| [1] |
People's Liberation Army Professional Committee of Critical Care Medicine, CMA Chinese Society of Laboratory Medicine. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult critical care patients in China[J]. Med J Chin PLA, 2020, 45(5): 457-474. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2020.05.01. |
| [2] |
GUYATT GH, OXMAN AD, VIST GE, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations[J]. BMJ, 2008, 336(7650): 924-926. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD. |
| [3] |
XIAO J, WANG F, WONG NK, et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71(1): 212-221. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.004. |
| [4] |
GANGIREDDY VG, KANNEGANTI PC, SRIDHAR S, et al. Management of thrombocytopenia in advanced liver disease[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 28(10): 558-564. DOI: 10.1155/2014/532191. |
| [5] |
MAAN R, de KNEGT RJ, VELDT BJ. Management of thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease: focus on pharmacotherapeutic strategies[J]. Drugs, 2015, 75(17): 1981-1992. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-015-0480-0. |
| [6] |
YOSHIDA M, TATEISHI R, HIROI S, et al. Changes in platelet counts and thrombocytopenia risk in patients with chronic liver disease with different etiologies using real-world Japanese data[J]. Adv Ther, 2022, 39(2): 992-1003. DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-02008-x. |
| [7] |
HUANG CE, CHANG JJ, WU YY, et al. Different impacts of common risk factors associated with thrombocytopenia in patients with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection[J]. Biomed J, 2022, 45(5): 788-797. DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.09.001. |
| [8] |
SCHARF RE. Thrombocytopenia and hemostatic changes in acute and chronic liver disease: Pathophysiology, clinical and laboratory features, and management[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(7): 1530. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071530. |
| [9] |
GALLO P, TERRACCIANI F, DI PASQUALE G, et al. Thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease: Physiopathology and new therapeutic strategies before invasive procedures[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(30): 4061-4074. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4061. |
| [10] |
LI SS, LIU Q, HUANG LW. Causes of thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2021, 13(2): 24-28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.02.005.
李尚书, 刘群, 黄丽雯. 慢性肝病血小板减少的原因[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(2): 24-28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.02.005.
|
| [11] |
PRADELLA P, BONETTO S, TURCHETTO S, et al. Platelet production and destruction in liver cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 54(5): 894-900. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.08.018. |
| [12] |
KAJIHARA M, KATO S, OKAZAKI Y, et al. A role of autoantibody-mediated platelet destruction in thrombocytopenia in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2003, 37(6): 1267-1276. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50209. |
| [13] |
UEMURA M, FUJIMURA Y, MATSUMOTO M, et al. Comprehensive analysis of ADAMTS13 in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2008, 99(6): 1019-1029. DOI: 10.1160/TH08-01-0006. |
| [14] |
SHAHIDI M. Thrombosis and von willebrand factor[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 906: 285-306. DOI: 10.1007/5584_2016_122. |
| [15] |
BROWN RS Jr. Current management of thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y), 2019, 15(3): 155-157.
|
| [16] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Expert Committee for Prevention and Management of Liver Inflammation. Consensus statement by the expert committee for prevention and management of liver inflammation in China[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2014, 7(1): 4-12. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2014.01.002. |
| [17] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis (2021)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(1): 42-49. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211112-00796 |
| [18] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [19] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hepatitis C(2019 version)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2670-2686. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.008. |
| [20] |
National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(5): 947-957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. |
| [21] |
Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for alcoholic liver disease: a 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(5): 939-946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.006. |
| [22] |
AL-SAMKARI H, SOFF GA. Clinical challenges and promising therapies for chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia[J]. Expert Rev Hematol, 2021, 14(5): 437-448. DOI: 10.1080/17474086.2021.1924053. |
| [23] |
SUN YH, LI L, HOU M, et al. Study on the Specific autoantibody in Nonimmune Thrombocytopenia in Malignant Tumor[J]. Cancer Res Clin, 2005, 17(3): 167-169. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-9801.2005.03.009. |
| [24] |
WANG HP. Adverse reactions associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor in treatment of liver cancer and related treatment measures[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(5): 985-991. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.003. |
| [25] |
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Group of CMA Chinese Society of Hematology. Chinese guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of adult primary immune thrombocytopenia(version 2020)[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2020, 41(8): 617-623. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.08.001. |
| [26] |
Tumor Support and Rehabilitation Therapy Group of CMA Chinese Society of Oncology. Consensus on clinical management of cancer therapy-related thrombocytopenia[J]. Tumor, 2021, 41(12): 812-827. DOI: 10.3781/j.issn.1000-7431.2021.2111-0882. |
| [27] |
National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5.0[M]. Rockville: HHS U S A Department of Health and Human Services, 2017.
|
| [28] |
LI Q, CHEN L, YU XH. Differentiation of bone marrow cell morphology of thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease and primary immune thrombocytopenia[J]. China J Prac Med, 2022, 49(8): 10-12. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115689-20220122-00349. |
| [29] |
Guidelines Working Committee of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer therapy-induced thrombocytopenia[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2022.
中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO) 肿瘤治疗所致血小板减少症诊疗指南2022[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2022.
|
| [30] |
TRIPODI A, PRIMIGNANI M, CHANTARANGKUL V, et al. Thrombin generation in patients with cirrhosis: the role of platelets[J]. Hepatology, 2006, 44(2): 440-445. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21266. |
| [31] |
TRIPODI A, PRIMIGNANI M, CHANTARANGKUL V, et al. Global hemostasis tests in patients with cirrhosis before and after prophylactic platelet transfusion[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33(3): 362-367. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12038. |
| [32] |
NORTHUP PG, FRIEDMAN LS, KAMATH PS. AGA clinical practice update on surgical risk assessment and perioperative management in cirrhosis: expert review[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17(4): 595-606. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.043. |
| [33] |
O'SHEA RS, DAVITKOV P, KO CW, et al. AGA clinical practice guideline on the management of coagulation disorders in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161(5): 1615-1627. e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.015. |
| [34] |
SCHIFFER CA, BOHLKE K, DELANEY M, et al. Platelet transfusion for patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(3): 283-299. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.1734. |
| [35] |
KUTER DJ. Treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with non-hematologic malignancies[J]. Haematologica, 2022, 107(6): 1243-1263. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.279512. |
| [36] |
YANG G, HUANG R, YANG S, et al. Effect of postdose fasting duration on hetrombopag olamine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 86(8): 1528-1536. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.14259. |
| [37] |
TERRAULT N, CHEN YC, IZUMI N, et al. Avatrombopag before procedures reduces need for platelet transfusion in patients with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155(3): 705-718. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.025. |
| [38] |
AFDHAL NH, GIANNINI EG, TAYYAB G, et al. Eltrombopag before procedures in patients with cirrhosis and thrombocytopenia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 367(8): 716-724. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110709. |
| [39] |
MOUSSA MM, MOWAFY N. Preoperative use of romiplostim in thrombocytopenic patients with chronic hepatitis C and liver cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28(2): 335-341. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07246.x. |
| [40] |
LINDQUIST I, OLSON SR, LI A, et al. The efficacy and safety of thrombopoietin receptor agonists in patients with chronic liver disease undergoing elective procedures: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Platelets, 2022, 33(1): 66-72. DOI: 10.1080/09537104.2020.1859102. |
| [41] |
KUTER DJ. Milestones in understanding platelet production: a historical overview[J]. Br J Haematol, 2014, 165(2): 248-258. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12781. |
| [42] |
ZHANG J, ZHOU XM. Administration of recombinant human thrombopoietin before operation in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and thrombocytopenia[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2020, 23(4): 552-555. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.04.025. |
| [43] |
FENG R, LIU Y, ZHU XL, et al. Recombinant human thrombopoietin increases platelet count in severe thrombocytopenic patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis: Multicentre real-world observational study[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29(5): 306-316. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13655. |
| [44] |
Inc P. NEUMEGA Instrument[EB/OL]. https://www.pfizer.com/products/product-de-tail/neumega.
|
| [45] |
Qilu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Package insert for recombinant human interleukin 11 for injection[EB/OL]. https://www.qilu-pharma.com/products_details/975814351594020864.html.
齐鲁制药有限公司. 注射用重组人白介素11说明书[EB/OL]. https://www.qilu-pharma.com/products_details/975814351594020864.html.
|
| [46] |
LIU BW, XIANG HL, LIANG J, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of recombinant human interleukin-11 and recombinant human thrombopoietin in the treating thrombocytopenia with hypersplenism in cirrhotic patients[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24(34): 4608-4614. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i34.4608. 刘保文, 向慧玲, 梁静, 等. 重组人白介素-11及重组人血小板生成素在治疗肝硬化脾功能亢进所致血小板减少的疗效对比[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24(34): 4608-4614. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i34.4608. |
| [47] |
QIAN JD, YAO TT, WANG Y, et al. Management strategies for chronic liver disease-related thrombocytopenia[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2021, 29(9): 896-899. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200609-00304. |
| [48] |
OGATA T, OKUDA K, SATO T, et al. Long-term outcome of splenectomy in advanced cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and thrombocytopenia[J]. Kurume Med J, 2013, 60(2): 37-45. DOI: 10.2739/kurumemedj.ms62010. |
| [49] |
KIM NH, KIM HJ, CHO YK, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of partial splenic embolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with thrombocytopenia who underwent transarterial chemoembolization[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2019, 34(30): e208. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e208. |
| [50] |
FENG K, MA K, LIU Q, et al. Randomized clinical trial of splenic radiofrequency ablation versus splenectomy for severe hypersplenism[J]. Br J Surg, 2011, 98(3): 354-361. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.7367. |
| [51] |
SHI XB, FENG JK, WANG JH, et al. Does splenectomy significantly improve the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with hypersplenism? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(8): 641. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-6748. |
| [52] |
WU Y, LI H, ZHANG T, et al. Splanchnic vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis after splenectomy or splenic artery embolization: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. Adv Ther, 2021, 38(4): 1904-1930. DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-01652-7. |
| [53] |
WANG Q, DANG T, MENG X, et al. Is concomitant splenectomy necessary in radical gastric cancer surgery? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2019, 15(2): e28-e35. DOI: 10.1111/ajco.13052. |
| [54] |
WANG JX, WEI FX, XIE WQ, et al. Recent understandings of splenectomy for hypersplenism in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2022, 31 (1): 123-131. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2022.01.014. |
| [55] |
CAO SS, GUAN Y, ZHANG XF, et al. Literature analysis of adverse drug reaction induced by thrombopoietin receptor agonists[J]. Chin J Drug Appl Monit, 2022, 19(1): 34-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8157.2022.01.010. |
| [56] |
GHANIMA W, COOPER N, RODEGHIERO F, et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists: ten years later[J]. Haematologica, 2019, 104(6): 1112-1123. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2018.212845. |
| [57] |
HERMANN E, FERDJALLAH A. Eltrombopag-induced metabolic acidosis and hepatic encephalopathy in pediatric ITP[J]. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol, 2022, 44(2): e453-e455. DOI: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000002300. |
| [58] |
Novartis Pharma Schwei AG. Instructions for Eltrombopag Olamine Tablets[EB/OL]. [2017-12-28]. https://zy.yaozh.com/instruct/sms20200619/2020060202.pdf.
|
| [59] |
XU WW, YANG L, GE JJ, et al. Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of rhIL-11 and rhTPO in the treatment of Thrombocytopenia caused by chemotherapy[J]. Systems Med, 2016, 1(12): 121-123. DOI: 10.19368/j.cnki.2096-1782.2016.12.121. |
| [60] |
YU J, DAI XF, LIU L, et al. Clinical studies of recombinant human thrombopoietin in treatment of gemzar and cisplatin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat, 2009, 16(5): 374-376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL200905019.htm |
| [61] |
HOU M, LI M, JIN Z, et al. Post-marketing study of recombinant human thrombopoietin injection for adverse drug reaction monitoring[J]. Chin J New Drugs Clin Remed, 2015, 34(8): 642-646. DOI: 10.14109/j.cnki.xyylc.2015.08.018. |
| [62] |
DAI XF, YU J, LIU L, et al. Value of recombinant human thrombopoietin in the treatmeat of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with solid tumor[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2008, 30(8): 623-625. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3766.2008.08.016. |
| [63] |
CSCO Anti-Lymphoma Alliance, CACA Committee of Cancer Rehabilitation and Palliative Care, Haematology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Chinese expert consensus on clinical application of recombinant human interleukin-11 in the treatment of thrombocytopenia (2018 edition)[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2018, 23(3): 260-266. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2018.03.014. |
| [64] |
TSOCHATZIS EA, SENZOLO M, GERMANI G, et al. Systematic review: portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 31(3): 366-374. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04182.x. |
| [65] |
CHEN H, TRILOK G, WANG F, et al. A single hospital study on portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients - clinical characteristics & risk factors[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2014, 139(2): 260-266.
|
| [66] |
FONT C, FARRU'S B, VIDAL L, et al. Incidental versus symptomatic venous thrombosis in cancer: a prospective observational study of 340 consecutive patients[J]. Ann Oncol, 2011, 22(9): 2101-2106. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdq720. |
| [67] |
Hepatobiliary Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus for management of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis(2020, Shanghai)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(12): 2667-2674. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.007. |
| [68] |
FALANGA A, LEADER A, AMBAGLIO C, et al. EHA guidelines on management of antithrombotic treatments in thrombocytopenic patients with cancer[J]. Hemasphere, 2022, 6(8): e750. DOI: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000750. |
| [69] |
Guidelines Working Committee of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thrombosis in Cancer Patients[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2020.
中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)肿瘤患者静脉血栓防治指南2020[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020.
|
| [70] |
SHEN T, LIU Y, SHANG J, et al. Incidence and etiology of drug-induced liver injury in mainland China[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(8): 2230-2241. e11. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.002. |
| [71] |
RUBBIA-BRANDT L, AUDARD V, SARTORETTI P, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2004, 15(3): 460-466. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh095. |
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
de LÉDINGHEN V, VILLATE A, ROBIN M, et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2020, 44(4): 480-485. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2020.03.019. |
| [74] |
ZHAO S, LAI RT, XIE Q. Diagnosis and clinical management of treatment-related toxicity with checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2020, 25(5): 451-455. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2020.05.002. |
| [75] |
Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. LiveTox: Clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury[EB/OL]. [2017-6-1]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547897/.
|
| [76] |
MCDONALD GB, FRESTON JW, BOYER JL, et al. Liver complications following treatment of hematologic malignancy with anti-CD22-calicheamicin (Inotuzumab Ozogamicin)[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(2): 831-844. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30222. |
| [77] |
JIANG LG, MENG HY, ZHANG HJ. Advances in research of radiation-induced liver damage[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2017, 25(20): 1811-1818. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v25.i20.1811. |
| [78] |
WEYCKER D, HATFIELD M, GROSSMAN A, et al. Risk and consequences of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in US clinical practice[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 151. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5354-5. |
| [79] |
CRIST M, HANSEN E, CHABLANI L, et al. Examining the bleeding incidences associated with targeted therapies used in metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2017, 120: 151-162. DOI: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.10.014. |
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
HADDAD TC, ZHAO S, LI M, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related thrombocytopenia: incidence, risk factors and effect on survival[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2022, 71(5): 1157-1165. DOI: 10.1007/s00262-021-03068-2. |
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Medical Association Publishing House, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, et al. Guideline for primary care of drug-induced liver injury (2019)[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2020, 19(10): 868-875. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200812-00900. |
| [84] |
BENCARDINO K, MAURI G, AMATU A, et al. Oxaliplatin immune-induced syndrome occurs with cumulative administration and rechallenge: Single institution series and systematic review study[J]. Clin Colorectal Cancer, 2016, 15(3): 213-221. DOI: 10.1016/j.clcc.2016.02.001. |
| [85] |
JÁCOME AA, OHINATA A, MAHVASH A, et al. Bevacizumab does not influence the efficacy of partial splenic embolization in the management of chemotherapy-induced hypersplenism[J]. Clin Colorectal Cancer, 2020, 19(4): e189-e199. DOI: 10.1016/j.clcc.2020.04.007. |
| [86] |
OVERMAN MJ, FERRAROTTO R, RAGHAV K, et al. The addition of bevacizumab to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy: impact upon hepatic sinusoidal injury and thrombocytopenia[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2018, 110(8): 888-894. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djx288. |
| [87] |
QDAISAT A, YEUNG SJ, ROJAS HERNANDEZ CH, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of intracranial hemorrhage in cancer patients visiting the emergency department[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(3): 643. DOI: 10.3390/jcm11030643. |





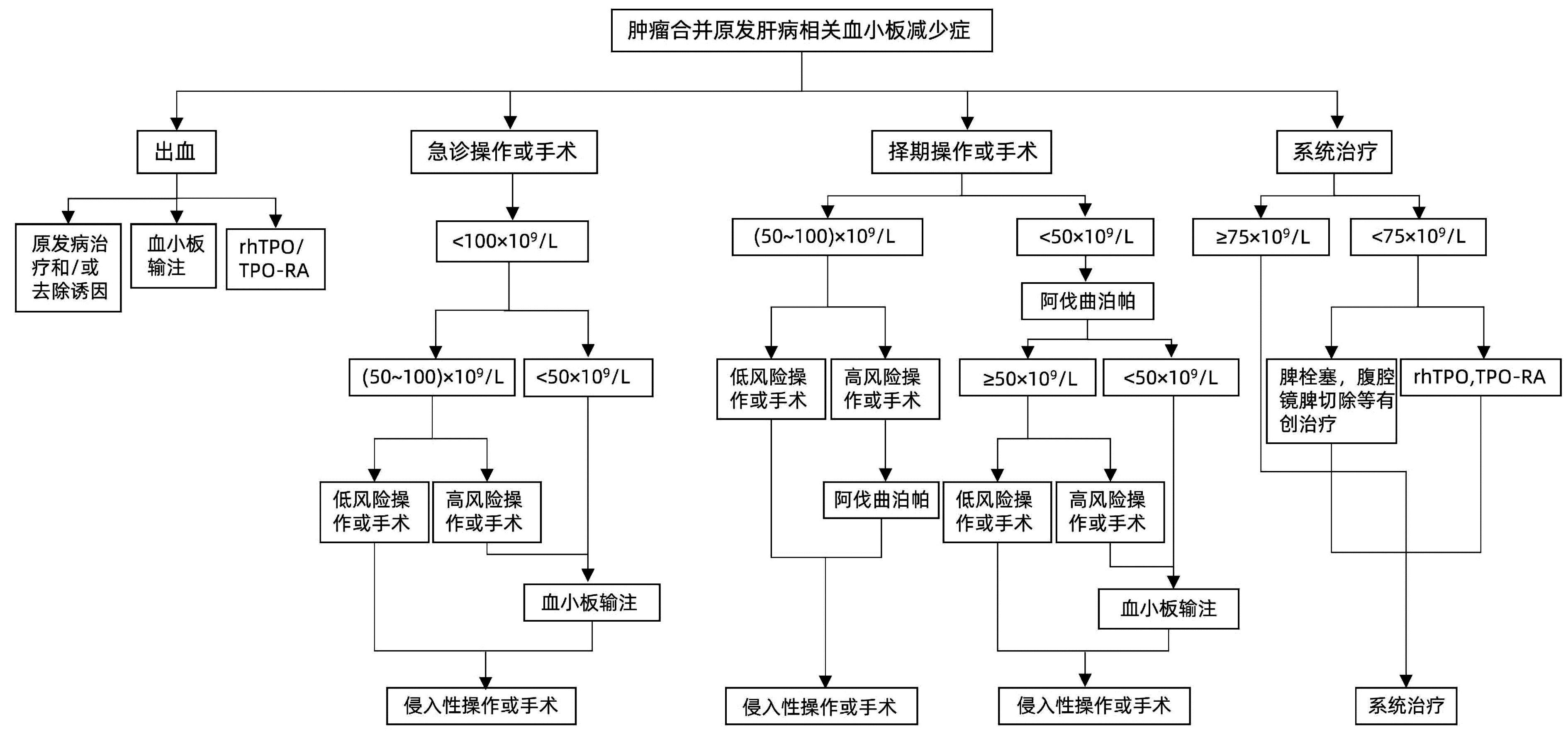




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
