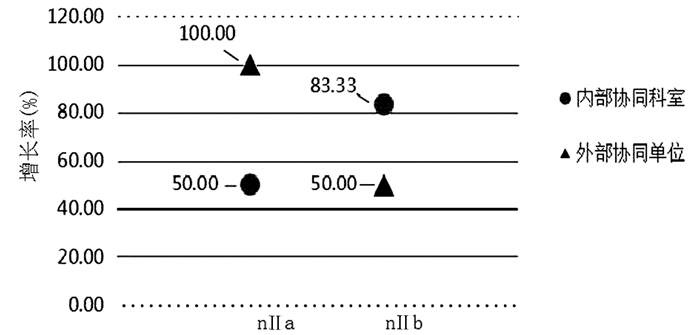
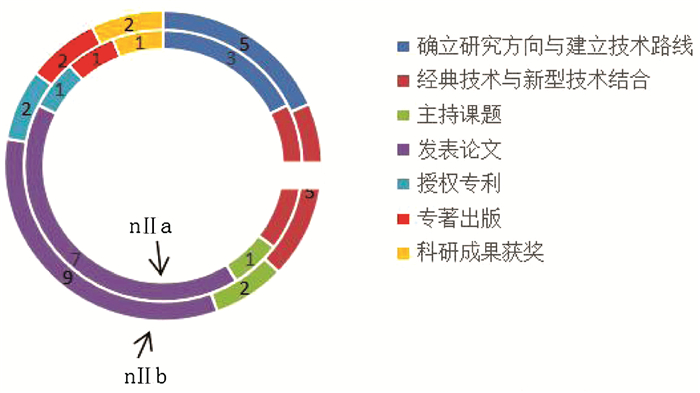
| [1] |
GAO HJ. Practice and thinking on the construction of new clinical medicine discipline of "patient-centered"[J]. Natl Med J China, 2020, 11(40): 3126-3129. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200324-00911. |
| [2] |
VERONICA S, THOMAS F. Collaborative innovation in ubiquitous systems[J]. J Intell Manuf, 2007, 18(5): 599-615. DOI: 10.1007/s10845-007-0064-2. |
| [3] |
HINRICHS MM, SEAGER TP, TRACY SJ, et al. Innovation in the knowledge age: Implications for collaborative science[J]. Environ Syst Decis, 2017, 37(2): 144-155. DOI: 10.1007/s10669-016-9610-9. |
| [4] |
van WEEL C, TURNBULL D, WHITEHEAD E, et al. International collaboration in innovating health systems[J]. Ann Fam Med, 2015, 13(1): 86-87. DOI: 10.1370/afm.1751. |
| [5] |
GOUGET B, TOUIMI B, JELLOUN M. The fifbcml: A mediterranean-leading platform for collaboration and innovation in lab medical[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2017, 55: s131. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2017-5001. |
| [6] |
RUAN B, YU Z, YANG S, et al. Establishment and development of national community-based collaborative innovation demonstration areas to achieve the control target of hepatitis B in China[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19(1): 617. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4150-9. |
| [7] |
POYAN MEHR A, SADEGHI-NAJAFABADI M, CHAU K, et al. The glomerular disease study and trial consortium: A grassroots initiative to foster collaboration and innovation[J]. Kidney Int Rep, 2019, 4(1): 20-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2018.09.012. |
| [8] |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. |
| [9] |
XIAO J, WANG F, WONG NK, et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71(1): 212-221. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.004. |
| [10] |
TAPPER EB, LOK AS. Use of liver imaging and biopsy in clinical practice[J]. N Eng J Med, 2017, 377(8): 756-768. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1610570. |
| [11] |
TORBENSON M, WASHINGTON K. Pathology of liver disease: Advances in the last 50 years[J]. Hum Pathol, 2020, 95: 78-98. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.08.023. |
| [12] |
TANG H, XU RR, JIANG LL, et al. A study of construction strategy for regional clinical pathology center of liver disease based on SWOT analysis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1582-1584. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.031. |
| [13] |
FU L, YIN L, ZHU ML, et al. Innovation system construction for China's basic and clinical medcine[J]. Eng Sci, 2017, 19(2): 72-78. DOI: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2017.02.012. |
| [14] |
ESLAM M, SANYAL AJ, GEORGE J, et al. MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(7): 1999-2014. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312. |
| [15] |
TANAKA N, KIMURA T, FUJIMORI N, et al. Current status, problems, and perspectives of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease research[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(2): 163-177. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i2.163. |
| [16] |
LI LJ, ZHENG SS, CHEN Z, et al. Theoretical innovation and technical breakthrough in the diagnosis and treatment of severe liver disease[J]. China Sci Technol Achievements, 2014, 15(1): 64-66. DOI: 10.3772/j.issn.1009-5659.2014.01.025. |
| [17] |
CHESBROUGH H. Open innovation: Where we've been and where we're going: The father of open innovation offers his assessment of the history and future of the model[J]. Res Technol Manage, 2012, 55(4): 20-27. DOI: 10.5437/08956308X5504085. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: