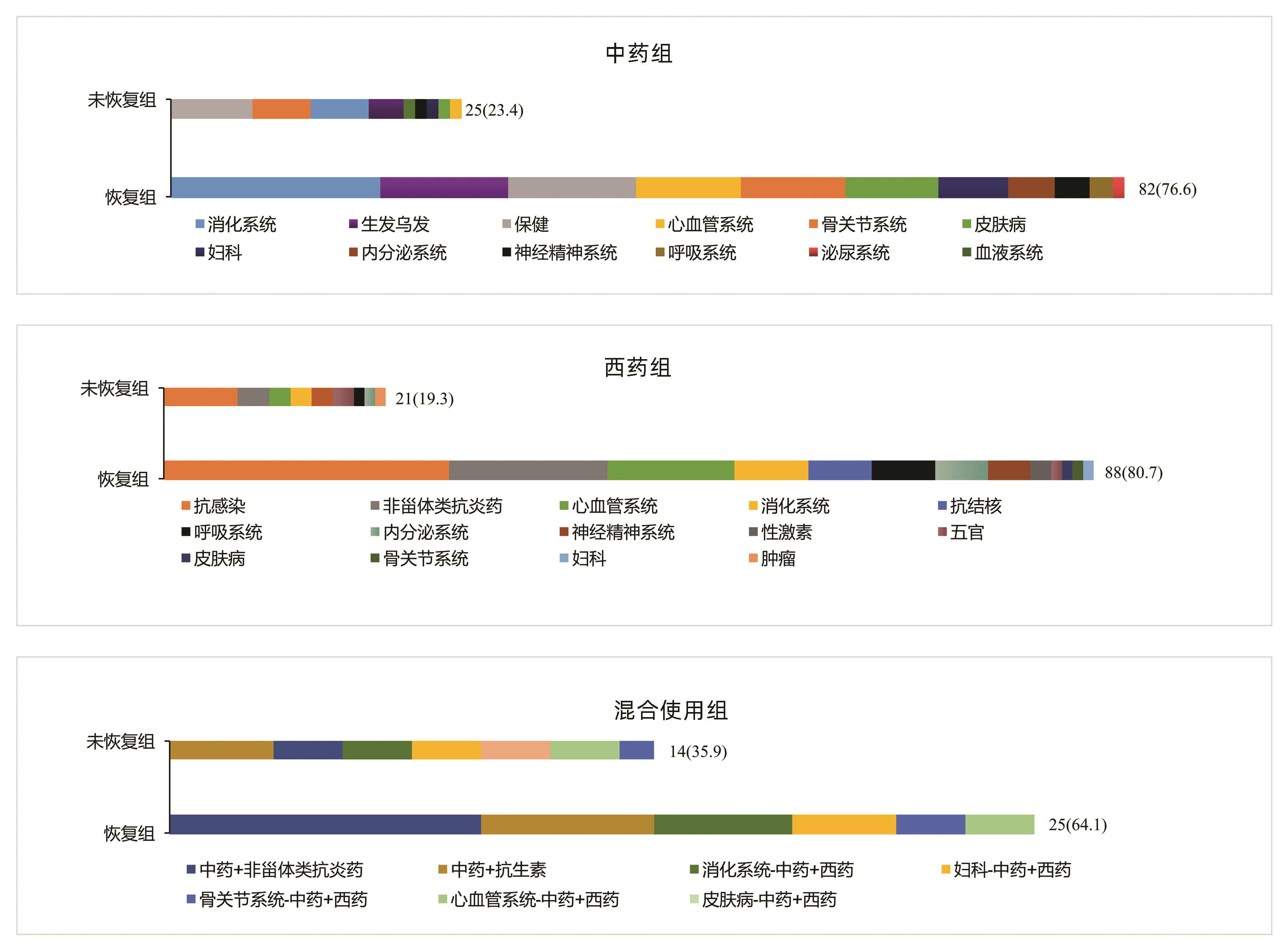
| [1] |
Drug-induced Liver Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the management of drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(11): 1752-1769. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.11.002. |
| [2] |
WANG Q, HUANG A, WANG JB, et al. Chronic drug-induced liver injury: Updates and future challenges[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 627133. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.627133. |
| [3] |
WANG Y, WANG Y, WANG L, et al. A comparison study of clinical features and prognosis between herbal and dietary supplements and Wester medicine induced liver injuries[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2021, 26(4): 364-369. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2021.04.007. |
| [4] |
JI TT, LU HY, TAN N, et al. A comparative analysis of the clinical features of acute and chronic drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(7): 1556-1561. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.07.021. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [7] |
FONTANA RJ, HAYASHI PH, BARNHART H, et al. Persistent liver biochemistry abnormalities are more common in older patients and those with cholestatic drug induced liver injury[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2015, 110(10): 1450-1459. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2015.283. |
| [8] |
MEDINA-CALIZ I, ROBLES-DIAZ M, GARCIA-MUÑOZ B, et al. Definition and risk factors for chronicity following acute idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(3): 532-542. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.003. |
| [9] |
CHALASANI N, BONKOVSKY HL, FONTANA R, et al. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: The DILIN prospective study[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(7): 1340-1352. e7. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.03.006. |
| [10] |
SHEN T, LIU Y, SHANG J, et al. Incidence and etiology of drug-induced liver injury in Mainland China[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(8): 2230-2241. e11. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.002. |
| [11] |
JING J, TESCHKE R. Traditional Chinese Medicine and herb-induced liver injury: Comparison with drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6(1): 57-68. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2017.00033. |
| [12] |
LI FL, HUANG ZG, GE CL, et al. Logistic regression analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2019, 27(4): 258-262. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4761.2019.04.007. |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
BJÖRNSSON E, KALAITZAKIS E, AV KLINTEBERG V, et al. Long- term follow-up of patients with mild to moderate drug-induced liver injury[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2007, 26(1): 79-85. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03355.x. |
| [15] |
LO RE V 3rd, HAYNES K, FORDE KA, et al. Risk of acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury: Evaluation of Hy's law and a new prognostic model[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13(13): 2360-2368. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.06.020. |



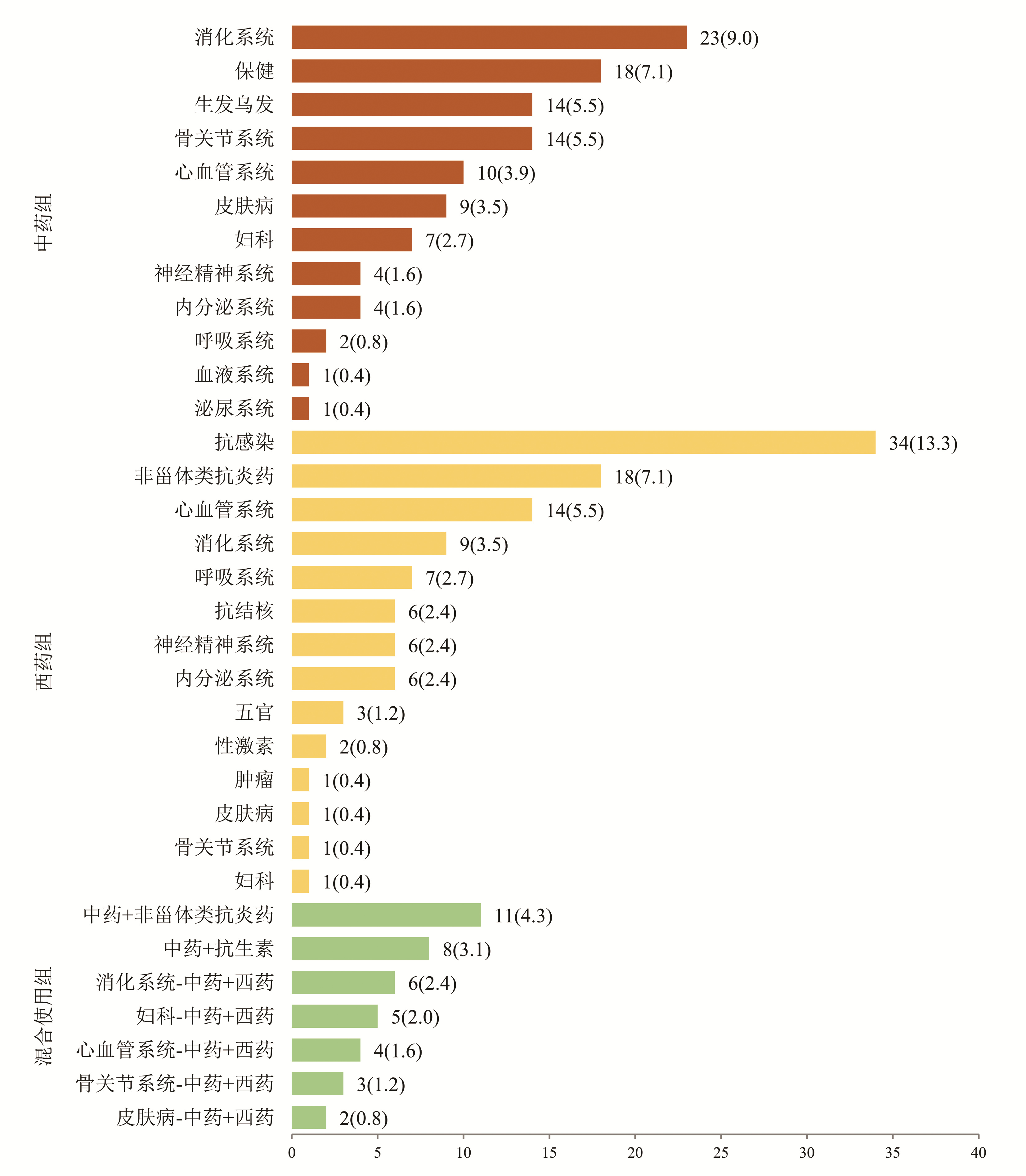




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: