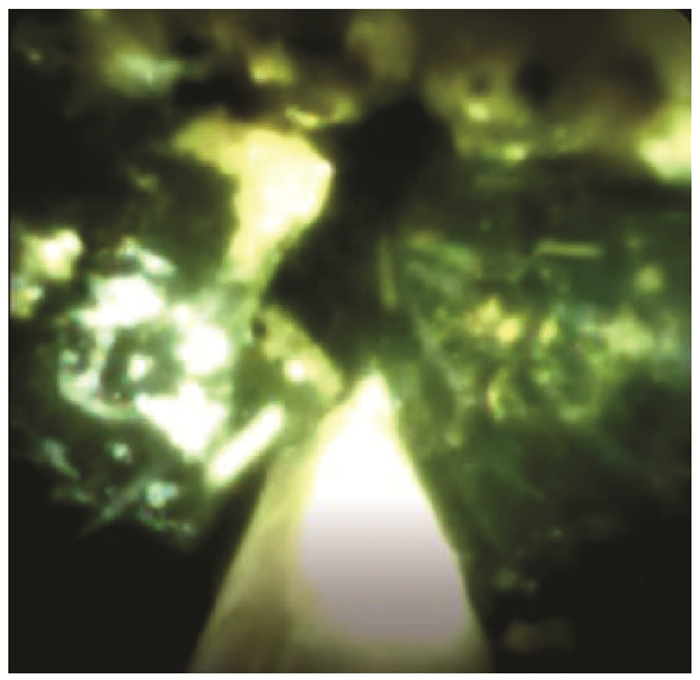
| [1] |
BOKEMEYER A, GERGES C, LANG D, et al. Digital single-operator video cholangioscopy in treating refractory biliary stones: A multicenter observational study[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34(5): 1914-1922. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-019-06962-0. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
KURIHARA T, YASUDA I, ISAYAMA H, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic single-operator cholangiopancreatoscopy in biliopancreatic diseases: Prospective multicenter study in Japan[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(5): 1891-1901. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1891. |
| [4] |
FRANZINI T, CARDARELLI-LEITE L, FIGUEIRA E, et al. SpyGlass percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy-guided lithotripsy of a large intrahepatic stone[J]. Endoscopy, 2017, 49(12): e292-292e293. DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-117943. |
| [5] |
ABURAJAB M, DUA K. Endoscopic management of difficult bile duct stones[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2018, 20(2): 8. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-018-0613-1. |
| [6] |
WONG JC, TANG RS, TEOH AY, et al. Efficacy and safety of novel digital single-operator peroral cholangioscopy-guided laser lithotripsy for complicated biliary stones[J]. Endosc Int Open, 2017, 5(1): e54-e58. DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-118701. |
| [7] |
LALEMAN W, VERRAES K, van STEENBERGEN W, et al. Usefulness of the single-operator cholangioscopy system SpyGlass in biliary disease: A single-center prospective cohort study and aggregated review[J]. Surg Endosc, 2017, 31(5): 2223-2232. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-016-5221-2. |
| [8] |
COLOMBI D, ARAGONA G, BODINI FC, et al. SpyGlass percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy-guided diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the ampullary region in a patient with bariatric biliopancreatic diversion[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2019, 18(3): 291-293. DOI: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2019.03.002. |
| [9] |
YAN S, TEJASWI S. Clinical impact of digital cholangioscopy in management of indeterminate biliary strictures and complex biliary stones: A single-center study[J]. Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc, 2019, 12: 2631774519853160. DOI: 10.1177/2631774519853160. |
| [10] |
CHEN YK. Preclinical characterization of the Spyglass peroral cholangiopancreatoscopy system for direct access, visualization, and biopsy[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2007, 65(2): 303-311. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.07.048. |
| [11] |
HAMMERLE CW, HAIDER S, CHUNG M, et al. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography complications in the era of cholangioscopy: Is there an increased risk?[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2012, 44(9): 754-758. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2012.04.024. |
| [12] |
KALAITZAKIS E, WEBSTER GJ, OPPONG KW, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic utility of single-operator peroral cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary lesions and bile duct stones[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 24(6): 656-664. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283526fa1. |
| [13] |
DU L, D′SOUZA P, THIESEN A, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures using the SpyGlass system: A case series[J]. Endoscopy, 2015, 47(11): 1054-1056. DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1392527. |
| [14] |
XU W, MIAO L, WANG ZF, et al. Application of SpyGlass TM DS direct visualization system in the diagnosis and treatment of biliary tract diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(11): 2626-2629. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.052. |








 本站查看
本站查看

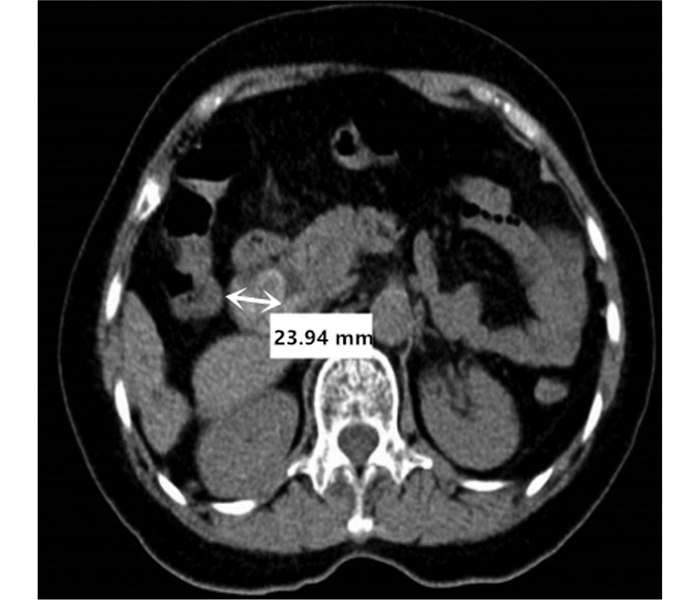




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: