| [1] |
XIAO HJ, HAN T. Prevention and treatment of malnutrition, sarcopenia, and osteoporosis in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(1): 26-30. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.006. |
| [2] |
Chinese Society of Osteoporosis and Bone Mineral Research. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of primary osteoporosis(2017)[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2019, 25(3): 281-309. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2019.03.001. |
| [3] |
SANTOS LA, LIMA TB, AUGUSTI L, et al. Handgrip strength as a predictor of bone mineral density in outpatients with cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 31(1): 229-234. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13062. |
| [4] |
ZHU X, YAN H, CHANG X, et al. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatic fibrosis and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose regulation[J]. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, 2020, 8(1): e000999. DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000999. |
| [5] |
ZHANG W, GONG H, SU Z, et al. Risk factors associated with hepatic osteopathy in HBV related cirrhosis measured by liver stiffness: An Observational study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(31): e16628. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016628. |
| [6] |
ZHANG Y, GAO X, LIU T, et al. Association between osteoporosis and hepatitis B cirrhosis: a case-control study[J]. Afr Health Sci, 2020, 20(4): 1610-1616. DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v20i4.13. |
| [7] |
EBADI M, TANDON P, MOCTEZUMA-VELAZQUEZ C, et al. Low subcutaneous adiposity associates with higher mortality in female patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(3): 608-616. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.04.015. |
| [8] |
HULDÉN E, CASTEDAL M, KARLSSON MK, et al. Osteoporosis in cirrhotics before and after liver transplantation: relation with malnutrition and inflammatory status[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2020, 55(3): 354-361. DOI: 10.1080/00365521.2020.1735507. |
| [9] |
SAEKI C, OIKAWA T, KANAI T, et al. Relationship between osteoporosis, sarcopenia, vertebral fracture, and osteosarcopenia in patients with primary biliary cholangitis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 33(5): 731-737. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001791. |
| [10] |
SAEKI C, TAKANO K, OIKAWA T, et al. Comparative assessment of sarcopenia using the JSH, AWGS, and EWGSOP2 criteria and the relationship between sarcopenia, osteoporosis, and osteosarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2019, 20(1): 615. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-019-2983-4. |
| [11] |
FUSARO M, CIANCIOLO G, BRANDI ML, et al. Vitamin K and osteoporosis[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(12): 3625. DOI: 10.3390/nu12123625. |
| [12] |
RUIZ-GASPÀ S, GUAÑABENS N, JURADO S, et al. Bile acids and bilirubin effects on osteoblastic gene profile. Implications in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis in liver diseases[J]. Gene, 2020, 725: 144167. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144167. |
| [13] |
JADZIC J, CVETKOVIC D, MILOVANOVIC P, et al. The micro-structural analysis of lumbar vertebrae in alcoholic liver cirrhosis[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2020, 31(11): 2209-2217. DOI: 10.1007/s00198-020-05509-7. |
| [14] |
WAKOLBINGER R, MUSCHITZ C, SCHERIAU G, et al. Bone microarchitecture and bone turnover in hepatic cirrhosis[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2019, 30(6): 1195-1204. DOI: 10.1007/s00198-019-04870-6. |
| [15] |
YANG YJ, KIM DJ. An overview of the molecular mechanisms contributing to musculoskeletal disorders in chronic liver disease: Osteoporosis, sarcopenia, and osteoporotic sarcopenia[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(5): 2604. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052604. |
| [16] |
MORADI M, DOUSTIMOTLAGH AH, DEHPOUR AR, et al. The influence of TRAIL, adiponectin and sclerostin alterations on bone loss in BDL-induced cirrhotic rats and the effect of opioid system blockade[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 233: 116706. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116706. |
| [17] |
WAKOLBINGER R, MUSCHITZ C, WALLWITZ J, et al. Serum levels of sclerostin reflect altered bone microarchitecture in patients with hepatic cirrhosis[J]. Wien Klin Wochenschr, 2020, 132(1-2): 19-26. DOI: 10.1007/s00508-019-01595-8. |
| [18] |
JEONG HM, KIM DJ. Bone diseases in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(17): 4270. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20174270. |
| [19] |
PAL CHINA S, SANYAL S, CHATTOPADHYAY N. Adiponectin signaling and its role in bone metabolism[J]. Cytokine, 2018, 112: 116-131. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.06.012. |
| [20] |
ROOMI AB, NORI W, Al-BADRY SH. The value of serum adiponectin in osteoporotic women: does weight have an effect?[J]. J Obes, 2021, 2021: 5325813. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5325813. |
| [21] |
DA SILVA TE, COSTA-SILVA M, CORREA CG, et al. Clinical significance of serum adiponectin and resistin levels in liver cirrhosis[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2018, 17(2): 286-299. DOI: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.8659. |
| [22] |
ZHANG HQ, WANG LJ, LIU SH, et al. Adiponectin regulates bone mass in AIS osteopenia via RANKL/OPG and IL6 pathway[J]. J Transl Med, 2019, 17(1): 64. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1805-7. |
| [23] |
PETRESCU AD, GRANT S, WILLIAMS E, et al. Leptin enhances hepatic fibrosis and inflammation in a mouse model of cholestasis[J]. Am J Pathol, 2022, 192(3): 484-502. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.11.008. |
| [24] |
MENG XH, TAN LJ, XIAO HM, et al. Examining the causal role of leptin in bone mineral density: A Mendelian randomization study[J]. Bone, 2019, 125: 25-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.05.006. |
| [25] |
SZALAY F, FOLHOFFER A, HORVÁTH A, et al. Serum leptin, soluble leptin receptor, free leptin index and bone mineral density in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2005, 17(9): 923-928. DOI: 10.1097/00042737-200509000-00007. |
| [26] |
ZHAO J, QIAO L, DONG J, et al. Antioxidant effects of irisin in liver diseases: mechanistic insights[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 3563518. DOI: 10.1155/2022/3563518. |
| [27] |
CHEN X, SUN K, ZHAO S, et al. Irisin promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by activating autophagy via the Wnt//β-catenin signal pathway[J]. Cytokine, 2020, 136: 155292. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155292. |
| [28] |
GOMARASCA M, BANFI G, LOMBARDI G. Myokines: The endocrine coupling of skeletal muscle and bone[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2020, 94: 155-218. DOI: 10.1016/bs.acc.2019.07.010. |
| [29] |
PAZGAN-SIMON M, ZUWALA-JAGIELLO J, MENZYK T, et al. Serum betatrophin and irisin levels in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2020, 71(1): 113-123. DOI: 10.26402/jpp.2020.1.11. |
| [30] |
WALUGA M, KUKLA M, KOTULSKI R, et al. Omentin, vaspin and irisin in chronic liver diseases[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2019, 70(2): 277-285. DOI: 10.26402/jpp.2019.2.11. |
| [31] |
SEELY KD, KOTELKO CA, DOUGLAS H, et al. The human gut microbiota: A key mediator of osteoporosis and osteogenesis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9452. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179452. |
| [32] |
CASTANEDA M, SMITH KM, NIXON JC, et al. Alterations to the gut microbiome impair bone tissue strength in aged mice[J]. Bone Rep, 2021, 14: 101065. DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101065. |
| [33] |
TANG R, WEI Y, LI Z, et al. A common variant in CLDN14 is associated with primary biliary cirrhosis and bone mineral density[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 19877. DOI: 10.1038/srep19877. |
| [34] |
YANAGAWA S, TAHARA H, TANAKA Y, et al. Analysis of risk factors affecting incidence of osteoporosis and fragility fractures in liver transplant recipients[J]. Ann Transplant, 2021, 26: e925475. DOI: 10.12659/AOT.925475. |
| [35] |
PUGLIESE N, ARCARI I, AGHEMO A, et al. Osteosarcopenia in autoimmune cholestatic liver diseases: Causes, management, and challenges[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(14): 1430-1443. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1430. |
| [36] |
GROVER I, GUNJAN D, SINGH N, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on vitamin D level and bone mineral density in patients with cirrhosis: A randomized clinical trial[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2021, 116(10): 2098-2104. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001272. |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
LIMA TB, SANTOS LAA, NUNES HRC, et al. Safety and efficacy of risedronate for patients with esophageal varices and liver cirrhosis: a non-randomized clinical trial[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 18958. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55603-y. |
| [39] |
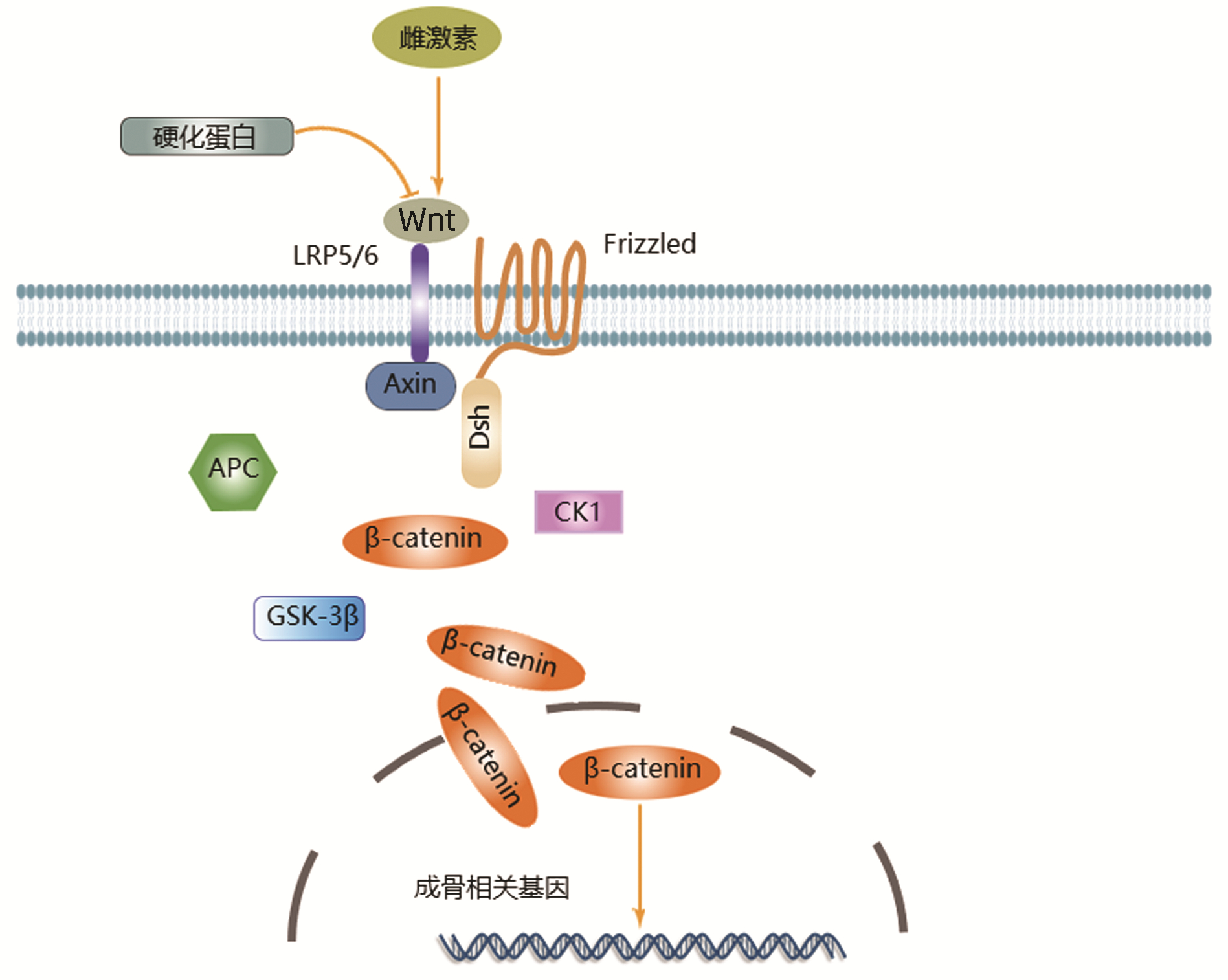
LI XN, WENG W, SHEN ZY, et al. Therapeutic effect of estradiol combined with 1, 25- dihydroxyvitamin D3 on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2021, 47(4): 857-864. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210406. |
| [40] |
RUDIC JS, POROPAT G, KRSTIC MN, et al. Hormone replacement for osteoporosis in women with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2011(12): CD009146. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009146.pub2. |
| [41] |
SAEKI C, SAITO M, OIKAWA T, et al. Effects of denosumab treatment in chronic liver disease patients with osteoporosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(33): 4960-4971. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4960. |
| [42] |
GKOUFA A, ANGELOUSI A, NEONAKI A, et al. Severe symptomatic hypocalcemia associated with denosumab administration in a patient with decompensated cirrhosis and renal dysfunction[J]. Ann Pharmacother, 2022, 56(7): 853-855. DOI: 10.1177/10600280211050216. |
| [43] |
ZHOU BS, CUI XC, LI CB. A clinical study of the effect of salmon calcitonin in patients with viral cirrhosis complicated with osteoporosis[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2018, 24(2): 226-229. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.02.018. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
