatigue in primary biliary cholangitis: A phase 2 randomized controlled trial[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(5): 1646-1657. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30099 |
| [17] |
DHIRAPONG A, LLEO A, YANG GX, et al. B cell depletion therapy exacerbates murine primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 53(2): 527-535. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24044 |
| [18] |
YIN YF, ZHANG X. B cell depletion in treating primary biliary cirrhosis: Pros and cons[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012, 18(30): 3938-3940. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3938 |
| [19] |
TAJIRI K, TSUNEYAMA K, MIYAZONO T, et al. A case of primary biliary cirrhosis that progressed rapidly after treatment involving rituximab[J]. Case Rep Gastroenterol, 2013, 7(1): 195-201. DOI: 10.1159/000351173 |



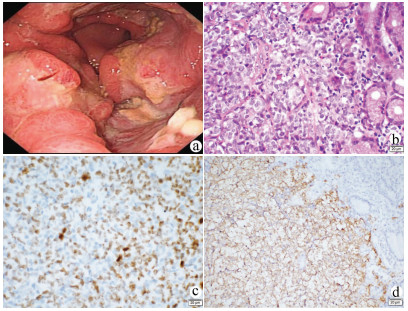




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: