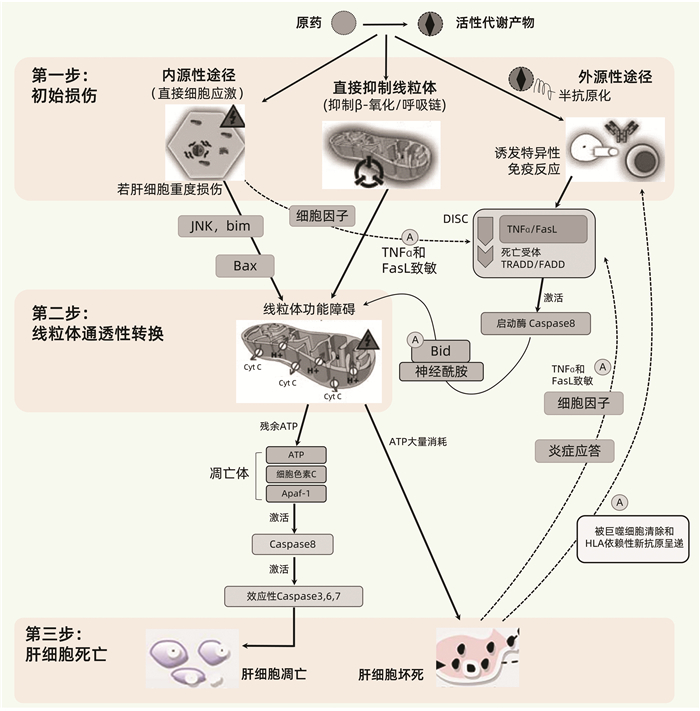
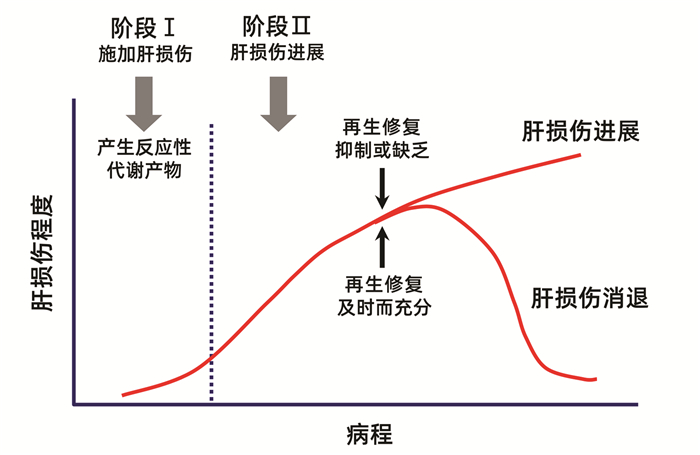
| [1] |
YU YC, MAO YM, CHEN CW, et al. CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11(3): 221-241. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9793-2. |
| [2] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(6): 1222-1261. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.014. |
| [3] |
CHALASANI NP, MADDUR H, RUSSO MW, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2021, 116(5): 878-898. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001259. |
| [4] |
DEVARBHAVI H, AITHAL G, TREEPRASERTSUK S, et al. Drug-induced liver injury: Asia Pacific Association of study of liver consensus guidelines[J]. Hepatol Int, 2021, 15(2): 258-282. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10144-3. |
| [5] |
BJÖRNSSON ES, BERGMANN OM, BJÖRNSSON HK, et al. Incidence, presentation, and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(7): 1419-1425, e1-e3; quiz e19-e20. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.006. |
| [6] |
TREEM WR, PALMER M, LONJON-DOMANEC I, et al. Consensus guidelines: Best practices for detection, assessment and management of suspected acute drug-induced liver injury during clinical trials in adults with chronic viral hepatitis and adults with cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis B, C and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Drug Saf, 2021, 44(2): 133-165. DOI: 10.1007/s40264-020-01014-2. |
| [7] |
LIU M, YANG XZ, YU YC. Current status of the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced cholestasis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(2): 115-120. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.02.003. |
| [8] |
CHEN K, GUO R, WEI C. Synonymous mutation rs2515641 affects CYP2E1 mRNA and protein expression and susceptibility to drug-induced liver injury[J]. Pharmacogenomics, 2020, 21(7): 459-470. DOI: 10.2217/pgs-2019-0151. |
| [9] |
CHEN R, WANG J, TANG SW, et al. CYP7A1, BAAT and UGT1A1 polymorphisms and susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis, 2016, 20(6): 812-818. DOI: 10.5588/ijtld.15.0450. |
| [10] |
ZHANG M, WANG S, WILFFERT B, et al. The association between the NAT2 genetic polymorphisms and risk of DILI during anti-TB treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2018, 84(12): 2747-2760. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13722. |
| [11] |
CHANHOM N, UDOMSINPRASERT W, CHAIKLEDKAEW U, et al. GSTM1 and GSTT1 genetic polymorphisms and their association with antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury[J]. Biomed Rep, 2020, 12(4): 153-162. DOI: 10.3892/br.2020.1275. |
| [12] |
DALY AK, DAY CP. Genetic factors in the pathogenesis of drug-induced liver injury[M]// KAPLOWITZ N, DELEVE LD. Drug-induced liver disease, 3rd ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2013: 215-225.
|
| [13] |
WATKINS PB, SELIGMAN PJ, PEARS JS, et al. Using controlled clinical trials to learn more about acute drug-induced liver injury[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48(5): 1680-1689. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22633. |
| [14] |
YANG WN, PANG LL, ZHOU JY, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of HLA and polygonum multiflorum-induced liver injury in the Han Chinese population[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(12): 1329-1339. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i12.1329. |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
HUI CL, LEE ZJ. Hepatic disorders associated with exogenous sex steroids: MR imaging findings[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2019, 44(7): 2436-2447. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-019-01941-4. |
| [17] |
LU ZN, LUO Q, ZHAO LN, et al. The mutational features of aristolochic acid-induced mouse and human liver cancers[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(3): 929-942. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30863. |
| [18] |
HOOFNAGLE JH, BJÖRNSSON ES. Drug-induced liver injury-types and phenotypes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381(3): 264-273. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1816149. |
| [19] |
ZHUGE Y, LIU Y, XIE W, et al. Expert consensus on the clinical management of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(4): 634-642. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14612. |
| [20] |
CHEN M, BORLAK J, TONG W. A Model to predict severity of drug-induced liver injury in humans[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(3): 931-940. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28678. |
| [21] |
MEHENDALE HM. Tissue repair: An important determinant of final outcome of toxicant-induced injury[J]. Toxicol Pathol, 2005, 33(1): 41-51. DOI: 10.1080/01926230590881808. |
| [22] |
ANAND SS, MURTHY SN, VAIDYA VS, et al. Tissue repair plays pivotal role in final outcome of liver injury following chloroform and allyl alcohol binary mixture[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2003, 41(8): 1123-1132. DOI: 10.1016/s0278-6915(03)00066-8. |
| [23] |
ANAND SS, SONI MG, VAIDYA VS, et al. Extent and timeliness of tissue repair determines the dose-related hepatotoxicity of chloroform[J]. Int J Toxicol, 2003, 22(1): 25-33. DOI: 10.1080/10915810305074. |
| [24] |
FONTANA RJ. Pathogenesis of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury and clinical perspectives[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(4): 914-928. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.032. |
| [25] |
HOU JX, YAN FQ, YU YC. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury with extrahepatic adverse drug reactions[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(3): 497-500. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.03.003. |
| [26] |
WANG DY, SALEM JE, COHEN JV, et al. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2018, 4(12): 1721-1728. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3923. |
| [27] |
POSTOW MA, SIDLOW R, HELLMANN MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378(2): 158-168. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1703481. |
| [28] |
VADDEPALLY RK, KHAREL P, PANDEY R, et al. Review of indications of FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors per NCCN guidelines with the level of evidence[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(3): 738. DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030738. |
| [29] |
PEERAPHATDIT TB, WANG J, ODENWALD MA, et al. Hepatotoxicity from immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and management recommendation[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72(1): 315-329. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31227. |
| [30] |
KOK B, LESTER E, LEE WM, et al. Acute liver failure from tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: Report of four cases and literature review[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2018, 63(6): 1654-1666. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-018-5023-6. |
| [31] |
LOPETUSO LR, MOCCI G, MARZO M, et al. Harmful effects and potential benefits of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α on the liver[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(8): 2199. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19082199. |
| [32] |
ZOUBEK ME, PINAZO-BANDERA J, ORTEGA-ALONSO A, et al. Liver injury after methylprednisolone pulses: A disputable cause of hepatotoxicity. A case series and literature review[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2019, 7(6): 825-837. DOI: 10.1177/2050640619840147. |
| [33] |
LOOMBA R, LIANG TJ. Hepatitis B reactivation associated with immune suppressive and biological modifier therapies: Current concepts, management strategies, and future directions[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152(6): 1297-1309. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.009. |
| [34] |
KAPILA N, AL-KHALLOUFI K, BEJARANO PA, et al. Fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis after kidney transplantation from HCV-viremic donors to HCV-negative recipients: A unique complication in the DAA era[J]. Am J Transplant, 2020, 20(2): 600-605. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15583. |
| [35] |
YU YC, HE CL, WANG YM. Recent progress of fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis or immunosuppression-induced liver failure[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2011, 24(3): 185-188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2011.03.018. |
| [36] |
RUSSMANN S, KULLAK-UBLICK GA, GRATTAGLIANO I. Current concepts of mechanisms in drug-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2009, 16(23): 3041-3053. DOI: 10.2174/092986709788803097. |
| [37] |
KRÄHENBUHL S, BRAUCHLI Y, KUMMER O, et al. Acute liver failure in two patients with regular alcohol consumption ingesting paracetamol at therapeutic dosage[J]. Digestion, 2007, 75(4): 232-237. DOI: 10.1159/000111032. |
| [38] |
GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2018, 25(3): 486-541. DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. |
| [39] |
TANG D, KANG R, BERGHE TV, et al. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death[J]. Cell Res, 2019, 29(5): 347-364. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-019-0164-5. |
| [40] |
COPPLE IM, GOLDRING CE, JENKINS RE, et al. The hepatotoxic metabolite of acetaminophen directly activates the Keap1-Nrf2 cell defense system[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48(4): 1292-1301. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22472. |
| [41] |
KALGUTKAR AS, GARDNER I, OBACH RS, et al. A comprehensive listing of bioactivation pathways of organic functional groups[J]. Curr Drug Metab, 2005, 6(3): 161-225. DOI: 10.2174/1389200054021799. |
| [42] |
SÉGUIN B, UETRECHT J. The danger hypothesis applied to idiosyncratic drug reactions[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2003, 3(4): 235-242. DOI: 10.1097/00130832-200308000-00001. |
| [43] |
WANG X, TOMSO DJ, CHORLEY BN, et al. Identification of polymorphic antioxidant response elements in the human genome[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2007, 16(10): 1188-1200. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddm066. |
| [44] |
GRATTAGLIANO I, LAUTERBURG BH, PORTINCASA P, et al. Mitochondrial glutathione content determines the rate of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in eu- and hypothyroid rats[J]. J Hepatol, 2003, 39(4): 571-579. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00317-9. |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
MALATO Y, NAQVI S, SCHVRMANN N, et al. Fate tracing of mature hepatocytes in mouse liver homeostasis and regeneration[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011, 121(12): 4850-4860. DOI: 10.1172/JCI59261. |
| [47] |
LIU L, YANNAM GR, NISHIKAWA T, et al. The microenvironment in hepatocyte regeneration and function in rats with advanced cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(5): 1529-1539. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24815. |
| [48] |
|








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: