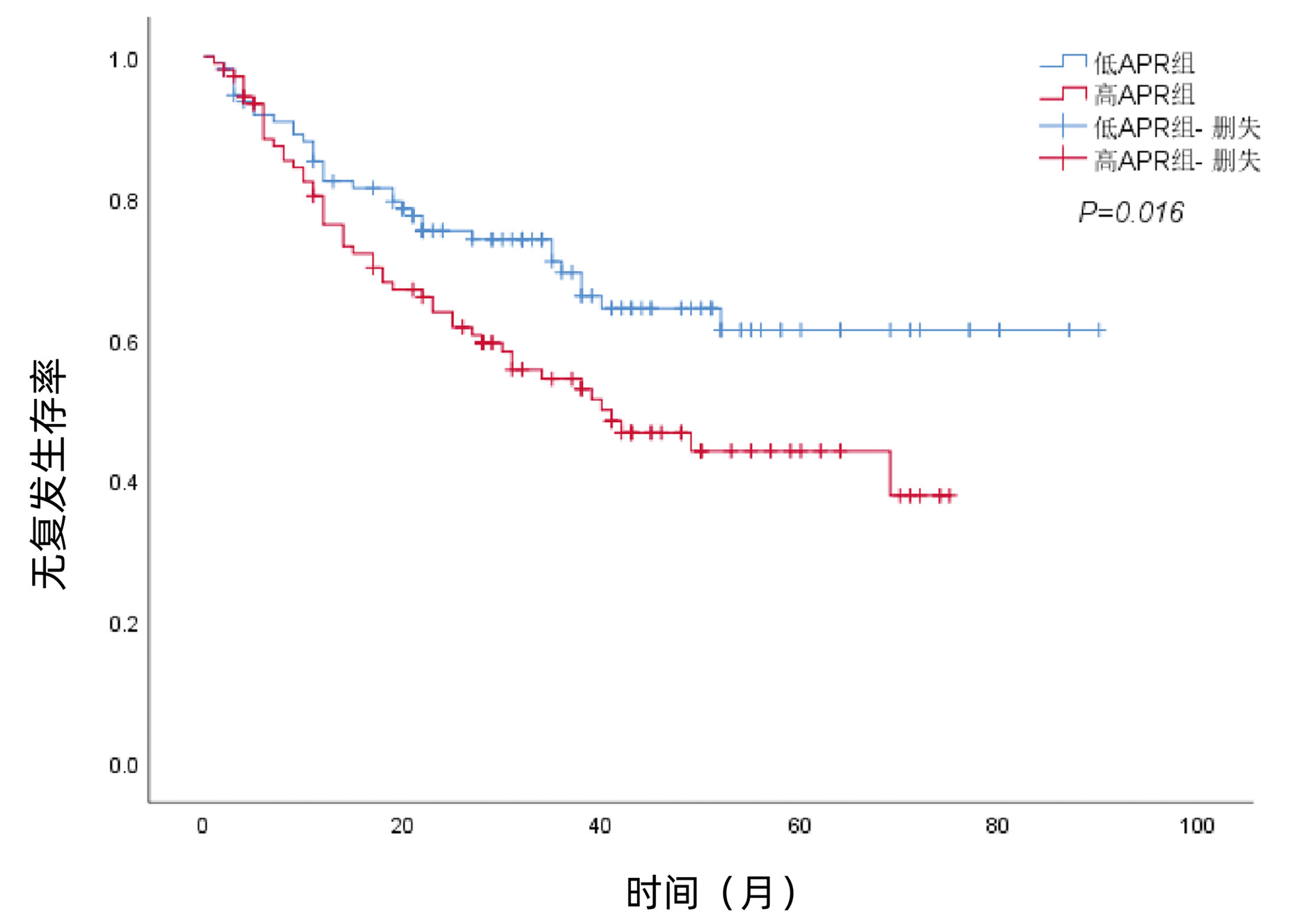
| [1] |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. |
| [2] |
ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10204): 1145-1158. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1. |
| [3] |
CHEN W, ZHENG R, BAADE PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21338. |
| [4] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(2): 288-303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. |
| [5] |
XU XF, XING H, HAN J, et al. Risk factors, patterns, and outcomes of late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter study from China[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019, 154(3): 209-217. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.4334. |
| [6] |
DHIR M, MELIN AA, DOUAIHER J, et al. A review and update of treatment options and controversies in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2016, 263(6): 1112-1125. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001556. |
| [7] |
AMISAKI M, SAITO H, TOKUYASU N, et al. Prognostic value of postoperative complication for early recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2018, 17(4): 323-329. DOI: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.03.016. |
| [8] |
YANG T, ZHANG J, LU JH, et al. Risk factors influencing postoperative outcomes of major hepatic resection of hepatocellular carcinoma for patients with underlying liver diseases[J]. World J Surg, 2011, 35(9): 2073-2082. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-011-1161-0. |
| [9] |
CHOK KS, NG KK, POON RT, et al. Impact of postoperative complications on long-term outcome of curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Br J Surg, 2009, 96(1): 81-87. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.6358. |
| [10] |
HARIMOTO N, SHIRABE K, IKEGAMI T, et al. Postoperative complications are predictive of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Surg Res, 2015, 199(2): 470-477. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.06.012. |
| [11] |
THELEN A, BENCKERT C, TAUTENHAHN HM, et al. Liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without cirrhosis[J]. Br J Surg, 2013, 100(1): 130-137. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.8962. |
| [12] |
LI Y, WANG JS, GUO Y, et al. Use of the alkaline phosphatase to prealbumin ratio as an independent predictive factor for the prognosis of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(44): 6963-6978. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.6963. |
| [13] |
RAHBARI NN, GARDEN OJ, PADBURY R, et al. Posthepatectomy liver failure: a definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery (ISGLS)[J]. Surgery, 2011, 149(5): 713-724. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.10.001. |
| [14] |
DINDO D, DEMARTINES N, CLAVIEN PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey[J]. Ann Surg, 2004, 240(2): 205-213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. |
| [15] |
CLAVIEN PA, BARKUN J, de OLIVEIRA ML, et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience[J]. Ann Surg, 2009, 250(2): 187-196. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b13ca2. |
| [16] |
HAARHAUS M, BRANDENBURG V, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, et al. Alkaline phosphatase: a novel treatment target for cardiovascular disease in CKD[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017, 13(7): 429-442. DOI: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.60. |
| [17] |
PARK JB, KANG DY, YANG HM, et al. Serum alkaline phosphatase is a predictor of mortality, myocardial infarction, or stent thrombosis after implantation of coronary drug- eluting stent[J]. Eur Heart J, 2013, 34(12): 920-931. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs419. |
| [18] |
LI JP, XU T, YANG FC, et al. Prognostic value of APAR for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after radical hepatectomy[J/CD]. Chin J Hepat Surg(Electronic Edition), 2021, 10(3): 279-284. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2021.03.010. |
| [19] |
BARGER A, BAKER K, DRISKELL E, et al. The use of alkaline phosphatase and runx2 to distinguish osteosarcoma from other common malignant primary bone tumors in dogs[J]. Vet Pathol, 2022, 59(3): 427-432. DOI: 10.1177/03009858221083035. |
| [20] |
YANG Y, ZHANG M, ZHANG W, et al. Sensitive sensing of alkaline phosphatase and γ-glutamyltranspeptidase activity for tumor imaging[J]. Analyst, 2022, 147(8): 1544-1550. DOI: 10.1039/d2an00163b. |
| [21] |
XIA F, NDHLOVU E, LIU Z, et al. Alpha-fetoprotein+alkaline phosphatase (A-A) score can predict the prognosis of patients with ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma underwent hepatectomy[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 9934189. DOI: 10.1155/2022/9934189. |
| [22] |
ZHANG K, DONG S, JING YH, et al. Albumin-to-alkaline phosphatase ratio serves as a prognostic indicator in unresectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 541. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07023-9. |
| [23] |
ZHOU S, JIANG W, WANG H, et al. Predictive value of pretreatment albumin-to-alkaline phosphatase ratio for overall survival for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(17): 6268-6280. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3244. |
| [24] |
CHEN XY, LAN M, ZHOU Y, et al. Risk factors for bone metastasis from renal cell cancer[J]. J Bone Oncol, 2017, 9: 29-33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbo.2017.10.004. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
DELLIÈRE S, CYNOBER L. Is transthyretin a good marker of nutritional status?[J]. Clin Nutr, 2017, 36(2): 364-370. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.06.004. |
| [27] |
BECK FK, ROSENTHAL TC. Prealbumin: a marker for nutritional evaluation[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2002, 65(8): 1575-1578.
|
| [28] |
SHEN Z, ZHANG J, ZHAO S, et al. Preoperative biliary drainage of severely obstructive jaundiced patients decreases overall postoperative complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy: A retrospective and propensity score- matched analysis[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20(3): 529-536. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.02.002. |
| [29] |
LOFTUS TJ, BROWN MP, SLISH JH, et al. Serum levels of prealbumin and albumin for preoperative risk stratification[J]. Nutr Clin Pract, 2019, 34(3): 340-348. DOI: 10.1002/ncp.10271. |
| [30] |
HUANG L, LI J, YAN JJ, et al. Prealbumin is predictive for postoperative liver insufficiency in patients undergoing liver resection[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012, 18(47): 7021-7025. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7021. |
| [31] |
LI JD, XU XF, HAN J, et al. Preoperative prealbumin level as an independent predictor of long-term prognosis after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-institutional study[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2019, 21(2): 157-166. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.06.1803. |
| [32] |
CHRYSOSTOMOU S, STATHAKIS C, PETRIKKOS G, et al. Assessment of prealbumin in hemodialysis and renal-transplant patients[J]. J Ren Nutr, 2010, 20(1): 44-51. DOI: 10.1053/j.jrn.2009.04.001. |
| [33] |
LIU F, CAI LY, ZHONG L, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease combined with serum prealbumin to predict the prognosis of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis[J]. J Dig Dis, 2010, 11(6): 352-357. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2010.00465.x. |
| [34] |
ROCHE M, LAW TY, KUROWICKI J, et al. Albumin, prealbumin, and transferrin may be predictive of wound complications following total knee arthroplasty[J]. J Knee Surg, 2018, 31(10): 946-951. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1672122. |
| [35] |
KALANTAR-ZADEH K, ANKER SD, HORWICH TB, et al. Nutritional and anti-inflammatory interventions in chronic heart failure[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2008, 101(11A): 89E-103E. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.03.007. |
| [36] |
WEN X, YAO M, LU Y, et al. Integration of prealbumin into Child-Pugh classification improves prognosis predicting accuracy in HCC patients considering curative surgery[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6(4): 377-384. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00004. |
| [37] |
JIA RR, ZHONG JH, HUO RR, et al. Correlation between serum prealbumin and prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2019, 119(6): 794-800. DOI: 10.1002/jso.25378. |
| [38] |
LI CX, ZHANG H, WU XF, et al. Clinical efficacy and prognostic factors analysis following curative hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with different China Liver Cancer Staging[J]. Chin J Surg, 2021, 59(2): 134-143. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20200803-00605. |
| [39] |
KIM JH, KIM JW, SEO JW, et al. Noninvasive tests for fibrosis predict 5-year mortality and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2016, 50(10): 882-888. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000574. |








 下载:
下载:





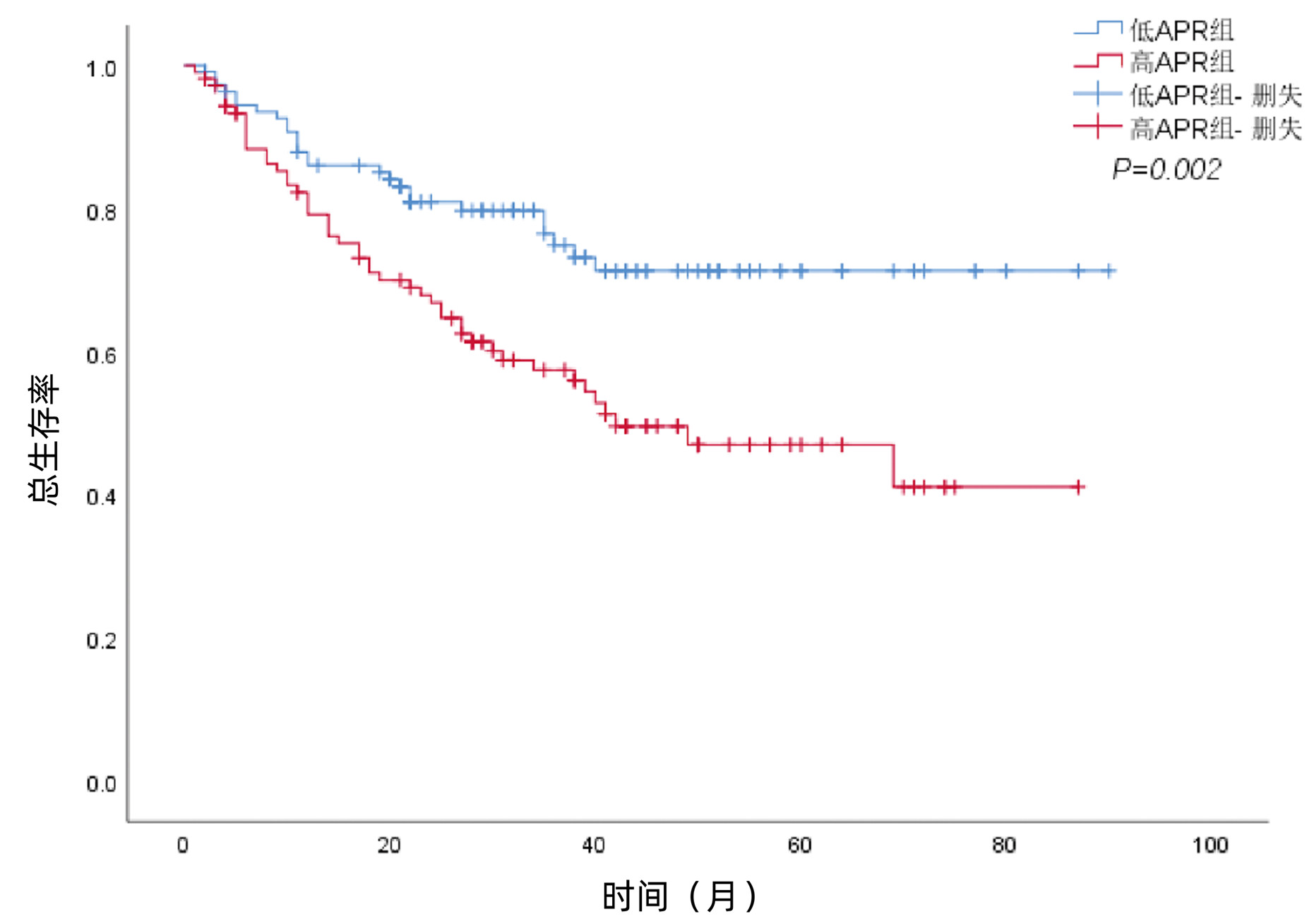




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: