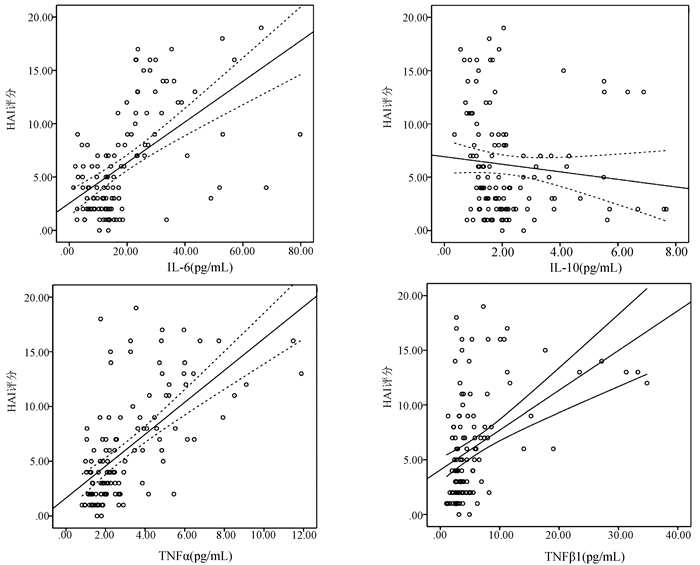
| [1] |
WEN H, VUITTON L, TUXUN T, et al. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 32(2): e00075-18. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00075-18. |
| [2] |
ZHAO SY, ZHU HH, WANG XQ, et al. Present situation and progress of comprehensive treatments for hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2019, 31(6): 676-678. DOI: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2018086. |
| [3] |
NONO JK, LUTZ MB, BREHM K. Expansion of host regulatory T cells by secreted products of the tapeworm echinococcus multilocularis[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 798. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00798. |
| [4] |
CAI J, HUANG L, WANG LJ, et al. The role of macrophage polarization in parasitic infections: A review[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2020, 32(4): 432-435. DOI: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2019252. |
| [5] |
International classification of ultrasound images in cystic echinococcosis for application in clinical and field epidemiological settings[J]. Acta Trop, 2003, 85(2): 253-261. DOI: 10.1016/s0001-706x(02)00223-1. |
| [6] |
Chinese Doctor Association, Chinese College of Surgeons, Echinococcosis Professional Committee. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of two types of hydatid disease (2015 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2015, 14(4): 253-264. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2015.04.001. |
| [7] |
WANG H, ZHANG CS, FANG BB, et al. Dual role of hepatic macrophages in the establishment of the echinococcus multilocularis metacestode in mice[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 600635. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.600635. |
| [8] |
KASIMU AHT, ABUDUSALAMU AN, TUERGANAILI AJ, et al. Analysis of hospital expenses for patients with end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis receiving ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2020, 38(1): 53-57. DOI: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.01.021. |
| [9] |
SUN YY, LI XF, MENG XM, et al. Macrophage phenotype in liver injury and repair[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2017, 85(3): 166-174. DOI: 10.1111/sji.12468. |
| [10] |
ZHANG K, SHI Z, ZHANG M, et al. Silencing lncRNA Lfar1 alleviates the classical activation and pyoptosis of macrophage in hepatic fibrosis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 132. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-2323-5. |
| [11] |
LIU X, LOU JL, BAI L, et al. Phenotypic transformation of macrophages in the liver during the development of liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Labeled Immunoassays Clin Med, 2019, 26(9): 1532-1536, 1564. DOI: 10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2019.09.020. |
| [12] |
JI C, ZHANG WJ, GUAN N, et al. Effect of M1 macrophages on immune status in chronic periodontitis model mice[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2020, 46(6): 1137-1142. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200605. |
| [13] |
ATRI C, GUERFALI FZ, LAOUINI D. Role of human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(6). DOI: 10.3390/ijms19061801. |
| [14] |
GUO ZJ, ZHAI HQ, WANG NN, et al. Study of macrophage polarization on pulmonary fibrosis and signaling pathway[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2018, 43(22): 4370-4379. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2018.0117. |
| [15] |
TACKE F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(6): 1300-1312. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026. |
| [16] |
E WJ, LU YL, ZHANG LQ, et al. Characteristics and clinical value of macrophage polarization in tissues and serum of patients with hepatic alveolar echinocococosis[J]. J Pract Med, 2020, 36(9): 1198-1202. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2020.09.016. |
| [17] |
LI X, JIN Q, YAO Q, et al. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates liver inflammation and fibrosis by regulating hepatic macrophages activation and polarization in mice[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 72. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00072. |
| [18] |
CHEN C, SHEN WT, LIU Y. Advances in research on the effect of macrophages in microenvironment on liver fibrosis due to schistosomiasis[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2020, 15(2): 241-245. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.200225. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: