| [1] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(10): 1847-1863. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.10.003. |
| [2] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(2): 406-460. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024. |
| [3] |
MARCIANO S, DÍAZ JM, DIRCHWOLF M, et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis: incidence, outcomes, and treatment strategies[J]. Hepat Med, 2019, 11: 13-22. DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S164250. |
| [4] |
CHINNOCK B, AFARIAN H, MINNIGAN H, et al. Physician clinical impression does not rule out spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients undergoing emergency department paracentesis[J]. Ann Emerg Med, 2008, 52(3): 268-273. DOI: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2008.02.016. |
| [5] |
TANDON P, RAMAN M, MOURTZAKIS M, et al. A practical approach to nutritional screening and assessment in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(3): 1044-1057. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29003. |
| [6] |
LI YT, HUANG JR, PENG ML. Current status and prospects of spontaneous peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 3743962. DOI: 10.1155/2020/3743962. |
| [7] |
MONTANO-LOZA AJ, MEZA-JUNCO J, PRADO CM, et al. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 10(2): 166-173, 173. e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.08.028. |
| [8] |
RODRIGUES SG, BRABANDT B, STIRNIMANN G, et al. Adipopenia correlates with higher portal pressure in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(9): 1672-1681. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14175. |
| [9] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Clinical guidelines on nutrition in end-stage liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(6): 1222-1230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.010. |
| [10] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [11] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [12] |
TERAKURA Y, SHIRAKI M, NISHIMURA K, et al. Indirect calorimetry and anthropometry to estimate energy metabolism in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo), 2010, 56(6): 372-379. DOI: 10.3177/jnsv.56.372. |
| [13] |
PENG S, PLANK LD, MCCALL JL, et al. Body composition, muscle function, and energy expenditure in patients with liver cirrhosis: a comprehensive study[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2007, 85(5): 1257-1266. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/85.5.1257. |
| [14] |
PRIETO-FRÍAS C, CONCHILLO M, PAYERAS M, et al. Factors related to increased resting energy expenditure in men with liver cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 28(2): 139-145. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000516. |
| [15] |
BELARMINO G, SINGER P, GONZALEZ MC, et al. Prognostic value of energy expenditure and respiratory quotient measuring in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Clin Nutr, 2019, 38(4): 1899-1904. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.07.001. |
| [16] |
de WAELE E, MALBRAIN M, SPAPEN H. Nutrition in Sepsis: A bench-to-bedside review[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(2): 395. DOI: 10.3390/nu12020395. |
| [17] |
KAO CC, GUNTUPALLI KK, BANDI V, et al. Whole-body CO2 production as an index of the metabolic response to sepsis[J]. Shock, 2009, 32(1): 23-28. DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181970f32. |
| [18] |
GLASS C, HIPSKIND P, TSIEN C, et al. Sarcopenia and a physiologically low respiratory quotient in patients with cirrhosis: a prospective controlled study[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2013, 114(5): 559-565. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01042.2012. |
| [19] |
TAJIKA M, KATO M, MOHRI H, et al. Prognostic value of energy metabolism in patients with viral liver cirrhosis[J]. Nutrition, 2002, 18(3): 229-234. DOI: 10.1016/s0899-9007(01)00754-7. |
| [20] |
NISHIKAWA H, ENOMOTO H, IWATA Y, et al. Prognostic significance of nonprotein respiratory quotient in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(3): e5800. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005800. |
| [21] |
LI A, MUKHOPADHYAY A. Correction to: Substrate utilization and energy expenditure pattern in sepsis by indirect calorimetry[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 660. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-03391-7. |
| [22] |
TANG L, YIN X. Diagnostic value of serum procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and neutrophil CD64 index in early diagnosis of neonatal infection with umbilical vein catheterization[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis(Electronic Edition), 2020, 14(4): 336-339. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2020.04.013. |
| [23] |
LI T, CHEN YY, SUN HS, et al. Application of hematology-related indexes in early diagnosis of bacterial infection of tumor patients in ICU[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2020, 46(4): 816-821. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200424. |
| [24] |
METWALLY K, FOUAD T, ASSEM M, et al. Predictors of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhotic ascites[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6(4): 372-376. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00001. |
| [25] |
ABDEL-RAZIK A, MOUSA N, ELHAMMADY D, et al. Ascitic fluid calprotectin and serum procalcitonin as accurate diagnostic markers for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Gut Liver, 2016, 10(4): 624-631. DOI: 10.5009/gnl15120. |
| [26] |
MIKUŁA T, SAPUŁA M, JABŁOŃSKA J, et al. Significance of heparin-binding protein and D-dimers in the early diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2018, 2018: 1969108. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1969108. |
| [27] |
SHEN HX, LOU XP, CHANG XW, et al. Risk factors for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients: A meta analysis[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24(12): 1903-1909. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i12.1903. |



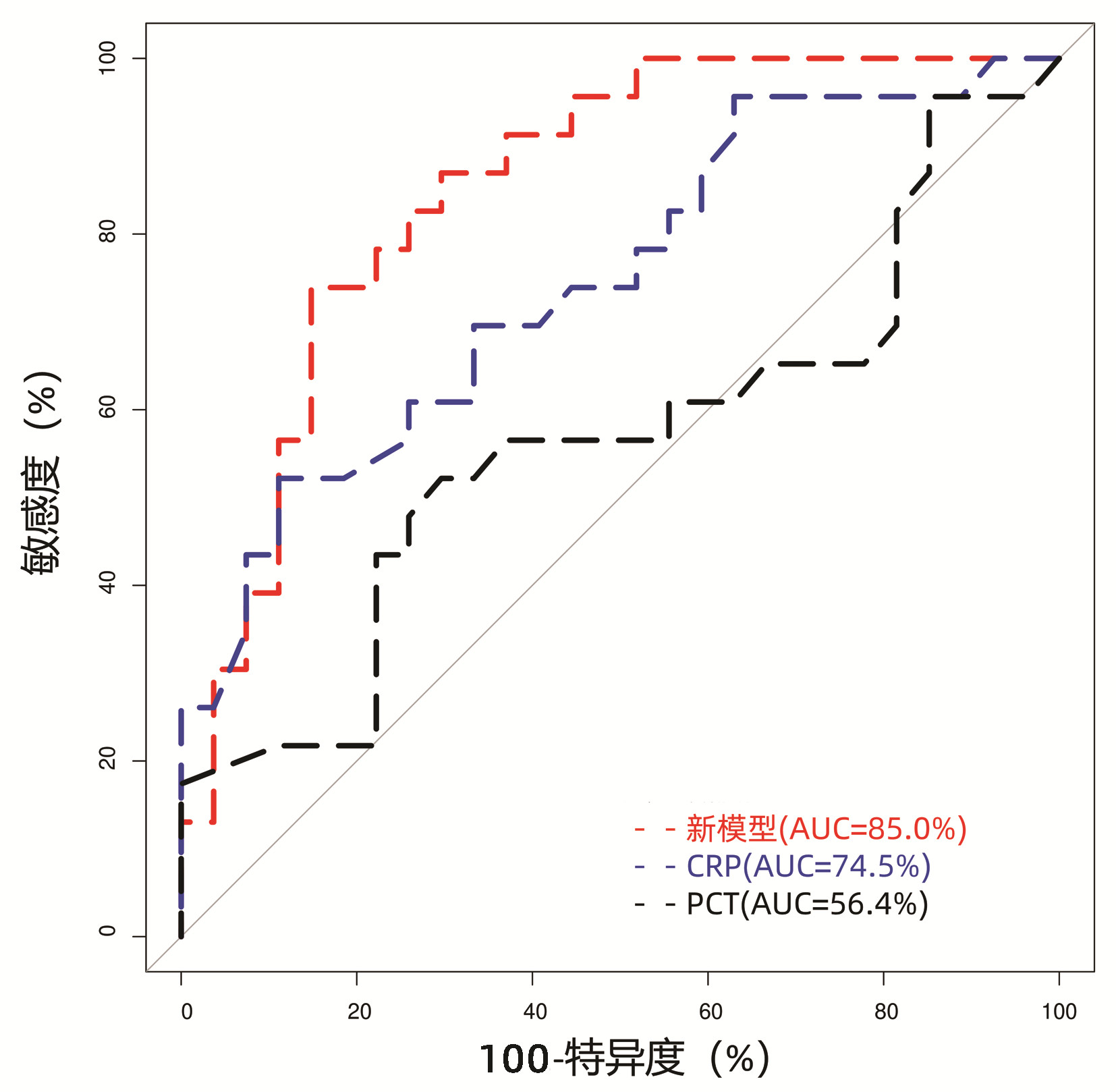




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: