| [1] |
HUANG DQ, EL-SERAG HB, LOOMBA R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(4): 223-238. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00381-6. |
| [2] |
Recommendations of the Polish Group of Experts for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (PGE-NAFLD), TOMASIEWICZ K, FLISIAK R, et al. Recommendations for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2018, 4(3): 153-157. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2018.78118. |
| [3] |
BERARDO C, di PASQUA LG, CAGNA M, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: current issues and future perspectives in preclinical and clinical research[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(24). DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249646. |
| [4] |
PAN M, CEDERBAUM AI, ZHANG YL, et al. Lipid peroxidation and oxidant stress regulate hepatic apolipoprotein B degradation and VLDL production[J]. J Clin Invest, 2004, 113(9): 1277-1287. DOI: 10.1172/JCI19197. |
| [5] |
BUZZETTI E, PINZANI M, TSOCHATZIS EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Metabolism, 2016, 65(8): 1038-1048. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012. |
| [6] |
HEBBARD L, GEORGE J. Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 8(1): 35-44. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.191. |
| [7] |
CAI J, ZHANG XJ, LI H. Progress and challenges in the prevention and control of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Med Res Rev, 2019, 39(1): 328-348. DOI: 10.1002/med.21515. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
SUMIDA Y, OKANOUE T, NAKAJIMA A, et al. Phase 3 drug pipelines in the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49(11): 1256-1262. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13425. |
| [10] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, RATZIU V, LOOMBA R, et al. Obeticholic acid for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: interim analysis from a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10215): 2184-2196. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)33041-7. |
| [11] |
POCKROS PJ, FUCHS M, FREILICH B, et al. CONTROL: A randomized phase 2 study of obeticholic acid and atorvastatin on lipoproteins in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(11): 2082-2093. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14209. |
| [12] |
SUMIDA Y, YONEDA M, OGAWA Y, et al. Current and new pharmacotherapy options for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother, 2020, 21(8): 953-967. DOI: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1744564. |
| [13] |
FIORUCCI S, BIAGIOLI M, SEPE V, et al. Bile acid modulators for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2020, 29(6): 623-632. DOI: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1763302. |
| [14] |
HARRISON SA, ROSSI SJ, PAREDES AH, et al. NGM282 improves liver fibrosis and histology in 12 weeks in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(4): 1198-1212. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30590. |
| [15] |
FRANCQUE S, SZABO G, ABDELMALEK MF, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(1): 24-39. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00366-5. |
| [16] |
GAWRIEH S, NOUREDDIN M, LOO N, et al. Saroglitazar, a PPAR-α/γ agonist, for treatment of NAFLD: A randomized controlled double-blind phase 2 trial[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74(4): 1809-1824. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31843. |
| [17] |
STAELS B, RUBENSTRUNK A, NOEL B, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of the dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta agonist, GFT505, in rodent models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(6): 1941-1952. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26461. |
| [18] |
HARRISON S, RATZIU V, ANSTEE QM, et al. Baseline levels of NIS4TM and other fibrosis biomarkers and prediction of histological progression to advanced fibrosis in NASH[J]. Hepatology 72(S1): 896A.
|
| [19] |
LEFERE S, PUENGEL T, HUNDERTMARK J, et al. Differential effects of selective- and pan-PPAR agonists on experimental steatohepatitis and hepatic macrophages[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(4): 757-770. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.025. |
| [20] |
VATNER DF, WEISMANN D, BEDDOW SA, et al. Thyroid hormone receptor-β agonists prevent hepatic steatosis in fat-fed rats but impair insulin sensitivity via discrete pathways[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2013, 305(1): E89- E100. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00573.2012. |
| [21] |
HARRISON SA, BASHIR MR, GUY CD, et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10213): 2012-2024. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32517-6. |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
SANYAL A, CHARLES ED, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI BA, et al. Pegbelfermin (BMS-986036), a PEGylated fibroblast growth factor 21 analogue, in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a trial[J]. Lancet, 2019, 392(10165): 2705-2717. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31785-9. |
| [24] |
HARRISON SA, RUANE PJ, FREILICH BL, et al. Efruxifermin in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a trial[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(7): 1262-1271. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01425-3. |
| [25] |
DOBRZYN P, DOBRZYN A, MIYAZAKI M, et al. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases fatty acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in liver[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(17): 6409-6414. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401627101. |
| [26] |
LOOMBA R, MOHSENI R, LUCAS KJ, et al. TVB-2640 (FASN Inhibitor) for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: FASCINATE-1, a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2a trial[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161(5): 1475-1486. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.025. |
| [27] |
KIM CW, ADDY C, KUSUNOKI J, et al. Acetyl CoA carboxylase inhibition reduces hepatic steatosis but elevates plasma triglycerides in mice and humans: a bedside to bench investigation[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 26(3): 576. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.011. |
| [28] |
CALLE RA, AMIN NB, CARVAJAL-GONZALEZ S, et al. ACC inhibitor alone or co-administered with a DGAT2 inhibitor in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Two parallel, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2a trials[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(10): 1836-1848. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01489-1. |
| [29] |
LOOMBA R, MORGAN E, WATTS L, et al. Novel antisense inhibition of diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5(9): 829-838. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30186-2. |
| [30] |
CUSI K, ALKHOURI N, HARRISON SA, et al. Efficacy and safety of PXL770, a direct AMP kinase activator, for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (STAMP-NAFLD): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 6(11): 889-902. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00300-9. |
| [31] |
ARMSTRONG MJ, GAUNT P, AITHAL GP, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10019): 679-690. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X. |
| [32] |
HARTMAN ML, SANYAL AJ, LOOMBA R, et al. Effects of novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide on biomarkers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2020, 43(6): 1352-1355. DOI: 10.2337/dc19-1892. |
| [33] |
CUI J, PHILO L, NGUYEN P, et al. Sitagliptin vs. placebo for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(2): 369-376. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.021. |
| [34] |
COLCA JR, MCDONALD WG, ADAMS WJ. MSDC-0602K, a metabolic modulator directed at the core pathology of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2018, 27(7): 631-636. DOI: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1494153. |
| [35] |
HARRISON SA, ALKHOURI N, DAVISON BA, et al. Insulin sensitizer MSDC-0602K in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase Ⅱb study[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72(4): 613-626. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.023. |
| [36] |
SAFADI R, BRAUN M, FRANCIS A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: A phase 2 double-blind study of namodenoson in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 54(11-12): 1405-1415. DOI: 10.1111/apt.16664. |
| [37] |
FRIEDMAN SL, RATZIU V, HARRISON SA, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of cenicriviroc for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(5): 1754-1767. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29477. |
| [38] |
RATZIU V, SANYAL A, HARRISON SA, et al. Cenicriviroc treatment for adults with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis: final analysis of the phase 2b CENTAUR study[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72(3): 892-905. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31108. |
| [39] |
ANSTEE QM, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI BA, WONG VW, et al. Cenicriviroc for the treatment of liver fibrosis in adults with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: AURORA Phase 3 study design[J]. Contemp Clin Trials, 2020, 89: 105922. DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2019.105922. |
| [40] |
BRENNER C, GALLUZZI L, KEPP O, et al. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59(3): 583-594. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033. |
| [41] |
HSU MC, LIU SH, WANG CW, et al. JKB-122 is effective, alone or in combination with prednisolone in Con A-induced hepatitis[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2017, 812: 113-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.07.012. |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
HARRISON SA, MARRI SR, CHALASANI N, et al. Randomised clinical study: GR-MD-02, a galectin-3 inhibitor, vs. placebo in patients having non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with advanced fibrosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 44(11-12): 1183-1198. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13816. |
| [44] |
CHALASANI N, ABDELMALEK MF, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Effects of belapectin, an inhibitor of galectin-3, in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with cirrhosis and portal hypertension[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(5): 1334-1345. e5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.296. |
| [45] |
HARRISON SA, ABDELMALEK MF, CALDWELL S, et al. Simtuzumab is ineffective for patients with bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis caused by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155(4): 1140-1153. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.006. |
| [46] |
MCPHERSON S, WILKINSON N, TINIAKOS D, et al. A randomised controlled trial of losartan as an anti-fibrotic agent in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0175717. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175717. |



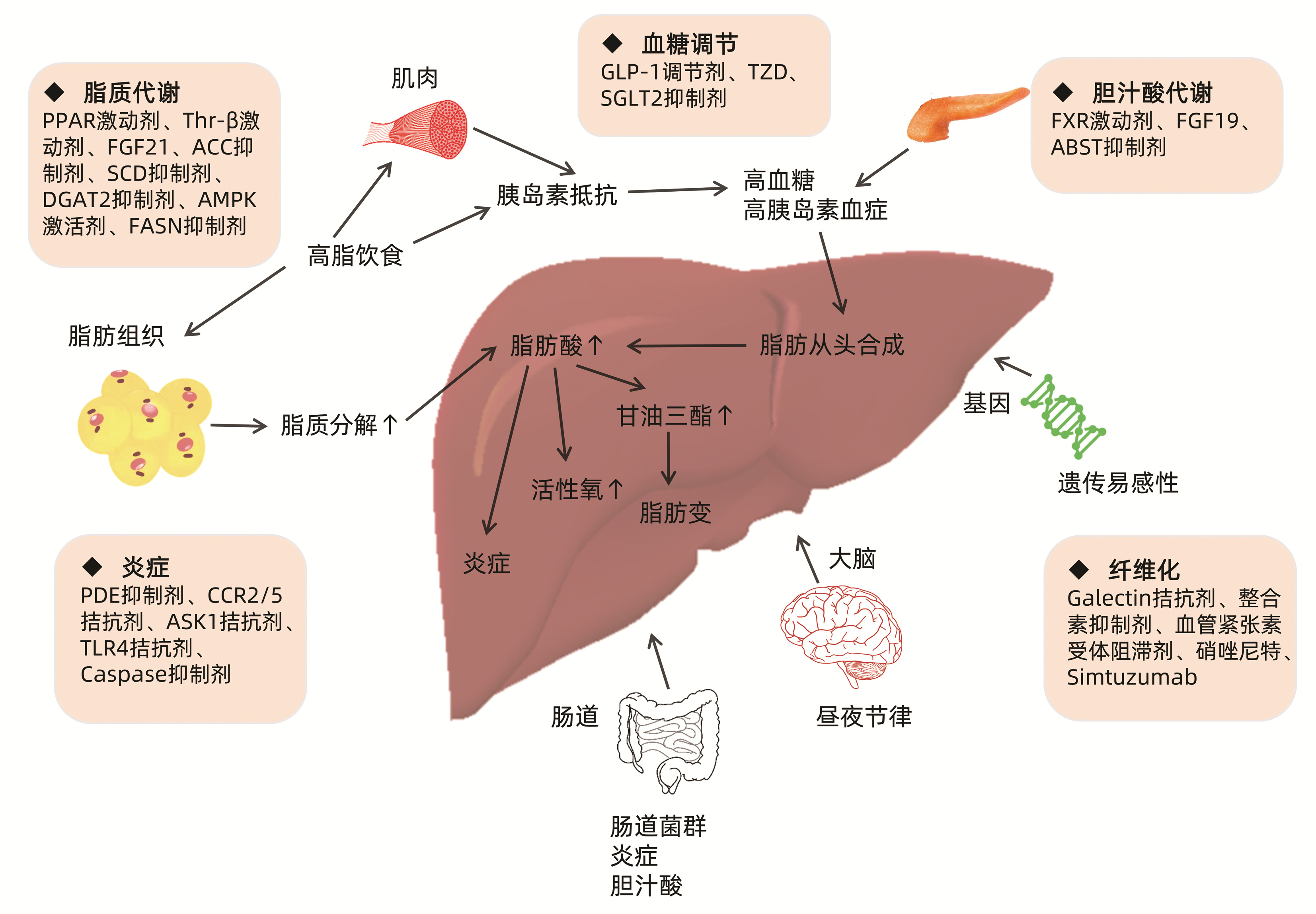




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: