| [1] |
EZHILARASAN D, SOKAL E, NAJIMI M. Hepatic fibrosis: It is time to go with hepatic stellate cell-specific therapeutic targets[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2018, 17(3): 192-197. DOI: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.04.003. |
| [2] |
SHAN L, LIU Z, CI L, et al. Research progress on the anti-hepatic fibrosis action and mechanism of natural products[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 75: 105765. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105765. |
| [3] |
ZHANG J, YANG A, WU Y, et al. Stachydrine ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and regulating MMPs/TIMPs system in rats[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 97: 1586-1594. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.117. |
| [4] |
Professional Committee of Liver Diseases, Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine (2019 edition)[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 39(11): 1286-1295. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.07.005. |
| [5] |
MINKWITZ S, SCHMOCK A, KURTOGLU A, et al. Time-dependent alterations of MMPs, TIMPs and tendon structure in human achilles tendons after acute rupture[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(10): 2199. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18102199. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
ROBERT S, GICQUEL T, VICTONI T, et al. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inflammasome pathway in molecular mechanisms of fibrosis[J]. Biosci Rep, 2016, 36(4): e00360. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160107. |
| [8] |
BREW K, NAGASE H. The tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): An ancient family with structural and functional diversity[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2010, 1803(1): 55-71. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.01.003. |
| [9] |
KNÄUPER V, BAILEY L, WORLEY JR, et al. Cellular activation of proMMP-13 by MT1-MMP depends on the C-terminal domain of MMP-13[J]. FEBS Lett, 2002, 532(1-2): 127-130. DOI: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03654-2. |
| [10] |
BOURBOULIA D, STETLER-STEVENSON WG. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): Positive and negative regulators in tumor cell adhesion[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2010, 20(3): 161-168. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.05.002. |
| [11] |
ONOZUKA I, KAKINUMA S, KAMIYA A, et al. Cholestatic liver fibrosis and toxin-induced fibrosis are exacerbated in matrix metalloproteinase-2 deficient mice[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2011, 406(1): 134-140. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.012. |
| [12] |
KOSSAKOWSKA AE, EDWARDS DR, LEE SS, et al. Altered balance between matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in experimental biliary fibrosis[J]. Am J Pathol, 1998, 153(6): 1895-1902. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65703-3. |
| [13] |
ROEB E, PURUCKER E, BREUER B, et al. TIMP expression in toxic and cholestatic liver injury in rat[J]. J Hepatol, 1997, 27(3): 535-544. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80359-5. |
| [14] |
MASHAYEKHI F, SABERI A, MASHAYEKHI S. Serum TIMP1 and TIMP2 concentration in patients with different grades of meningioma[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2018, 170: 84-87. DOI: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.05.001. |
| [15] |
KUNZ P, SÄHR H, LEHNER B, et al. Elevated ratio of MMP2/MMP9 activity is associated with poor response to chemotherapy in osteosarcoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2016, 16: 223. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2266-5. |
| [16] |
XU F, LIU C, ZHOU D, et al. TGFβ/SMAD pathway and its regulation in hepatic fibrosis[J]. J Histochem Cytochem, 2016, 64(3): 157-167. DOI: 10.1369/0022155415627681. |
| [17] |
SUN H, FENG J, TANG L. Function of TREM1 and TREM2 in liver-related diseases[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(12): 2626. DOI: 10.3390/cells9122626. |
| [18] |
HASSAN MH, GHOBARA MM. Antifibrotic effect of meloxicam in rat liver: Role of nuclear factor kappa B, proinflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 2016, 389(9): 971-983. DOI: 10.1007/s00210-016-1263-1. |
| [19] |
KARIMI J, MOHAMMADALIPOUR A, SHEIKH N, et al. Protective effects of combined Losartan and Nilotinib on carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4))-induced liver fibrosis in rats[J]. Drug Chem Toxicol, 2020, 43(5): 468-478. DOI: 10.1080/01480545.2018.1504960. |
| [20] |
XIE AZ, LYU C, SHI QL, et al. Research progress on prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis by traditional Chinese medicine[J]. China Med Herald, 2020, 17(17): 34-37.
谢爱泽, 吕超, 石清兰, 等. 中医药防治肝纤维化机制的研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2020, 17(17): 34-37.
|
| [21] |
LI J, XU YL, LUO S, et al. Jiawei Yinchen Sini Decoction on MMP1 and TIMPs in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis mice[J]. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med, 2016, 43(6): 1315-1317. DOI: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2016.06.068. |
| [22] |
LI SM, DAI LJ, FENG L. Effects of Xiaoyao San-containing serum on secretion of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 in human hepatic astrocytes[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2016, 27(9): 2134-2136. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2016.09.029. |
| [23] |
TIAN XH, WANG Q, SHANG LZ. Role and correlation study of Chaihu Shugan powder on signal pathway of TGF-beta 1/p38MAPK in rat hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chin J Basic Med Tradit Chin Med, 2016, 22(1): 62-65.
田新红, 王琦, 尚立芝. 柴胡疏肝散对肝纤维化大鼠TGF-β1/p38MAPK信号通路的作用及相关性研究[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2016, 22(1): 62-65.
|
| [24] |
AL-OLAYAN EM, EL-KHADRAGY MF, ALAJMI RA, et al. Ceratonia siliqua pod extract ameliorates Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis and oxidative stress[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2016, 16(1): 434. DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1389-1. |
| [25] |
WEN B, SUN HT, HE SQ, et al. Effects of Biejiajian Pill on Wnt signal pathway molecules β-catenin and GSK-3β and down-stream proteins in hepatic stellate cells[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharma, 2017, 32(9): 3997-4000.
文彬, 孙海涛, 贺松其, 等. 鳖甲煎丸对肝星状细胞中Wnt信号通路信号分子β-catenin、GSK-3β及下游蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(9): 3997-4000.
|
| [26] |
HUANG H, KANG Y, HUANG XP, et al. Effect of total flavone from Litchi chinensis Sonn on Smad3, Smad4 and TIMP-1 expression in a rat model of liver fibrosis[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24(2): 176-186. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i2.176. 黄红, 康毅, 黄旭平, 等. 荔枝核总黄酮对大鼠肝纤维化Smad3、Smad4及TIMP-1信号表达的影响[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24(2): 176-186. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i2.176. |
| [27] |
ZHAN YY, TIAN LP, WANG JH, et al. Effect of extract of seed melon on the hepatic expressions of cytokines in mice with hepatic fibrosis[J]. J Shihezi Univ Nat Sci, 2016, 34(6): 739-745. DOI: 10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2016.06.014. |
| [28] |
AN ZX, HE YL, WANG M. Influence of TGF and MMP in dendrobium nobile polyose on hepatic fibrosis rats[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 35(3): 530-533. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2017.03.004. |
| [29] |
XIONG S, GAO JR, HU ZL. Effect of Carapax Trionycis in inhibiting activation of rat hepatic stellate cell induced by TGF-β[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2017, 23(19): 155-159. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017190155. |
| [30] |
ZHENG YF, ZHANG YJ, GUO H. Effect of flavonoids from (Maxim) on fibrosing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice[J]. China J Mod Med, 2017, 27(14): 28-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.14.006. |
| [31] |
ZHANG B, TAN YJ, HUANG QJ, et al. Effects of water extract of Mallotus apelta (Lour. ) Muell. -Arg. root on hepatic stellate cells activation and ECM secretion in rats[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2019, 34(9): 4287-4290.
章波, 檀燕君, 黄秋洁, 等. 白背叶根水提物对大鼠肝星状细胞活化及细胞外基质分泌的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(9): 4287-4290.
|
| [32] |
CHEN K, XU JW, ZHOU Q, et al. Effects of all-trans retinioc acid on expressions of COL1α2, MMP-2, TIMP-1, and signaling pathway in TGF-β1-simulated rat hepatic stellate cells[J]. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ Med Sci, 2019, 36(8): 857-861. DOI: 10.7652/jdyxb201706014. 陈珂, 许君望, 周琦, 等. 全反式维甲酸对TGF-β1刺激的肝星状细胞COL1α2、MMP-2、TIMP-1以及信号通路的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 38(6): 857-861. DOI: 10.7652/jdyxb201706014. |
| [33] |
DONG ZC, GAO Q, MAO JN. The regulatory effect of bilobalide on hepatic fibrosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis rat via TLR4/TAK1/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Shenyang Pharm Univ, 2019, 36(8): 716-722. DOI: 10.14066/j.cnki.cn21-1349/r.2019.08.012. |
| [34] |
GUO L, LI HZ, WEI YJ. Protective effect of ferulic acid on hepatocytes in rat liver fibrosis and its potential mechanism[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2019, 18(4): 357-361. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2019.04.006. |
| [35] |
TANG AC, WEI YF, LIU XH. Protective effect and mechanism of tadehaginoside on hepatic fibrosis model mice induced by carbon tetrachloride[J]. China Pharm, 2020, 31(2): 190-195. DOI: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2020.02.12. |
| [36] |
ABU-ELSAAD NM, ELKASHEF WF. Modified citrus pectin stops progression of liver fibrosis by inhibiting galectin-3 and inducing apoptosis of stellate cells[J]. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2016, 94(5): 554-562. DOI: 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0284. |
| [37] |
BINGÜL İ, BAŞARAN-KÜÇÜKGERGIN C, AYD 1N AF, et al. Betaine treatment decreased oxidative stress, inflammation, and stellate cell activation in rats with alcoholic liver fibrosis[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2016, 45: 170-178. DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.05.033. |
| [38] |
CLICHICI S, OLTEANU D, FILIP A, et al. Beneficial effects of silymarin after the discontinuation of CCl 4-induced liver fibrosis[J]. J Med Food, 2016, 19(8): 789-797. DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2015.0104. |
| [39] |
THIRUPATHI A, SILVEIRA PC, NESI RT, et al. β-Amyrin, a pentacyclic triterpene, exhibits anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects on dimethyl nitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in male rats[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2017, 36(2): 113-122. DOI: 10.1177/0960327116638727. |
| [40] |
MORTEZAEE K, MAJIDPOOR J, DANESHI E, et al. Post-treatment of melatonin with CCl(4) better reduces fibrogenic and oxidative changes in liver than melatonin co-treatment[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(2): 1716-1725. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.26331. |
| [41] |
LIN LB, QUE RY, LIU JK. Effect of saikosaponin-d on expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in activated HSC-T6 cells: Underlying mechanism[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24(8): 1159-1165. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i8.1159. 林柳兵, 阙任烨, 刘进锴. 柴胡皂苷d对活化的HSC-T6细胞MMP-1、TIMP-1表达的影响及其分子机制[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24(8): 1159-1165. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i8.1159. |
| [42] |
QUE R, SHEN Y, REN J, et al. Estrogen receptor-β-dependent effects of saikosaponind on the suppression of oxidative stress-induced rat hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41(3): 1357-1364. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3349. |
| [43] |
SADEK KM, SALEH EA, NASR SM. Molecular hepatoprotective effects of lipoic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Hepatoprotection at molecular level[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2018, 37(2): 142-154. DOI: 10.1177/0960327117693066. |
| [44] |
SALAMA SM, IBRAHIM I, SHAHZAD N, et al. Hepatoprotectivity of Panduratin A against liver damage: In vivo demonstration with a rat model of cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide[J]. APMIS, 2018, 126(9): 710-721. DOI: 10.1111/apm.12878. |
| [45] |
LIU X, HUANG K, NIU Z, et al. Protective effect of isochlorogenic acid B on liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis of mice[J]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2019, 124(2): 144-153. DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.13122. |
| [46] |
ZHOU X, YU L, ZHOU M, et al. Dihydromyricetin ameliorates liver fibrosis via inhibition of hepatic stellate cells by inducing autophagy and natural killer cell-mediated killing effect[J]. Nutr Metab (Lond), 2021, 18(1): 64. DOI: 10.1186/s12986-021-00589-6. |
| [47] |
|










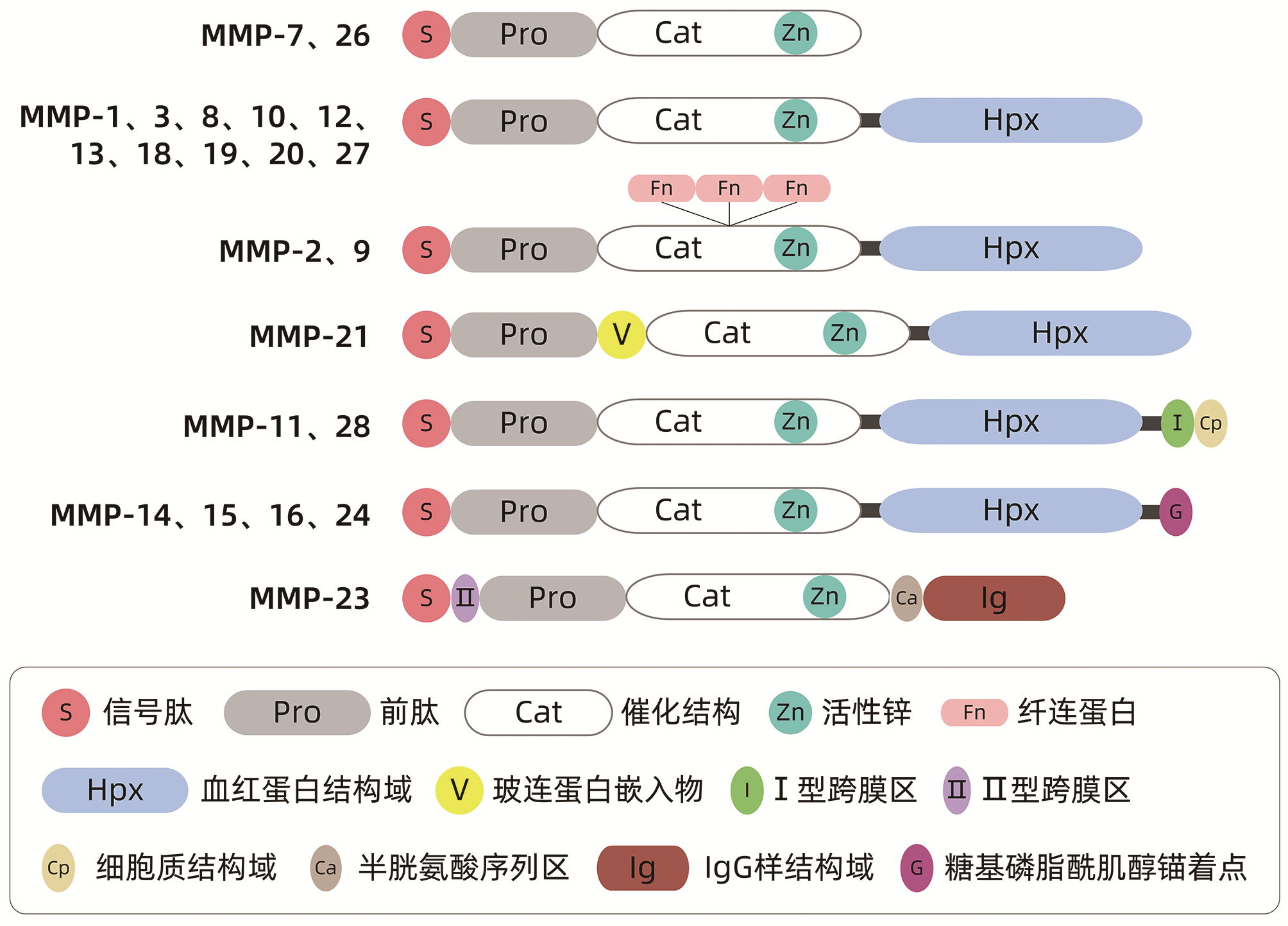




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: