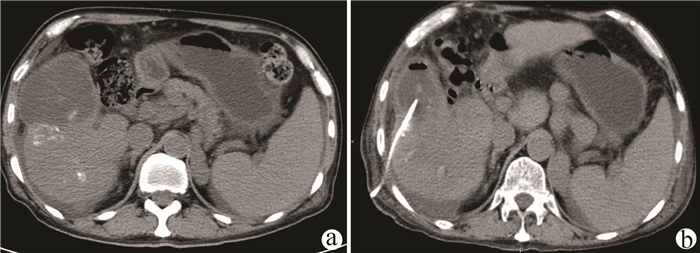
| [1] |
BROWN DB, GESCHWIND JF, SOULEN MC, et al. Society of Interventional Radiology position statement on chemoembolization of hepatic malignancies[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2009, 20(7 Suppl): s317-323. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2009.04.015. |
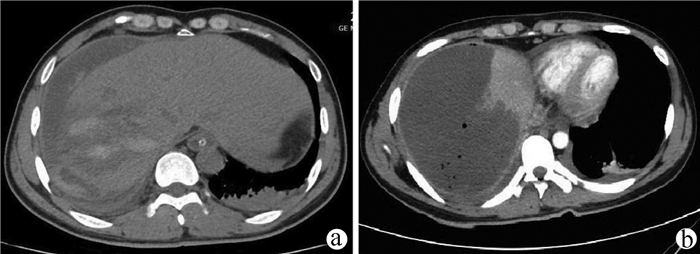
| [2] |
NAULT JC, SUTTER O, NAHON P, et al. Percutaneous treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: State of the art and innovations[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(4): 783-797. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.10.004. |
| [3] |
LI M, LU YY, DONG JH, et al. Clinical effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation in treatment of advanced primary liver cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(12): 2720-2724. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.016. |
| [4] |
LI JH, YAO RR, SHEN HJ, et al. Clostridium perfringens infection after transarterial chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(14): 4397-4401. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4397. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
WI JW, CHO EA, JUN CH, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of pyogenic liver abscess in elderly Korean patients[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2015, 66(1): 27-32. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.1.27. |
| [7] |
CAI MT, LIANG LC. Pathogen distribution and drug resistance in liver cancer patients with liver abscess after transarterial chemoembolization or ablation[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(1): 118-122. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.026. |
| [8] |
ZHU QL, XIANG XX, YUAN LY, et al. Clinical effect of ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage in treatment of liver abscess[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(6): 1318-1321. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.027. |
| [9] |
PICKENS RC, JENSEN S, SULZER JK, et al. Minimally invasive surgical management as effective first-line treatment of large pyogenic hepatic abscesses[J]. Am Surg, 2019, 85(8): 813-820.
|
| [10] |
BEI YF. Clinical effect and feasibility of laparoscopic catheter drainage versus incision and drainage in treatment of liver abscess[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2015, 20(6): 499. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2015.06.025. |
| [11] |
SHIN JU, KIM KM, SHIN SW, et al. A prediction model for liver abscess developing after transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2014, 46(9): 813-817. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2014.05.003. |
| [12] |
JIA Z, TU J, CAO C, et al. Liver abscess following transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of 23 cases[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2018, 14(Supplement): S628-S633. DOI: 10.4103/0973-1482.199385. |



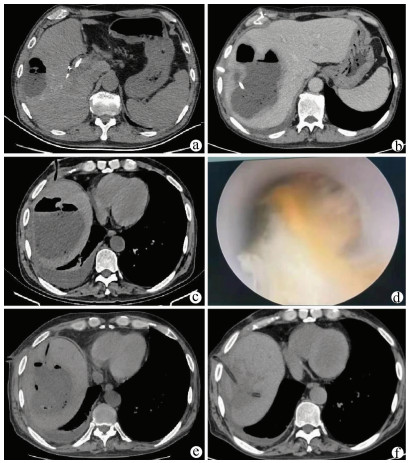




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: