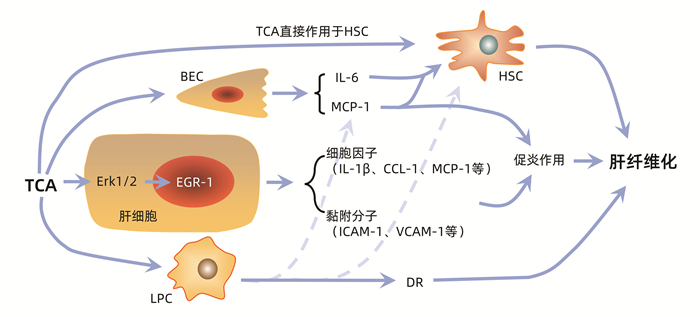
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
PAROLA M, PINZANI M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 65: 37-55. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.09.002. |
| [3] |
TROTTIER J, BIAŁEK A, CARON P, et al. Profiling circulating and urinary bile acids in patients with biliary obstruction before and after biliary stenting[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(7): e22094. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022094. |
| [4] |
JIA W, WEI M, RAJANI C, et al. Targeting the alternative bile acid synthetic pathway for metabolic diseases[J]. Protein Cell, 2021, 12(5): 411-425. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00804-9. |
| [5] |
KIRIYAMA Y, NOCHI H. The biosynthesis, signaling, and neurological functions of bile acids[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(6): 232. DOI: 10.3390/biom9060232. |
| [6] |
TICHO AL, MALHOTRA P, DUDEJA PK, et al. Intestinal absorption of bile acids in health and disease[J]. Compr Physiol, 2019, 10(1): 21-56. DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c190007. |
| [7] |
KOK B, ABRALDES JG. Child-Pugh classification: Time to abandon?[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2019, 39(1): 96-103. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1676805. |
| [8] |
RIMINI M, ROVESTI G, CASADEI-GARDINI A. Child Pugh and ALBI grade: Past, present or future?[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(17): 1044. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-3709. |
| [9] |
WANG X, XIE G, ZHAO A, et al. Serum bile acids are associated with pathological progression of hepatitis B-induced cirrhosis[J]. J Proteome Res, 2016, 15(4): 1126-1134. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00217. |
| [10] |
LIU Z, ZHANG Z, HUANG M, et al. Taurocholic acid is an active promoting factor, not just a biomarker of progression of liver cirrhosis: Evidence from a human metabolomic study and in vitro experiments[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2018, 18(1): 112. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0842-7. |
| [11] |
HORVATITS T, DROLZ A, ROEDL K, et al. Serum bile acids as marker for acute decompensation and acute-on-chronic liver failure in patients with non-cholestatic cirrhosis[J]. Liver Int, 2017, 37(2): 224-231. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13201. |
| [12] |
KHOMICH O, IVANOV AV, BARTOSCH B. Metabolic hallmarks of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis[J]. Cells, 2019, 9(1): 24. DOI: 10.3390/cells9010024. |
| [13] |
MU M, ZUO S, WU RM, et al. Ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2018, 12: 4107-4115. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S186726. |
| [14] |
FAN Y, LI Y, CHU Y, et al. Toll-like receptors recognize intestinal microbes in liver cirrhosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 608498. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.608498. |
| [15] |
SEKI E, de MINICIS S, OSTERREICHER CH, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis[J]. Nat Med, 2007, 13(11): 1324-1332. DOI: 10.1038/nm1663. |
| [16] |
FABREGAT I, CABALLERO-DíAZ D. Transforming growth factor-β-induced cell plasticity in liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Front Oncol, 2018, 8: 357.
|
| [17] |
CAJA L, DITURI F, MANCARELLA S, et al. TGF-β and the tissue microenvironment: Relevance in fibrosis and cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(5): 1294. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19051294. |
| [18] |
GHAFOORY S, VARSHNEY R, ROBISON T, et al. Platelet TGF-β1 deficiency decreases liver fibrosis in a mouse model of liver injury[J]. Blood Adv, 2018, 2(5): 470-480. DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017010868. |
| [19] |
PAIK YH, SCHWABE RF, BATALLER R, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells[J]. Hepatology, 2003, 37(5): 1043-1055. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50182. |
| [20] |
WEI S, MA X, ZHAO Y. Mechanism of hydrophobic bile acid-induced hepatocyte injury and drug discovery[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 1084. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01084. |
| [21] |
ALLEN K, JAESCHKE H, COPPLE BL. Bile acids induce inflammatory genes in hepatocytes: A novel mechanism of inflammation during obstructive cholestasis[J]. Am J Pathol, 2011, 178(1): 175-186. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.026. |
| [22] |
ALLEN K, KIM ND, MOON JO, et al. Upregulation of early growth response factor-1 by bile acids requires mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2010, 243(1): 63-67. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.11.013. |
| [23] |
GUJRAL JS, LIU J, FARHOOD A, et al. Functional importance of ICAM-1 in the mechanism of neutrophil-induced liver injury in bile duct-ligated mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2004, 286(3): G499-507. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00318.2003. |
| [24] |
CAI X, LI Z, ZHANG Q, et al. CXCL6-EGFR-induced Kupffer cells secrete TGF-β1 promoting hepatic stellate cell activation via the SMAD2/BRD4/C-MYC/EZH2 pathway in liver fibrosis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(10): 5050-5061. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13787. |
| [25] |
KIM ND, MOON JO, SLITT AL, et al. Early growth response factor-1 is critical for cholestatic liver injury[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2006, 90(2): 586-595. DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfj111. |
| [26] |
MARRA F, ROMANELLI RG, GIANNINI C, et al. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 as a chemoattractant for human hepatic stellate cells[J]. Hepatology, 1999, 29(1): 140-148. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510290107. |
| [27] |
QUECK A, BODE H, USCHNER FE, et al. Systemic MCP-1 levels derive mainly from injured liver and are associated with complications in cirrhosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 354. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00354. |
| [28] |
RAMM GA, SHEPHERD RW, HOSKINS AC, et al. Fibrogenesis in pediatric cholestatic liver disease: Role of taurocholate and hepatocyte-derived monocyte chemotaxis protein-1 in hepatic stellate cell recruitment[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 49(2): 533-544. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22637. |
| [29] |
LI L, WEI W, LI Z, et al. The spleen promotes the secretion of CCL2 and supports an M1 dominant phenotype in hepatic macrophages during liver fibrosis[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(2): 557-574. DOI: 10.1159/000495276. |
| [30] |
SUN T, ANNUNZIATO S, TCHORZ JS. Hepatic ductular reaction: A double-edged sword[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(21): 9223-9224. DOI: 10.18632/aging.102386. |
| [31] |
SATO K, MARZIONI M, MENG F, et al. Ductular reaction in liver diseases: pathological mechanisms and translational significances[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(1): 420-430. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30150. |
| [32] |
POZNIAK KN, PEAREN MA, PEREIRA TN, et al. Taurocholate induces biliary differentiation of liver progenitor cells causing hepatic stellate cell chemotaxis in the ductular reaction: Role in pediatric cystic fibrosis liver disease[J]. Am J Pathol, 2017, 187(12): 2744-2757. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.08.024. |
| [33] |
RUDDELL RG, KNIGHT B, TIRNITZ-PARKER JE, et al. Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling regulates hepatic stellate cell function and wound healing in a murine model of chronic liver injury[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 49(1): 227-239. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22597. |
| [34] |
TIRNITZ-PARKER JE, OLYNYK JK, RAMM GA. Role of TWEAK in coregulating liver progenitor cell and fibrogenic responses[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(3): 1198-1201. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26701. |
| [35] |
LAMIREAU T, ZOLTOWSKA M, LEVY E, et al. Effects of bile acids on biliary epithelial cells: Proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine secretion[J]. Life Sci, 2003, 72(12): 1401-1411. DOI: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)02408-6. |
| [36] |
XIANG DM, SUN W, NING BF, et al. The HLF/IL-6/STAT3 feedforward circuit drives hepatic stellate cell activation to promote liver fibrosis[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(9): 1704-1715. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313392. |
| [37] |
REMMLER J, SCHNEIDER C, TREUNER-KAUEROFF T, et al. Increased level of interleukin 6 associates with increased 90-day and 1-year mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16(5): 730-737. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.017. |
| [38] |
LABENZ C, TOENGES G, HUBER Y, et al. Raised serum Interleukin-6 identifies patients with liver cirrhosis at high risk for overt hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(10): 1112-1119. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15515. |
| [39] |
DU PLESSIS J, VANHEEL H, JANSSEN CE, et al. Activated intestinal macrophages in patients with cirrhosis release NO and IL-6 that may disrupt intestinal barrier function[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 58(6): 1125-1132. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.038. |
| [40] |
MANCINELLI R, ONORI P, GAUDIO E, et al. Taurocholate feeding to bile duct ligated rats prevents caffeic acid-induced bile duct damage by changes in cholangiocyte VEGF expression[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2009, 234(4): 462-474. DOI: 10.3181/0808-RM-255. |
| [41] |
GAUDIO E, BARBARO B, ALVARO D, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates rat cholangiocyte proliferation via an autocrine mechanism[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(4): 1270-1282. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.034. |



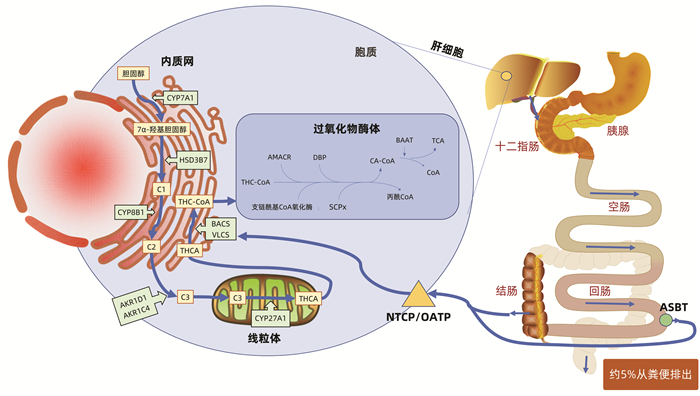




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: