| [1] |
BUZZETTI E, PINZANI M, TSOCHATZIS EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Metabolism, 2016, 65(8): 1038-1048. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012. |
| [2] |
SAAD ZA, KHODEER DM, ZAITONE SA, et al. Exenatide ameliorates experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats via suppression of toll-like receptor 4/NFκB signaling: Comparison to metformin[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 253: 117725. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117725. |
| [3] |
FITZGERALD KA, KAGAN JC. Toll-like receptors and the control of immunity[J]. Cell, 2020, 180(6): 1044-1066. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.041. |
| [4] |
WANG Y, ZHANG S, LI H, et al. Small-molecule modulators of toll-like receptors[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2020, 53(5): 1046-1055. DOI: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00631. |
| [5] |
FUSELLA F, SECLÌ L, CANNATA C, et al. The one thousand and one chaperones of the NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2020, 77(12): 2275-2288. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03402-z. |
| [6] |
VALIZADEH A, MAJIDINIA M, SAMADI-KAFIL H, et al. The roles of signaling pathways in liver repair and regeneration[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28336. |
| [7] |
CSAK T, VELAYUDHAM A, HRITZ I, et al. Deficiency in myeloid differentiation factor-2 and toll-like receptor 4 expression attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2011, 300(3): G433-G441. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00163.2009. |
| [8] |
CHEN SN, TAN Y, XIAO XC, et al. Effect of TLR4 gene knockout on acute liver injury in septic mice[J]. J Pract Med, 2020, 36(11): 1425-1428. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2020.11.004. |
| [9] |
XU HC, GAO Y, MENG YN, et al. Correlation between TLR4 gene and its methylation level in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rats[J]. Tianjin Med J, 2020, 48(7): 625-629. DOI: 10.11958/20193587. 徐慧超, 高艳, 孟雅楠, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎大鼠TLR4基因及其甲基化水平的相关性研究[J]. 天津医药, 2020, 48(7): 625-629. DOI: 10.11958/20193587. |
| [10] |
SWANTEK JL, TSEN MF, COBB MH, et al. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase modulates host responsiveness to endotoxin[J]. J Immunol, 2000, 164(8): 4301-4306. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.8.4301. |
| [11] |
SONG IJ, YANG YM, INOKUCHI-SHIMIZU S, et al. The contribution of toll-like receptor signaling to the development of liver fibrosis and cancer in hepatocyte-specific TAK1-deleted mice[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018, 142(1): 81-91. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31029. |
| [12] |
HE Q, ZENG J, YAO K, et al. Long-term subcutaneous injection of lipopolysaccharides and high-fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through IKKε/ NF-κB signaling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 532(3): 362-369. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.036. |
| [13] |
CHEN CY, KAO CL, LIU CM. The cancer prevention, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidation of bioactive phytochemicals targeting the TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(9): 2729. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092729. |
| [14] |
MITCHELL JP, CARMODY RJ. NF-κB and the transcriptional control of inflammation[J]. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 2018, 335: 41-84. DOI: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.07.007. |
| [15] |
YAO Q, LI S, LI X, et al. Myricetin modulates macrophage polarization and mitigates liver inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2020, 7: 71. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00071. |
| [16] |
MARCOLIN E, SAN-MIGUEL B, VALLEJO D, et al. Quercetin treatment ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Nutr, 2012, 142(10): 1821-1828. DOI: 10.3945/jn.112.165274. |
| [17] |
LIU J, YUAN Y, GONG X, et al. Baicalin and its nanoliposomes ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via suppression of TLR4 signaling cascade in mice[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 80: 106208. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106208. |
| [18] |
ZHOU GY, YI YX, JIN LX, et al. The protective effect of juglanin on fructose-induced hepatitis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through TLR4 and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways in fructose-fed rats[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2016, 81: 318-328. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.04.013. |
| [19] |
ZHANG KF, JIN L. Protective effect and mechanism of dicliptera chinensis polysaccharides on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats based on PPAR-γ and TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Clin Med, 2019, 35(4): 103-107. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2019.04.020. |
| [20] |
WANG JQ, LI J, ZOU YH, et al. Therapeutic effects of Total Flavonoids of Litsea Coreana leve on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and its partly mechanisms of action[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2012, 28(3): 412-416. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2012.03.026. |
| [21] |
DONG ZC, GAO Q, MAO JN. The regulatory effect of bilobalide on hepatic fibrosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis rat via TLR4/TAK1/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Shenyang Pharm Univ, 2019, 36(8): 716-722. DOI: 10.14066/j.cnki.cn21-1349/r.2019.08.012. |
| [22] |
BAI JH, LIANG ZQ, ZHAO RH, et al. Effect of artesunate on the expression of TLR4 and MyD88 in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Acta Univ Med Anhui, 2017, 52(10): 1468-1471. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2017.10.011. |
| [23] |
LIU BF, ZHOU DS, LIANG ZQ, et al. The effects of artesunate on the expression of NF-κB、TNF-αin liver tissues of mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Clin Med, 2014, 30(5): 23-26. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2014.05.008. |
| [24] |
LIU YL, ZHANG QZ, WANG YR, et al. Astragaloside IV improves high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats by regulating inflammatory factors level via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 605064. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.605064. |
| [25] |
SHEN S, WANG K, ZHI Y, et al. Gypenosides improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat diet induced through regulating LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19(22): 3042-3053. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1829800. |
| [26] |
CHEN C, FENG CS, ZHANG WL, et al. Effects of shikonin on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and its molecular mechanism[J]. Immunol J, 2021, 37(1): 60-66. DOI: 10.13431/j.cnki.immunol.j.20210009. |
| [27] |
ZHAO ZM, WU JZ, YAO Z, et al. Effects of Cassia glycosides on the rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through Toll-like receptor 4 and nuclear factor-κB[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol, 2019, 35(22): 2863-2867. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2019.22.024. |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
WANG L, JIA Z, WANG B, et al. Berberine inhibits liver damage in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2020, 31(12): 902-909. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19568. |
| [30] |
SONG CY, SHI J, ZENG X, et al. Sophocarpine alleviates hepatocyte steatosis through activating AMPK signaling pathway[J]. Toxicol In Vitro, 2013, 27(3): 1065-1071. DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.01.020. |
| [31] |
SONG CY, ZENG X, WANG Y, et al. Sophocarpine attenuates toll-like receptor 4 in steatotic hepatocytes to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines synthesis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(2): 405-412. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12691. |
| [32] |
FENG D, ZOU J, SU D, et al. Curcumin prevents high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in ApoE(-/-) mice by improving intestinal barrier function and reducing endotoxin and liver TLR4/NF-κB inflammation[J]. Nutr Metab (Lond), 2019, 16: 79. DOI: 10.1186/s12986-019-0410-3. |
| [33] |
LIN P, LU J, WANG Y, et al. Naturally occurring stilbenoid TSG reverses non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases via gut-liver axis[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): e0140346. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140346. |
| [34] |
MA JM, GAO LL, ZHANG MW, et al. Role and mechanism of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide combined with aerobic exercise in improving nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in rats[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(6): 1348-1353. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn. 1001-5256.2021.06.026.
马佳敏, 高璐璐, 张梦伟, 等. 枸杞多糖联合有氧运动对非酒精性脂肪肝炎大鼠模型的改善作用及其机制研究[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(6): 1348-1353. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn. 1001-5256.2021.06.026.
|
| [35] |
LIU B, DENG X, JIANG Q, et al. Scoparone alleviates inflammation, apoptosis and fibrosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in mice[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 75: 105797. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105797. |
| [36] |
LU S, ZHANG T, GU W, et al. Volatile oil of amomum villosum inhibits nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the gut-liver axis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2018, 2018: 3589874. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3589874. |
| [37] |
SHU X, WANG M, XU H, et al. Extracts of salvia-nelumbinis naturalis ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via inhibiting gut-derived endotoxin mediated TLR4/NF-κB activation[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2017, 2017: 9208314. DOI: 10.1155/2017/9208314. |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
ZHANG SS, LI JX. Expert consensus on TCM diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (2017)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(12): 2270-2274. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.12.002. |
| [40] |
GAO GY, LI S, XUE JD, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types and syndrome elements of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(1): 89-93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.018. |
| [41] |
TRIPATHI A, DEBELIUS J, BRENNER DA, et al. The gut-liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15(7): 397-411. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0011-z. |
| [42] |
ZHANG Y, ZHU X, ZHENG D, et al. Effects of qutan huoxue formula on the SOCS1/TLR4 signaling pathway in NASH model mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2020, 2020: 1570918. DOI: 10.1155/2020/1570918. |
| [43] |
MA W, YANG JY, AN L, et al. Mechanism of Fuzilizhong decoction alleviating inflammatory damage of rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J pathophysiol, 2020, 36(12): 2258-2263. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2020.12.019. |
| [44] |
GUO YY, SUN XQ, FANG J, et al. Effect of modified Zexietang on expression of proteins related to inflammatory pathway in NAFLD rat[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form, 2017, 23(5): 90-94. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017050090. |
| [45] |
ZHANG HO, LIN QX, XU MJ, et al. Study on the influence of Jianpiqinghuafang on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med on Liver, 2019, 29(2): 163-166. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2019.02.021. |
| [46] |
LIU J, ZHUANG ZJ, TIAN J, et al. Effect of compound Zhajin granule on Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mice[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med on Liver, 2016, 36(4): 460-465. DOI: 10.7661/CJIM.2016.04.0460. |
| [47] |
XIANG J, SHI JP, CHEN HJ, et al. Effect of complex prescription Zhajin drug granules on expression of Toll-like receptor 4 in rats with NASH[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 35(7): 1719-1723. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2017.07.023. |
| [48] |
YANG JM, SUN Y, WANG M, et al. Regulatory effect of a Chinese herbal medicine formula on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(34): 5105-5119. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5105. |



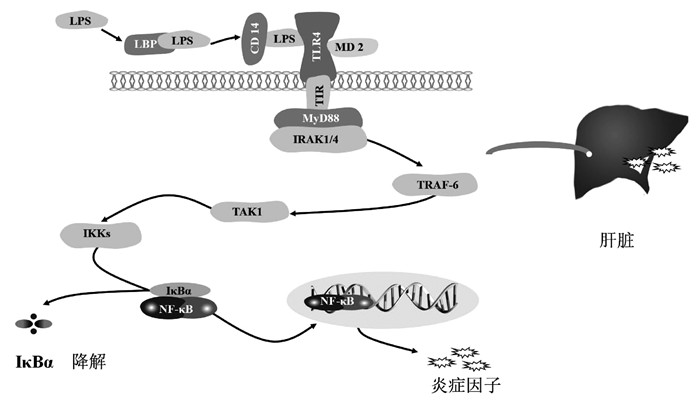




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: