| [1] |
VEGE SS, ZIRING B, JAIN R, et al. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(4): 819-822; quize12-13. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.015. |
| [2] |
TANAKA M, FERNÁNDEZ-DEL CASTILLO C, KAMISAWA T, et al. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas[J]. Pancreatology, 2017, 17(5): 738-753. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.07.007. |
| [3] |
European Study Group on Cystic Tumours of the Pancreas. European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(5): 789-804. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316027. |
| [4] |
ELTA GH, ENESTVEDT BK, SAUER BG, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: diagnosis and management of pancreatic cysts[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2018, 113(4): 464-479. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2018.14. |
| [5] |
FERNÁNDEZ-DEL CASTILLO C, TARGARONA J, THAYER SP, et al. Incidental pancreatic cysts: clinicopathologic characteristics and comparison with symptomatic patients[J]. Arch Surg, 2003, 138(4): 427-423; discussion 433-434. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.138.4.427. |
| [6] |
SUGIYAMA M, ATOMI Y. Intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas: imaging studies and treatment strategies[J]. Ann Surg, 1998, 228(5): 685-691. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199811000-00008. |
| [7] |
PARRA-HERRAN CE, GARCIA MT, HERRERA L, et al. Cystic lesions of the pancreas: clinical and pathologic review of cases in a five year period[J]. JOP, 2010, 11(4): 358-364.
|
| [8] |
WALSH RM, HENDERSON JM, VOGT DP, et al. Prospective preoperative determination of mucinous pancreatic cystic neoplasms[J]. Surgery, 2002, 132(4): 628-633; discussion 633-634. DOI: 10.1067/msy.2002.127543. |
| [9] |
GOH BK, TAN YM, CHEOW PC, et al. Cystic lesions of the pancreas: an appraisal of an aggressive resectional policy adopted at a single institution during 15 years[J]. Am J Surg, 2006, 192(2): 148-154. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.02.020. |
| [10] |
ANAND N, SAMPATH K, WU BU. Cyst features and risk of malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 11(8): 913-921; quiz e59-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.010. |
| [11] |
HWANG J, KIM YK, MIN JH, et al. Comparison between MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasonography for differentiating malignant from benign mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(1): 179-187. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-017-4926-5. |
| [12] |
DU C, CHAI NL, LINGHU EQ, et al. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of detailed structures of pancreatic cystic neoplasms[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(17): 3184-3192. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3184. |
| [13] |
JANG DK, SONG BJ, RYU JK, et al. Preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: the accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound and cross-sectional imaging[J]. Pancreas, 2015, 44(8): 1329-1333. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000396. |
| [14] |
LU X, ZHANG S, MA C, et al. The diagnostic value of EUS in pancreatic cystic neoplasms compared with CT and MRI[J]. Endosc Ultrasound, 2015, 4(4): 324-329. DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.170425. |
| [15] |
KAUHANEN S, RINTA-KⅡKKA I, KEMPPAINEN J, et al. Accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT, multidetector CT, and MR imaging in the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts: a prospective single-center study[J]. J Nucl Med, 2015, 56(8): 1163-1168. DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.114.148940. |
| [16] |
DUCONSEIL P, TURRINI O, EWALD J, et al. 'Peripheric' pancreatic cysts: performance of CT scan, MRI and endoscopy according to final pathological examination[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2015, 17(6): 485-489. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12388. |
| [17] |
KHASHAB MA, KIM K, LENNON AM, et al. Should we do EUS/FNA on patients with pancreatic cysts? The incremental diagnostic yield of EUS over CT/MRI for prediction of cystic neoplasms[J]. Pancreas, 2013, 42(4): 717-721. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182883a91. |
| [18] |
SAITO M, ISHIHARA T, TADA M, et al. Use of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with dual-phase imaging to identify intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 11(2): 181-186. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.037. |
| [19] |
de JONG K, NIO CY, MEARADJI B, et al. Disappointing interobserver agreement among radiologists for a classifying diagnosis of pancreatic cysts using magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Pancreas, 2012, 41(2): 278-282. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31822899b6. |
| [20] |
KIM JH, EUN HW, PARK HJ, et al. Diagnostic performance of MRI and EUS in the differentiation of benign from malignant pancreatic cyst and cyst communication with the main duct[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2012, 81(11): 2927-2935. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.12.019. |
| [21] |
SAHANI DV, SAINANI NI, BLAKE MA, et al. Prospective evaluation of reader performance on MDCT in characterization of cystic pancreatic lesions and prediction of cyst biologic aggressiveness[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2011, 197(1): W53- W61. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.10.5866. |
| [22] |
LEE HJ, KIM MJ, CHOI JY, et al. Relative accuracy of CT and MRI in the differentiation of benign from malignant pancreatic cystic lesions[J]. Clin Radiol, 2011, 66(4): 315-321. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2010.06.019. |
| [23] |
PONGPORNSUP S, PIYAPITTAYANAN S, CHAROENSAK A. MDCT imaging findings for characterization pancreatic cystic lesion: differentiation between benign and malignant pattern[J]. J Med Assoc Thai, 2011, 94(3): 369-378.
|
| [24] |
HONG HS, YUN M, CHO A, et al. The utility of F-18 FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2010, 35(10): 776-779. DOI: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181e4da32. |
| [25] |
SAINANI NI, SAOKAR A, DESHPANDE V, et al. Comparative performance of MDCT and MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography in characterizing small pancreatic cysts[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2009, 193(3): 722-731. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.08.1253. |
| [26] |
FISHER WE, HODGES SE, YAGNIK V, et al. Accuracy of CT in predicting malignant potential of cystic pancreatic neoplasms[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2008, 10(6): 483-490. DOI: 10.1080/13651820802291225. |
| [27] |
VISSER BC, MUTHUSAMY VR, YEH BM, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of cystic pancreatic lesions[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2008, 10(1): 63-69. DOI: 10.1080/13651820701883155. |
| [28] |
SPERTI C, BISSOLI S, PASQUALI C, et al. 18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography enhances computed tomography diagnosis of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Ann Surg, 2007, 246(6): 932-937; discussion 937-939. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815c2a29. |
| [29] |
TANN M, SANDRASEGARAN K, JENNINGS SG, et al. Positron- emission tomography and computed tomography of cystic pancreatic masses[J]. Clin Radiol, 2007, 62(8): 745-751. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2007.01.023. |
| [30] |
SONG SJ, LEE JM, KIM YJ, et al. Differentiation of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms from other pancreatic cystic masses: comparison of multirow-detector CT and MR imaging using ROC analysis[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2007, 26(1): 86-93. DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21001. |
| [31] |
GERKE H, JAFFE TA, MITCHELL RM, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound and computer tomography are inaccurate methods of classifying cystic pancreatic lesions[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2006, 38(1): 39-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2005.09.023. |
| [32] |
SPERTI C, PASQUALI C, DECET G, et al. F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in differentiating malignant from benign pancreatic cysts: a prospective study[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2005, 9(1): 22-28; discussion 28-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.gassur.2004.10.002. |
| [33] |
UDARE A, AGARWAL M, ALABOUSI M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of MRI for differentiation of benign and malignant pancreatic cystic lesions compared to CT and endoscopic ultrasound: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 54(4): 1126-1137. DOI: 10.1002/jmri.27606. |
| [34] |
TIRKES T, PATEL AA, TAHIR B, et al. Pancreatic cystic neoplasms and post-inflammatory cysts: interobserver agreement and diagnostic performance of MRI with MRCP[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2021, 46(9): 4245-4253. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-021-03116-6. |
| [35] |
TIRKES T, AISEN AM, CRAMER HM, et al. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas; findings on magnetic resonance imaging with pathological, surgical, and clinical correlation[J]. Abdom Imaging, 2014, 39(5): 1088-1101. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-014-0138-5. |
| [36] |
PAUSAWASDI N, RATANACHU-EK T. Endoscopic ultrasonography evaluation for pancreatic cysts: Necessity or overkill?[J]. Dig Endosc, 2017, 29(4): 444-454. DOI: 10.1111/den.12873. |
| [37] |
de JONG K, VAN HOOFT JE, NIO CY, et al. Accuracy of preoperative workup in a prospective series of surgically resected cystic pancreatic lesions[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2012, 47(8-9): 1056-1063. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2012.674970. |
| [38] |
ZHU H, JIANG F, ZHU J, et al. Assessment of morbidity and mortality associated with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dig Endosc, 2017, 29(6): 667-675. DOI: 10.1111/den.12851. |
| [39] |
COLÁN-HERNÁNDEZ J, SENDINO O, LORAS C, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not required for endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration of pancreatic cystic lesions, based on a randomized trial[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(6): 1642-1649.e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.025. |
| [40] |
Expert Committee on Endoscopic Ultrasonography of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese guideline for the clinical practice of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration/biopsy (2021, Shanghai)[J]. Chin J Dig Endosc, 2021, 38(5): 337-360. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321463-20210302-00143. |
| [41] |
LEUNG KK, ROSS WA, EVANS D, et al. Pancreatic cystic neoplasm: the role of cyst morphology, cyst fluid analysis, and expectant management[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2009, 16(10): 2818-2824. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-009-0502-9. |
| [42] |
BICK BL, ENDERS FT, LEVY MJ, et al. The string sign for diagnosis of mucinous pancreatic cysts[J]. Endoscopy, 2015, 47(7): 626-631. DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1391484. |
| [43] |
OH SH, LEE JK, LEE KT, et al. The combination of cyst fluid carcinoembryonic antigen, cytology and viscosity increases the diagnostic accuracy of mucinous pancreatic cysts[J]. Gut Liver, 2017, 11(2): 283-289. DOI: 10.5009/gnl15650. |
| [44] |
KHAMAYSI I, ABU AMMAR A, VASILYEV G, et al. Differentiation of pancreatic cyst types by analysis of rheological behavior of pancreatic cyst fluid[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 45589. DOI: 10.1038/srep45589. |
| [45] |
HAKIM S, CORONEL E, GONZÁLEZ G, et al. An international study of interobserver variability of "string sign" of pancreatic cysts among experienced endosonographers[J]. Endosc Ultrasound, 2021, 10(1): 39-50. DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_73_20. |
| [46] |
GIANNONE F, CRIPPA S, ALEOTTI F, et al. Improving diagnostic accuracy and appropriate indications for surgery in pancreatic cystic neoplasms: the role of EUS[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2022, 96(4): 648-656.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.05.009. |
| [47] |
STELOW EB, STANLEY MW, BARDALES RH, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. The findings and limitations of cytologic samples obtained by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2003, 120(3): 398-404. DOI: doi: 10.1309/CEPK-542W-3885-2LP8.
|
| [48] |
THOSANI N, THOSANI S, QIAO W, et al. Role of EUS-FNA-based cytology in the diagnosis of mucinous pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2010, 55(10): 2756-2766. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-010-1361-8. |
| [49] |
WANG QX, XIAO J, ORANGE M, et al. EUS-guided FNA for diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: a meta-analysis[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2015, 36(3): 1197-1209. DOI: 10.1159/000430290. |
| [50] |
van der WAAIJ LA, van DULLEMEN HM, PORTE RJ. Cyst fluid analysis in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: a pooled analysis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2005, 62(3): 383-389. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5107(05)01581-6. |
| [51] |
CIZGINER S, TURNER BG, BILGE AR, et al. Cyst fluid carcinoembryonic antigen is an accurate diagnostic marker of pancreatic mucinous cysts[J]. Pancreas, 2011, 40(7): 1024-1028. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31821bd62f. |
| [52] |
BRUGGE WR, LEWANDROWSKI K, LEE-LEWANDROWSKI E, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: a report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study[J]. Gastroenterology, 2004, 126(5): 1330-1336. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.02.013. |
| [53] |
van HUIJGEVOORT N, HOOGENBOOM SA, LEKKERKERKER SJ, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of carcinoembryonic antigen in differentiating mucinous and non-mucinous pancreatic cystic neoplasms—a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis[J]. Endoscopy, 2018, 50(4): ePP033.
|
| [54] |
RIBALDONE DG, BRUNO M, GAIA S, et al. Differential diagnosis of pancreatic cysts: A prospective study on the role of intra-cystic glucose concentration[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2020, 52(9): 1026-1032. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.06.038. |
| [55] |
MOHAN BP, MADHU D, KHAN SR, et al. Intracystic glucose levels in differentiating mucinous from nonmucinous pancreatic cysts: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2022, 56(2): e131-e136. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001507. |
| [56] |
MCCARTY TR, GARG R, RUSTAGI T. Pancreatic cyst fluid glucose in differentiating mucinous from nonmucinous pancreatic cysts: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2021, 94(4): 698-712.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.04.025. |
| [57] |
KOVACEVIC B, KLAUSEN P, HASSELBY JP, et al. A novel endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle microbiopsy procedure improves diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions[J]. Endoscopy, 2018, 50(11): 1105-1111. DOI: 10.1055/a-0625-6440. |
| [58] |
YANG D, SAMARASENA JB, JAMIL LH, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy in the evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions: a multicenter study[J]. Endosc Int Open, 2018, 6(12): E1423-E1430. DOI: 10.1055/a-0770-2700. |
| [59] |
ZHANG ML, ARPIN RN, BRUGGE WR, et al. Moray micro forceps biopsy improves the diagnosis of specific pancreatic cysts[J]. Cancer Cytopathol, 2018, 126(6): 414-420. DOI: 10.1002/cncy.21988. |
| [60] |
CRINÕ SF, BERNARDONI L, BROZZI L, et al. Association between macroscopically visible tissue samples and diagnostic accuracy of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy sampling of pancreatic cystic lesions[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2019, 90(6): 933-943. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.05.009. |
| [61] |
WESTERVELD DR, PONNIAH SA, DRAGANOV PV, et al. Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy versus EUS-FNA of pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Endosc Int Open, 2020, 8(5): E656-E667. DOI: 10.1055/a-1119-6543. |
| [62] |
MCCARTY T, RUSTAGI T. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy improves diagnostic yield for pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Endosc Int Open, 2020, 8(10): E1280-E1290. DOI: 10.1055/a-1194-4085. |
| [63] |
YANG D, TRINDADE AJ, YACHIMSKI P, et al. Histologic analysis of endoscopic ultrasound-guided through the needle microforceps biopsies accurately identifies mucinous pancreas cysts[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17(8): 1587-1596. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.027. |
| [64] |
KRISHNA SG, HART PA, MALLI A, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided confocal laser endomicroscopy increases accuracy of differentiation of pancreatic cystic lesions[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(2): 432-440.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.06.010. |
| [65] |
BERTANI H, PEZZILLI R, PIGÕ F, et al. Needle-based confocal endomicroscopy in the discrimination of mucinous from non-mucinous pancreatic cystic lesions[J]. World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2021, 13(11): 555-564. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i11.555. |
| [66] |
HAO S, DING W, JIN Y, et al. Appraisal of EUS-guided needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in the diagnosis of pancreatic lesions: A single Chinese center experience[J]. Endosc Ultrasound, 2020, 9(3): 180-186. DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_9_20. |
| [67] |
WANG X, HU J, YANG F, et al. Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy for diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: a meta-analysis[J]. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol, 2022, 31(5): 653-663. DOI: 10.1080/13645706.2021.1888750. |
| [68] |
KONJETI VR, MCCARTY TR, RUSTAGI T. Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) for evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2022, 56(1): 72-80. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001468. |
| [69] |
LE PEN C, PALAZZO L, NAPOLÉON B. A health economic evaluation of needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy for the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts[J]. Endosc Int Open, 2017, 5(10): E987-E995. DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-117947. |
| [70] |
KOVACEVIC B, ANTONELLI G, KLAUSEN P, et al. EUS-guided biopsy versus confocal laser endomicroscopy in patients with pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Endosc Ultrasound, 2021, 10(4): 270-279. DOI: 10.4103/EUS-D-20-00172. |
| [71] |
NAKAI Y, IWASHITA T, PARK DH, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic cysts: EUS-guided, through-the-needle confocal laser-induced endomicroscopy and cystoscopy trial: DETECT study[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015, 81(5): 1204-1214. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.10.025. |
| [72] |
KRISHNA SG, SWANSON B, HART PA, et al. Validation of diagnostic characteristics of needle based confocal laser endomicroscopy in differentiation of pancreatic cystic lesions[J]. Endosc Int Open, 2016, 4(11): E1124-E1135. DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-116491. |
| [73] |
KATO T, TSUKAMOTO Y, NAITOH Y, et al. Ultrasonographic and endoscopic ultrasonographic angiography in pancreatic mass lesions[J]. Acta Radiol, 1995, 36(4): 381-387. DOI: 10.3109/02841859509173393 |
| [74] |
DIETRICH CF, IGNEE A, FREY H. Contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound with low mechanical index: a new technique[J]. Z Gastroenterol, 2005, 43(11): 1219-1223. DOI: 10.1055/s-2005-858662. |
| [75] |
QUAIA E. Classification and safety of microbubble-based contrast agents[M]. Contrast media in ultrasonography: Springer, 2005, 3-14.
|
| [76] |
SEICEAN A, BADEA R, STAN-IUGA R, et al. The added value of real-time harmonics contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography for the characterisation of pancreatic diseases in routine practice[J]. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2010, 19(1): 99-104.
|
| [77] |
SAKAMOTO H, KITANO M, KAMATA K, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic tumors by endoscopic ultrasonography[J]. World J Radiol, 2010, 2(4): 122-134. DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i4.122. |
| [78] |
YAMASHITA Y, UEDA K, ITONAGA M, et al. Usefulness of contrast-enhanced endoscopic sonography for discriminating mural nodules from mucous clots in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: a single-center prospective study[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2013, 32(1): 61-68. DOI: 10.7863/jum.2013.32.1.61. |
| [79] |
FUJITA M, ITOI T, IKEUCHI N, et al. Effectiveness of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound for detecting mural nodules in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas and for making therapeutic decisions[J]. Endosc Ultrasound, 2016, 5(6): 377-383. DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.190927. |
| [80] |
ZHONG L, CHAI N, LINGHU E, et al. A prospective study on contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound for differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2019, 64(12): 3616-3622. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-019-05718-z. |
| [81] |
LISOTTI A, NAPOLEON B, FACCIORUSSO A, et al. Contrast-enhanced EUS for the characterization of mural nodules within pancreatic cystic neoplasms: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2021, 94(5): 881-889.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.028. |
| [82] |
van HUIJGEVOORT N, DEL CHIARO M, WOLFGANG CL, et al. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: current evidence and guidelines[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(11): 676-689. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0195-x. |
| [83] |
OHNO E, HIROOKA Y, ITOH A, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: differentiation of malignant and benign tumors by endoscopic ultrasound findings of mural nodules[J]. Ann Surg, 2009, 249(4): 628-634. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181a189a8. |
| [84] |
MARCHEGIANI G, ANDRIANELLO S, BORIN A, et al. Systematic review, meta-analysis, and a high-volume center experience supporting the new role of mural nodules proposed by the updated 2017 international guidelines on IPMN of the pancreas[J]. Surgery, 2018, 163(6): 1272-1279. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.01.009. |
| [85] |
KAMATA K, TAKENAKA M, MINAGA K, et al. Value of additional endoscopic ultrasonography for surveillance after surgical removal of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms[J]. Dig Endosc, 2018, 30(5): 659-666. DOI: 10.1111/den.13176. |
| [86] |
CHEN YK, PLESKOW DK. SpyGlass single-operator peroral cholangiopancreatoscopy system for the diagnosis and therapy of bile-duct disorders: a clinical feasibility study (with video)[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2007, 65(6): 832-841. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.01.025. |
| [87] |
MIURA T, IGARASHI Y, OKANO N, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis of intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas by means of peroral pancreatoscopy using a small-diameter videoscope and narrow-band imaging[J]. Dig Endosc, 2010, 22(2): 119-123. DOI: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2010.00926.x. |
| [88] |
YAMAO K, OHASHI K, NAKAMURA T, et al. Efficacy of peroral pancreatoscopy in the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2003, 57(2): 205-209. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2003.72. |
| [89] |
ARNELO U, SⅡKI A, SWAHN F, et al. Single-operator pancreatoscopy is helpful in the evaluation of suspected intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN)[J]. Pancreatology, 2014, 14(6): 510-514. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.08.007. |
| [90] |
TRINDADE AJ, BENIAS PC, KURUPATHI P, et al. Digital pancreatoscopy in the evaluation of main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: a multicenter study[J]. En doscopy, 2018, 50(11): 1095-1098. DOI: 10.1055/a-0596-7374. |
| [91] |
NAGAYOSHI Y, ASO T, OHTSUKA T, et al. Peroral pancreatoscopy using the SpyGlass system for the assessment of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2014, 21(6): 410-417. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.44. |
| [92] |
PARBHU SK, SIDDIQUI AA, MURPHY M, et al. Efficacy, safety, and outcomes of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with per-oral pancreatoscopy: a multicenter experience[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2017, 51(10): e101-101e105. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000796. |
| [93] |
de JONG DM, STASSEN P, GROOT KOERKAMP B, et al. The role of pancreatoscopy in the diagnostic work-up of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Endoscopy, 2023, 55(1): 25-35. DOI: 10.1055/a-1869-0180. |
| [94] |
VEHVILÄINEN S, FAGERSTRÖM N, VALENTE R, et al. Single-operator peroral pancreatoscopy in the preoperative diagnostics of suspected main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: efficacy and novel insights on complications[J]. Surg Endosc, 2022, 36(10): 7431-7443. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-022-09156-3. |
| [95] |
SCHEIMAN JM, HWANG JH, MOAYYEDI P. American gastroenterological association technical review on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(4): 824-848.e22. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.014. |
| [96] |
GRIFFIN JF, PAGE AJ, SAMAHA GJ, et al. Patients with a resected pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm have a better prognosis than patients with an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: A large single institution series[J]. Pancreatology, 2017, 17(3): 490-496. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.04.003. |
| [97] |
EGAWA S, TAKEDA K, FUKUYAMA S, et al. Clinicopathological aspects of small pancreatic cancer[J]. Pancreas, 2004, 28(3): 235-240. DOI: 10.1097/00006676-200404000-00004. |
| [98] |
ISHIKAWA O, OHIGASHI H, IMAOKA S, et al. Minute carcinoma of the pancreas measuring 1 cm or less in diameter-collective review of Japanese case reports[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 1999, 46(25): 8-15.
|
| [99] |
CRIPPA S, FERNÁNDEZ-DEL CASTILLO C, SALVIA R, et al. Mucin-producing neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of distinguishing clinical and epidemiologic characteristics[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 8(2): 213-219. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.10.001. |
| [100] |
OYAMA H, TADA M, TAKAGI K, et al. Long-term risk of malignancy in branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(1): 226-237.e5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.032. |
| [101] |
LI Y, ZHU Z, PENG L, et al. The pathological features and prognoses of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and mucinous cystic neoplasm after surgical resection: a single institution series[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2020, 18(1): 287. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-020-02063-8. |
| [102] |
NILSSON LN, KEANE MG, SHAMALI A, et al. Nature and management of pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN): A systematic review of the literature[J]. Pancreatology, 2016, 16(6): 1028-1036. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2016.09.011. |
| [103] |
JAIS B, REBOURS V, MALLEO G, et al. Serous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: a multinational study of 2622 patients under the auspices of the International Association of Pancreatology and European Pancreatic Club (European Study Group on Cystic Tumors of the Pancreas)[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(2): 305-312. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309638. |
| [104] |
REID MD, CHOI HJ, MEMIS B, et al. Serous neoplasms of the pancreas: a clinicopathologic analysis of 193 cases and literature review with new insights on macrocystic and solid variants and critical reappraisal of so-called "serous cystadenocarcinoma"[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2015, 39(12): 1597-1610. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000559. |
| [105] |
SALOM F, PIEDRA W, BURGOS H. Tumor growth rate of pancreatic serous cystadenomas: Endosonographic follow-up with volume measurement to predict cyst enlargement[J]. Pancreatology, 2019, 19(1): 122-126. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2018.11.007. |
| [106] |
LIU H, CUI Y, SHAO J, et al. The diagnostic role of CT, MRI/MRCP, PET/CT, EUS and DWI in the differentiation of benign and malignant IPMN: A meta-analysis[J]. Clin Imaging, 2021, 72: 183-193. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.11.018. |
| [107] |
SULTANA A, JACKSON R, TIM G, et al. What is the best way to identify malignant transformation within pancreatic IPMN: A systematic review and meta-analyses[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2015, 6(12): e130. DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2015.60. |
| [108] |
HUYNH T, ALI K, VYAS S, et al. Comparison of imaging modalities for measuring the diameter of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20(3): 448-453. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.02.013. |
| [109] |
IPPOLITO D, MAINO C, PECORELLI A, et al. Incidental pancreatic cystic lesions: comparison between CT with model-based algorithm and MRI[J]. Radiography (Lond), 2021, 27(2): 554-560. DOI: 10.1016/j.radi.2020.11.016. |
| [110] |
BOOS J, BROOK A, CHINGKOE CM, et al. MDCT vs. MRI for incidental pancreatic cysts: measurement variability and impact on clinical management[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2017, 42(2): 521-530. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-016-0883-8. |
| [111] |
BORASCHI P, TARANTINI G, DONATI F, et al. Side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: outcome of MR imaging surveillance over a 10 years follow-up[J]. Eur J Radiol Open, 2020, 7: 100250. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2020.100250. |
| [112] |
VULLIERME MP, GREGORY J, REBOURS V, et al. MRI is useful to suggest and exclude malignancy in mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(2): 1297-1307. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-021-08091-6. |
| [113] |
LEE JE, CHOI SY, MIN JH, et al. Determining malignant potential of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: CT versus MRI by using revised 2017 international consensus guidelines[J]. Radiology, 2019, 293(1): 134-143. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2019190144. |
| [114] |
LAYNE KA, DARGAN PI, ARCHER J, et al. Gadolinium deposition and the potential for toxicological sequelae - A literature review of issues surrounding gadolinium-based contrast agents[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2018, 84(11): 2522-2534. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13718. |
| [115] |
NOUGARET S, REINHOLD C, CHONG J, et al. Incidental pancreatic cysts: natural history and diagnostic accuracy of a limited serial pancreatic cyst MRI protocol[J]. Eur Radiol, 2014, 24(5): 1020-1029. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-014-3112-2. |
| [116] |
MACARI M, LEE T, KIM S, et al. Is gadolinium necessary for MRI follow-up evaluation of cystic lesions in the pancreas? Preliminary results[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2009, 192(1): 159-164. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.08.1068. |
| [117] |
ZHONG N, ZHANG L, TAKAHASHI N, et al. Histologic and imaging features of mural nodules in mucinous pancreatic cysts[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 10(2): 192-198, 198.e1-2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.09.029. |
| [118] |
DAS A, WELLS CD, NGUYEN CC. Incidental cystic neoplasms of pancreas: what is the optimal interval of imaging surveillance?[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2008, 103(7): 1657-1662. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01893.x. |
| [119] |
HAN Y, LEE H, KANG JS, et al. Progression of Pancreatic Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Associates With Cyst Size[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(3): 576-584. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.013. |
| [120] |
KIM KW, PARK SH, PYO J, et al. Imaging features to distinguish malignant and benign branch-duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a meta-analysis[J]. Ann Surg, 2014, 259(1): 72-81. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31829385f7. |
| [121] |
KWONG WT, LAWSON RD, HUNT G, et al. Rapid growth rates of suspected pancreatic cyst branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms predict malignancy[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2015, 60(9): 2800-2806. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-015-3679-8. |
| [122] |
KOLB JM, ARGIRIADI P, LEE K, et al. Higher growth rate of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms associates with worrisome features[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16(9): 1481-1487. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.02.050. |
| [123] |
KANG MJ, JANG JY, KIM SJ, et al. Cyst growth rate predicts malignancy in patients with branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 9(1): 87-93. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.09.008. |
| [124] |
ZHAO W, LIU S, CONG L, et al. Imaging features for predicting high-grade dysplasia or malignancy in branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(2): 1297-1312. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-021-10662-2. |
| [125] |
YAMAZAKI T, TOMODA T, KATO H, et al. Risk factors for the development of high-risk stigmata in branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms[J]. Intern Med, 2021, 60(20): 3205-3211. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7168-21. |
| [126] |
DEL CHIARO M, BECKMAN R, ATEEB Z, et al. Main duct dilatation is the best predictor of high-grade dysplasia or invasion in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Ann Surg, 2020, 272(6): 1118-1124. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003174. |
| [127] |
SUN L, WANG Y, JIANG F, et al. Prevalence of pancreatic cystic lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging in the Chinese population[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(9): 1656-1662. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14658. |



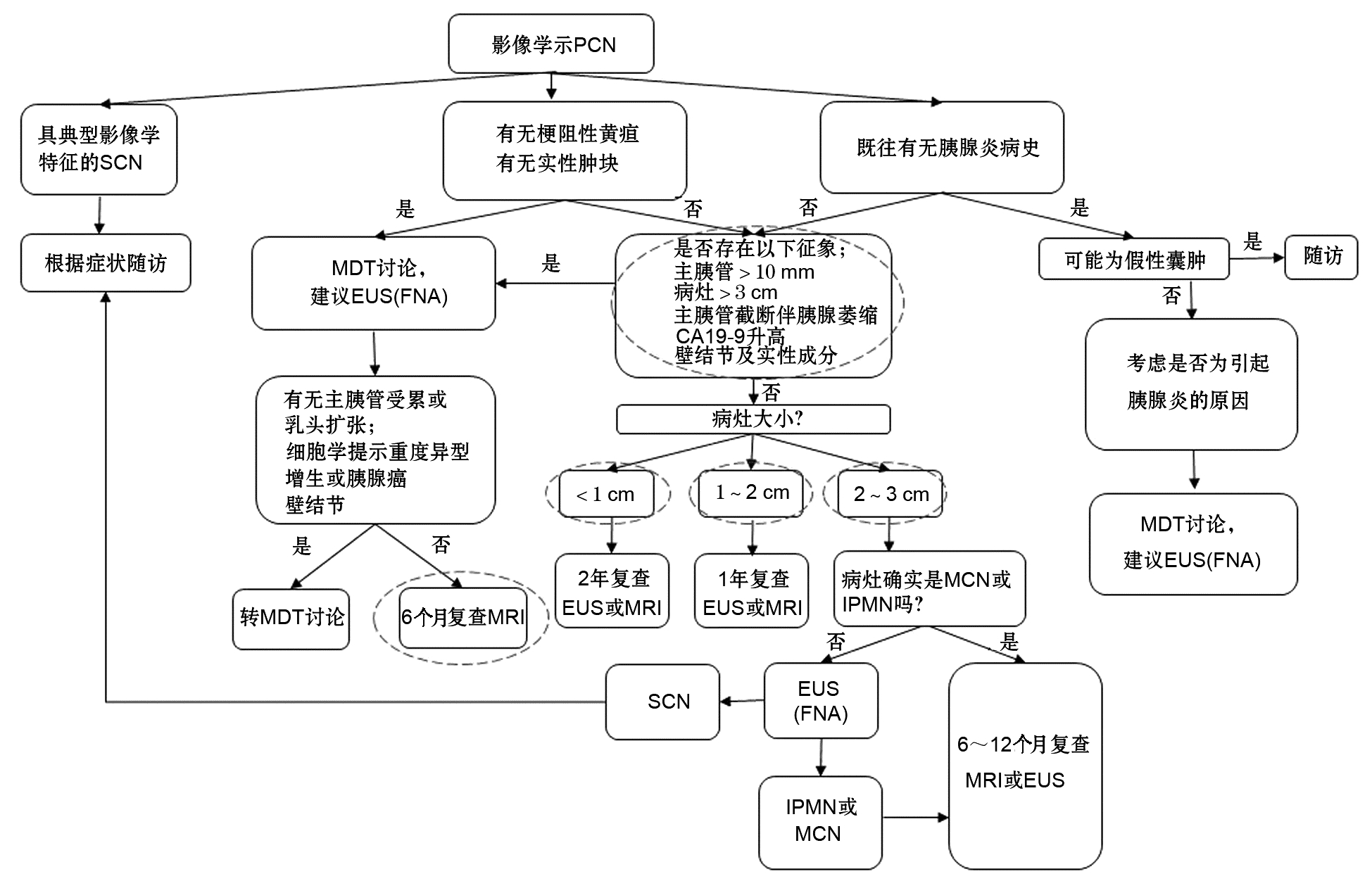




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: