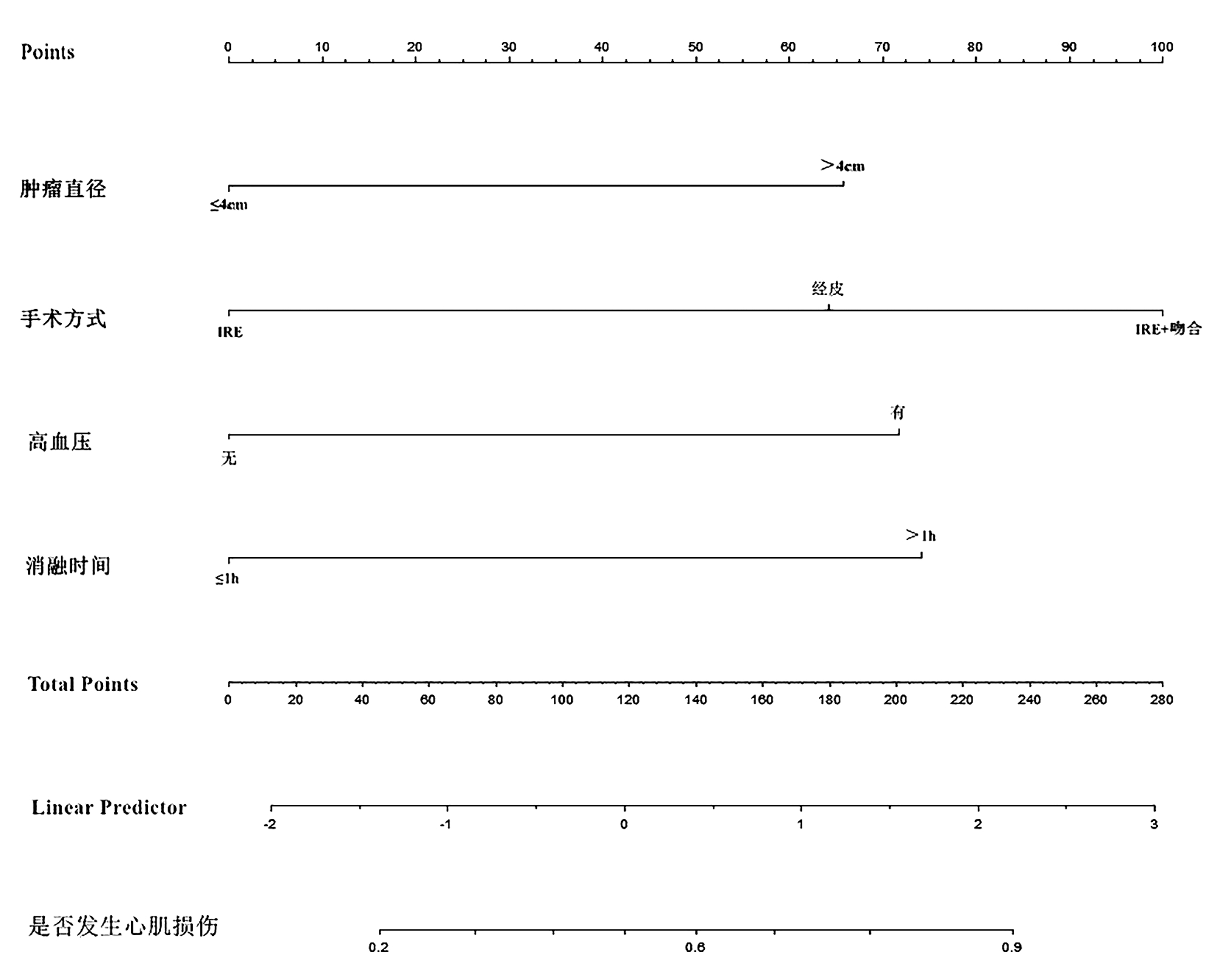
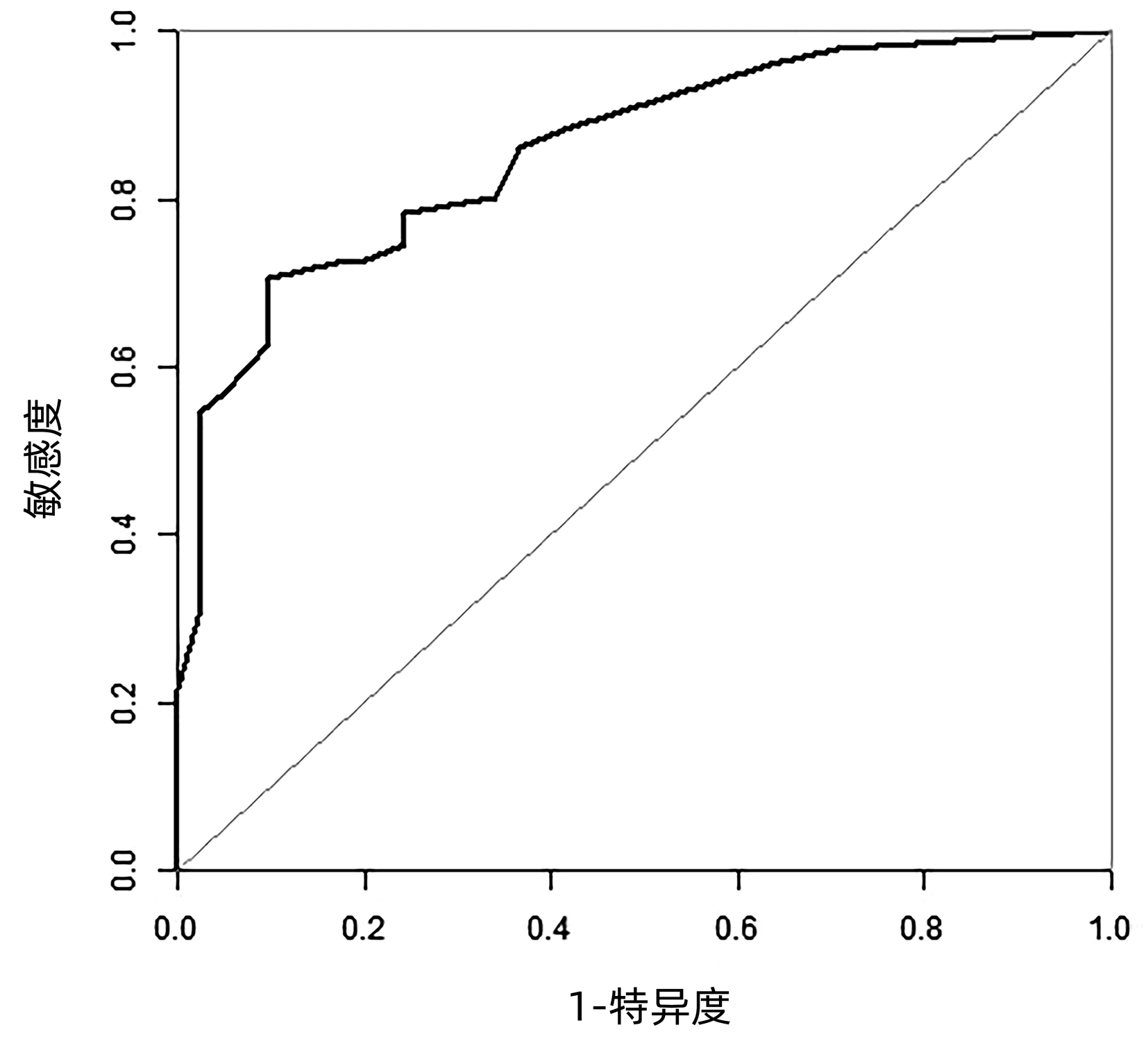
| [1] |
SIEGELl RL, MILLER KD, JEMAL A, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21590. |
| [2] |
KWON W, THOMAS A, KLUGER MD, et al. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Semin Oncol, 2021, 48(1): 84-94. DOI: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2021.02.004. |
| [3] |
HOLLAND MM, BHUTIANI N, KRUSE EJ, et al. A prospective, multi-institution assessment of irreversible electroporation for treatment of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: initial outcomes from the AHPBA pancreatic registry[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2019, 21(8): 1024-1031. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.12.004. |
| [4] |
TIMMER F, GEBOERS B, NIEUWENHUIZEN S, et al. Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: percutaneous management using ablation, brachytherapy, intra-arterial chemotherapy, and intra-tumoral immunotherapy[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2021, 23(6): 68. DOI: 10.1007/s11912-021-01057-3. |
| [5] |
GARCIA PA, ROSSMEISL JH JR, NEAL NE 2ND, et al. A parametric study delineating irreversible electroporation from thermal damage based on a minimally invasive intracranial procedure[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2011, 10: 34. DOI: 10.1186/1475-925X-10-34. |
| [6] |
KOSTRZEWA M, TUELUEMEN E, RUDIC B, et al. Cardiac impact of R-wave triggered irreversible electroporation therapy[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2018, 15(12): 1872-1879. DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.07.013. |
| [7] |
LI J, WANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Cardiac impact of high-frequency irreversible electroporation using an asymmetrical waveform on liver in vivo[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2021, 21(1): 581. DOI: 10.1186/s12872-021-02412-9. |
| [8] |
RUETZLER K, SMILOWITZ NR, BERGER JS, et al. Diagnosis and management of patients with myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery: a scientific statement from the american heart association[J]. Circulation, 2021, 144(19): e287-e305. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001024. |
| [9] |
NARAYANAN G, BILIMORIA MM, HOSEIN PJ, et al. Multicenter randomized controlled trial and registry study to assess the safety and efficacy of the NanoKnife Ⓡ system for the ablation of stage 3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma: overview of study protocols[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 785. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08474-4. |
| [10] |
GEBOERS B, SCHEFFER HJ, GRAYBILL PM, et al. High-voltage electrical pulses in oncology: irreversible electroporation, electrochemotherapy, gene electrotransfer, electrofusion, and electroimmunotherapy[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(2): 254-272. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020192190. |
| [11] |
RUARUS A, VROOMEN L, GEBOERS B, et al. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation in locally advanced and recurrent pancreatic cancer (PANFIRE-2): A multicenter, prospective, single-arm, phase Ⅱ study[J]. Radiology, 2020, 294(1): 212-220. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2019191109. |
| [12] |
DU PRÉ BC, VAN DRIEL VJ, van WESSEL H, et al. Minimal coronary artery damage by myocardial electroporation ablation[J]. Europace, 2013, 15(1): 144-149. DOI: 10.1093/europace/eus171. |
| [13] |
STILLSTRÖM D, BEERMANN M, ENGSTRAND J, et al. Initial experience with irreversible electroporation of liver tumours[J]. Eur J Radiol Open, 2019, 6: 62-67. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2019.01.004. |
| [14] |
DRIGGIN E, MADHAVAN MV, BIKDELI B, et al. Cardiovascular considerations for patients, health care workers, and health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 75(18): 2352-2371. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.031. |
| [15] |
MORENO MU, EIROS R, GAVIRA JJ, et al. The hypertensive myocardium: from microscopic lesions to clinical complications and outcomes[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2017, 101(1): 43-52. DOI: 10.1016/j.mcna.2016.08.002. |
| [16] |
LACKNER I, WEBER B, PRESSMAR J, et al. Cardiac alterations following experimental hip fracture-inflammaging as independent risk factor[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 895888. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.895888. |
| [17] |
SUGRUE A, VAIDYA V, WITT C, et al. Irreversible electroporation for catheter-based cardiac ablation: a systematic review of the preclinical experience[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2019, 55(3): 251-265. DOI: 10.1007/s10840-019-00574-3. |
| [18] |
ZHAO K, ZHANG Y, LI J, et al. Modified glucose-insulin-potassium regimen provides cardioprotection with improved tissue perfusion in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass surgery[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2020, 9(6): e012376. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012376. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: