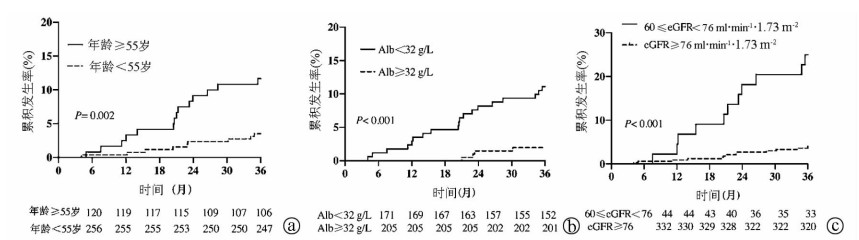
| [1] |
FABRIZI F, CERUTTI R, RIDRUEJO E. Hepatitis B virus infection as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease[J]. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol, 2019, 12(9): 867-874. DOI: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1657828. |
| [2] |
HONG YS, RYU S, CHANG Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and development of chronic kidney disease: A cohort study[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2018, 19(1): 353. DOI: 10.1186/s12882-018-1154-4. |
| [3] |
CHACKO EC, SURRUN SK, MUBARACK SANI TP, et al. Chronic viral hepatitis and chronic kidney disease[J]. Postgrad Med J, 2010, 86(1018): 486-492. DOI: 10.1136/pgmj.2009.092775. |
| [4] |
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10225): 709-733. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. |
| [5] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [6] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. |
| [7] |
STEVENS PE, LEVIN A, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2013, 158(11): 825-830. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00007. |
| [8] |
LEVEY AS, BOSCH JP, LEWIS JB, et al. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: A new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group[J]. Ann Intern Med, 1999, 130(6): 461-470. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-6-199903160-00002. |
| [9] |
CARNEY EF. Glomerular filtration rate: CKD risk factors are associated with increased single-nephron GFR[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017, 13(8): 443. DOI: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.95. |
| [10] |
ISHANI A, XUE JL, HIMMELFARB J, et al. Acute kidney injury increases risk of ESRD among elderly[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2009, 20(1): 223-228. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007080837. |
| [11] |
LOW S, LIM SC, ZHANG X, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for chronic kidney disease progression in type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a 13-year study in Singapore[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2017, 123: 49-54. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.11.008. |
| [12] |
CHEN PM, WADA T, CHIANG CK. Prognostic value of proteinuria and glomerular filtration rate on Taiwanese patients with diabetes mellitus and advanced chronic kidney disease: A single center experience[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2017, 21(2): 307-315. DOI: 10.1007/s10157-016-1290-8. |
| [13] |
KEANE WF, ZHANG Z, LYLE PA, et al. Risk scores for predicting outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy: The RENAAL study[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2006, 1(4): 761-767. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01381005. |
| [14] |
KIKUCHI H, KANDA E, MANDAI S, et al. Combination of low body mass index and serum albumin level is associated with chronic kidney disease progression: The chronic kidney disease-research of outcomes in treatment and epidemiology (CKD-ROUTE) study[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2017, 21(1): 55-62. DOI: 10.1007/s10157-016-1251-2. |
| [15] |
TRAWALÉ JM, PARADIS V, RAUTOU PE, et al. The spectrum of renal lesions in patients with cirrhosis: A clinicopathological study[J]. Liver Int, 2010, 30(5): 725-732. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02182.x. |
| [16] |
MORINAGA J, KADOMATSU T, MIYATA K, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 increases renal fibrosis by accelerating transforming growth factor-β signaling in chronic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 89(2): 327-341. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.021. |
| [17] |
SI J, YU C, GUO Y, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection and total and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study of 0.5 million people[J]. BMJ Open, 2019, 9(4): e027696. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027696. |
| [18] |
SARAFIDIS PA, RUILOPE LM. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and renal injury: Mechanisms and implications[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2006, 26(3): 232-244. DOI: 10.1159/000093632. |
| [19] |
LAMPERTICO P, CHAN HL, JANSSEN HL, et al. Review article: Long-term safety of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues in HBV-monoinfected patients[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 44(1): 16-34. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13659. |
| [20] |
HAGER MR, NARLA AD, TANNOCK LR. Dyslipidemia in patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. Rev Endocr Metab Disord, 2017, 18(1): 29-40. DOI: 10.1007/s11154-016-9402-z. |










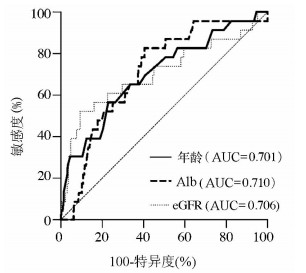




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: