| [1] |
|
| [2] |
LI J, ZOU B, YEO YH, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(5): 389-398. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1. |
| [3] |
YAN J, XIE W, OU WN, et al. Epidemiological survey and risk factor analysis of fatty liver disease of adult residents, Beijing, China[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28(10): 1654-1659. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12290. |
| [4] |
KUANG S, ZHENG J, YANG H, et al. Structure insight of GSDMD reveals the basis of GSDMD autoinhibition in cell pyroptosis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017, 114(40): 10642-10647. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1708194114. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
PUGLIESE N, PLAZ TORRES MC, PETTA S, et al. Is there an 'ideal' diet for patients with NAFLD?[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2022, 52(3): e13659. DOI: 10.1111/eci.13659. |
| [7] |
BOISE LH, COLLINS CM. Salmonella-induced cell death: apoptosis, necrosis or programmed cell death?[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2001, 9(2): 64-67. DOI: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)01937-5. |
| [8] |
SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death[J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7575): 660-665. DOI: 10.1038/nature15514. |
| [9] |
KAYAGAKI N, STOWE IB, LEE BL, et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling[J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7575): 666-671. DOI: 10.1038/nature15541. |
| [10] |
HIRSOVA P, GORES GJ. Death receptor-mediated cell death and proinflammatory signaling in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 1(1): 17-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2014.11.005. |
| [11] |
D'ARCY MS. Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2019, 43(6): 582-592. DOI: 10.1002/cbin.11137. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
BATTAGLIA AM, CHIRILLO R, AVERSA I, et al. Ferroptosis and cancer: Mitochondria meet the "iron maiden" cell death[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(6): 1505. DOI: 10.3390/cells9061505. |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
SARHAN J, LIU BC, MUENDLEIN HI, et al. Caspase-8 induces cleavage of gasdermin D to elicit pyroptosis during Yersinia infection[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115(46): E10888-E10897. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1809548115. |
| [16] |
TANG R, XU J, ZHANG B, et al. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in anticancer immunity[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 110. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00946-7. |
| [17] |
GAUTHERON J, GORES GJ, RODRIGUES C. Lytic cell death in metabolic liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(2): 394-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.001. |
| [18] |
COLAK Y, HASAN B, ERKALMA B, et al. Pathogenetic mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and inhibition of the inflammasome as a new therapeutic target[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2021, 45(4): 101710. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101710. |
| [19] |
LOZANO-RUIZ B, GONZÁLEZ-NAVAJAS JM. The emerging relevance of AIM2 in liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(18): 6535. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21186535. |
| [20] |
AL MAMUN A, WU Y, JIA C, et al. Role of pyroptosis in liver diseases[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 84: 106489. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106489. |
| [21] |
WANG Y, GAO W, SHI X, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7661): 99-103. DOI: 10.1038/nature22393. |
| [22] |
XU W, CHE Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Apaf-1 pyroptosome senses mitochondrial permeability transition[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(2): 424-436. e10. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.018. |
| [23] |
XU B, JIANG M, CHU Y, et al. Gasdermin D plays a key role as a pyroptosis executor of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in humans and mice[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(4): 773-782. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.040. |
| [24] |
ZHU Y, ZHAO H, LU J, et al. Caspase-11-mediated hepatocytic pyroptosis promotes the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 12(2): 653-664. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.04.009. |
| [25] |
MITSUYOSHI H, YASUI K, HARA T, et al. Hepatic nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptors pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasomes are associated with the histologic severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatol Res, 2017, 47(13): 1459-1468. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12883. |
| [26] |
CSAK T, PILLAI A, GANZ M, et al. Both bone marrow-derived and non-bone marrow-derived cells contribute to AIM2 and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in a MyD88-dependent manner in dietary steatohepatitis[J]. Liver Int, 2014, 34(9): 1402-1413. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12537. |
| [27] |
GONG Z, ZHANG X, SU K, et al. Deficiency in AIM2 induces inflammation and adipogenesis in white adipose tissue leading to obesity and insulin resistance[J]. Diabetologia, 2019, 62(12): 2325-2339. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-019-04983-x. |
| [28] |
YU X, HAO M, LIU Y, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis activation via mitophagy[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 864: 172715. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172715. |
| [29] |
MAI W, XU Y, XU J, et al. Berberine inhibits nod-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via the ROS/TXNIP axis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 185. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00185. |
| [30] |
RUAN S, HAN C, SHENG Y, et al. Antcin A alleviates pyroptosis and inflammatory response in Kupffercells of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by targeting NLRP3[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 100: 108126. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108126. |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
DEWIDAR B, MEYER C, DOOLEY S, et al. TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis-updated 2019[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(11): 1419. DOI: 10.3390/cells8111419. |
| [33] |
WU J, LIN S, WAN B, et al. Pyroptosis in liver disease: New insights into disease mechanisms[J]. Aging Dis, 2019, 10(5): 1094-1108. DOI: 10.14336/AD.2019.0116. |
| [34] |
INZAUGARAT ME, JOHNSON CD, HOLTMANN TM, et al. NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation in hepatic stellate cells induces liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(2): 845-859. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30252. |
| [35] |
GAUL S, LESZCZYNSKA A, ALEGRE F, et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74(1): 156-167. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.041. |
| [36] |
GUO B, FU S, ZHANG J, et al. Targeting inflammasome/IL-1 pathways for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36107. DOI: 10.1038/srep36107. |
| [37] |
ZHANG X, LI C, CHEN D, et al. H. pylori CagA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome to promote gastric cancer cell migration and invasion[J]. Inflamm Res, 2022, 71(1): 141-155. DOI: 10.1007/s00011-021-01522-6. |
| [38] |
GARCÍA-PRAS E, FERNÁNDEZ-IGLESIAS A, GRACIA-SANCHO J, et al. Cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma: Pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 14(1): 48. DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010048. |
| [39] |
YAN H, LUO B, WU X, et al. Cisplatin induces pyroptosis via activation of MEG3/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(10): 2606-2621. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.60292. |
| [40] |
ZHOU CB, FANG JY. The role of pyroptosis in gastrointestinal cancer and immune responses to intestinal microbial infection[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2019, 1872(1): 1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.05.001. |
| [41] |
HUANG DQ, EL-SERAG HB, LOOMBA R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(4): 223-238. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00381-6. |
| [42] |
CHEN YF, QI HY, WU FL. Euxanthone exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-invasive activities in hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing pyroptosis: preliminary results[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(23): 8186-8196. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16511. |
| [43] |
WEI Q, MU K, LI T, et al. Deregulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic parenchymal cells during liver cancer progression[J]. Lab Invest, 2014, 94(1): 52-62. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.126. |
| [44] |
WEI Q, ZHU R, ZHU J, et al. E2-induced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome triggers pyroptosis and inhibits autophagy in HCC cells[J]. Oncol Res, 2019, 27(7): 827-834. DOI: 10.3727/096504018X15462920753012. |
| [45] |
ZHANG Y, YANG H, SUN M, et al. Alpinumisoflavone suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and metastasis via NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2020, 72(5): 1370-1382. DOI: 10.1007/s43440-020-00064-8. |










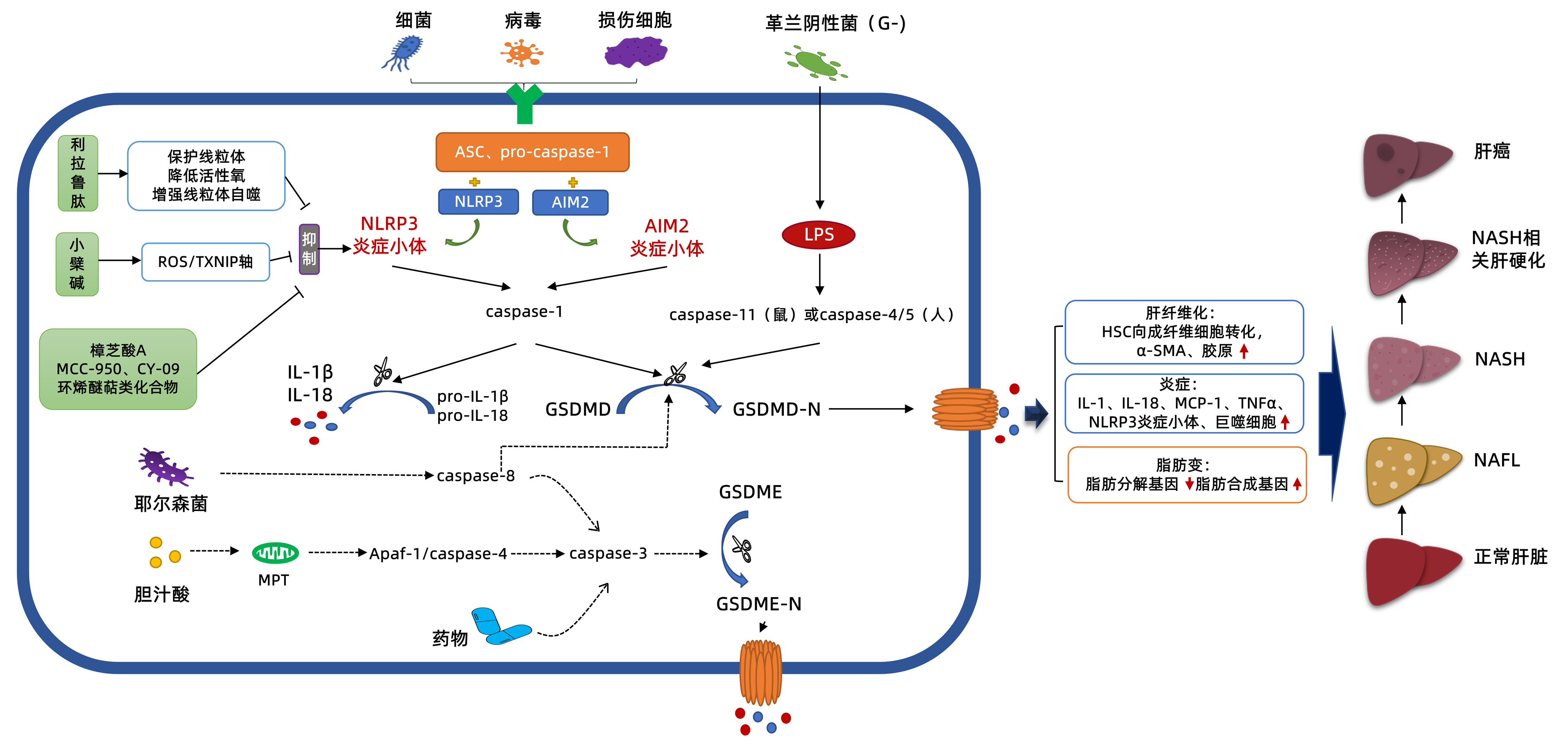




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: