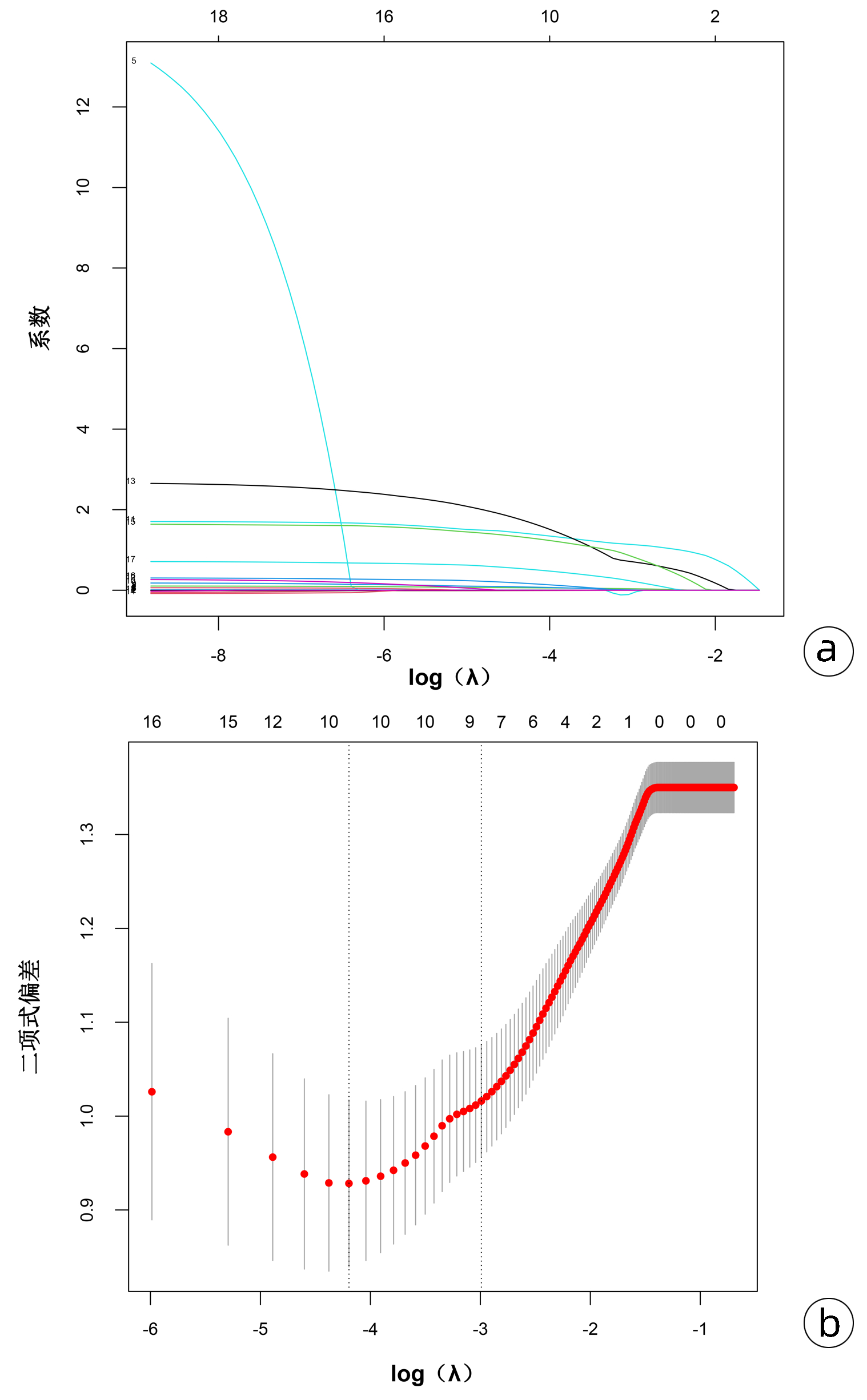
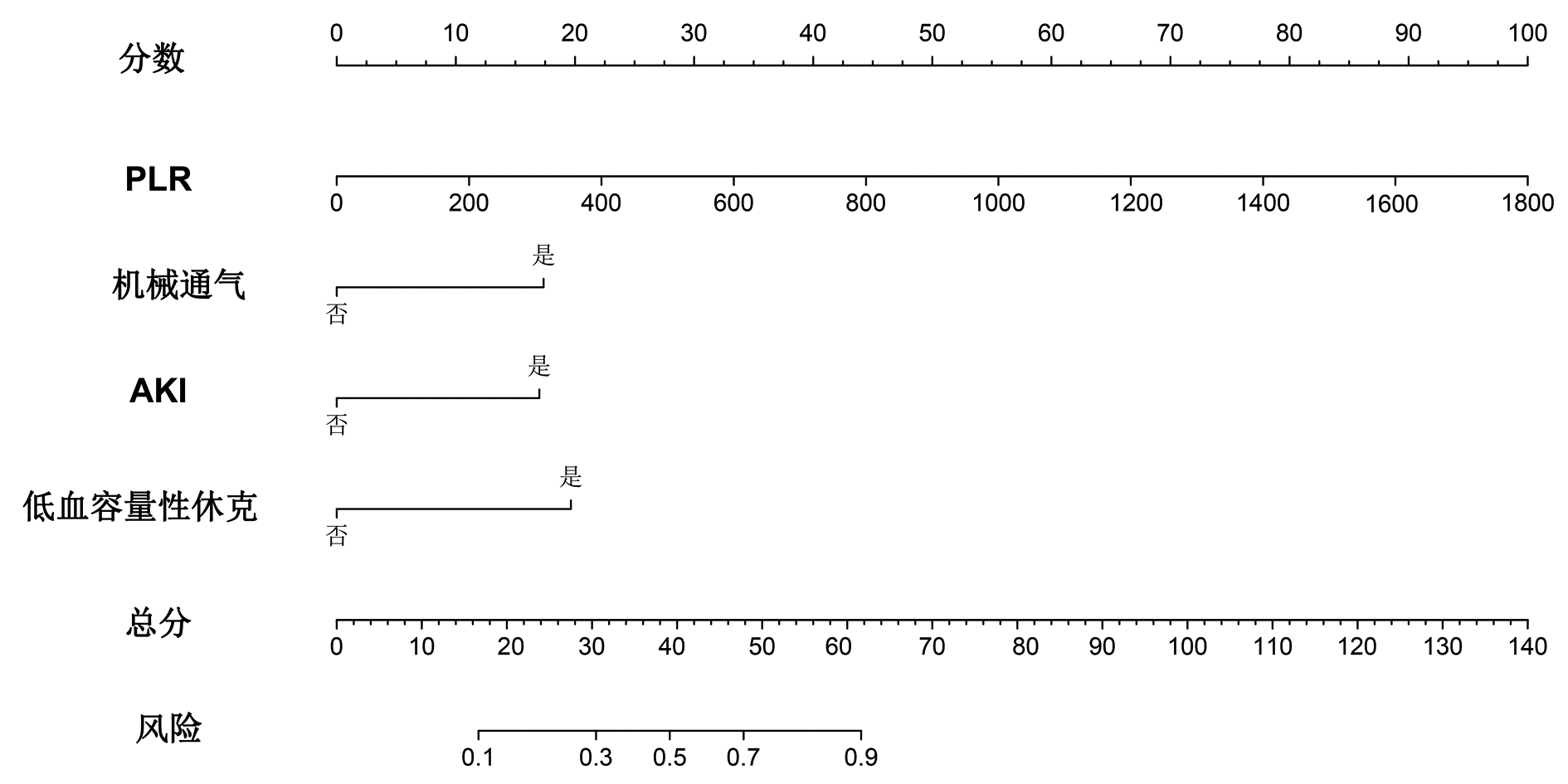
| [1] |
VANZANT EL, LOPEZ CM, OZRAZGAT-BASLANTI T, et al. Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome after severe blunt trauma[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2014, 76(1): 21-29. DOI: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3182ab1ab5. |
| [2] |
GENTILE LF, CUENCA AG, EFRON PA, et al. Persistent inflammation and immunosuppression: a common syndrome and new horizon for surgical intensive care[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2012, 72(6): 1491-1501. DOI: 10.1097/TA.0b013e318256e000. |
| [3] |
MIRA JC, GENTILE LF, MATHIAS BJ, et al. Sepsis pathophysiology, chronic critical illness, and persistent inflammation-immunosuppression and catabolism syndrome[J]. Crit Care Med, 2017, 45(2): 253-262. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002074. |
| [4] |
NAKAMURA K, OGURA K, NAKANO H, et al. C-reactive protein clustering to clarify persistent inflammation, immunosuppression and catabolism syndrome[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2020, 46(3): 437-443. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-019-05851-3. |
| [5] |
EFRON PA, MOHR AM, BIHORAC A, et al. Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism and the development of chronic critical illness after surgery[J]. Surgery, 2018, 164(2): 178-184. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.04.011. |
| [6] |
XU D, XUN J. Persistentinflammation-immunosuppression-catabolism syndrome in severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J Chin Pract Diagn Ther, 2018, 32(7): 725-728. DOI: 10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2018.07.030. |
| [7] |
YANG R, DU LL, ZHANG ZD, et al. Clinical observation of severe patients with persistent inflammation immunosuppression catabolism syndrome[J]. China J Emerg Resuscitation Disaster Med, 2021, 16(8): 919-921. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6966.2021.08.021. |
| [8] |
KOUPENOVA M, CLANCY L, CORKREY HA, et al. Circulating platelets as mediators of immunity, inflammation, and thrombosis[J]. Circ Res, 2018, 122(2): 337-351. DOI: 10.1161/circresaha.117.310795. |
| [9] |
ZHOU H, MEI X, HE X, et al. Severity stratification and prognostic prediction of patients with acute pancreatitis at early phase: A retrospective study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(16): e15275. DOI: 10.1097/md.0000000000015275. |
| [10] |
HAWKINS RB, RAYMOND SL, STORTZ JA, et al. Chronic critical illness and the persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1511. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01511. |
| [11] |
CHEN MY, CHEN MX, WANG MX, et al. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in severe acute pancreatitis: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2022, 25(30): 3834-3842. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0452. |
| [12] |
WANG X, ZHUANG X, WEI R, et al. Protective effects of Acanthopanax vs. Ulinastatin against severe acute pancreatitis-induced brain injury in rats[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2015, 24(2): 285-298. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.12.020. |
| [13] |
WANG Y, QI WJ, ZENG YW, et al. Mechanism of action of magnolol in the treatment of acute lung injury in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(12): 2782-2787. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.028. |
| [14] |
WANG X, WANG XK, CEN RF, et al. Influence of Xuebijing injection on clinical effects and cellular immune function of patients with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J New Drugs Clin Rem, 2015, 34(6): 476-479. DOI: 10.14109/j.cnki.xyylc.2015.06.016. |
| [15] |
WANG P, LI L, LAN D, et al. Effects of hemofiltration therapy on biochemical indexes, liver and kidney function and inflammatory factors in patients with severe acute pancreatitis complicated with abdominal compartment syndrome[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2022, 21(4): 384-388. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.04.014. |
| [16] |
SU HY, MO ZX, CHEN R, et al. Effect of thymosin α1 on immunity, metabolism and prognosis in elderly patients with sepsis followed by persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome[J]. J Pract Med, 2018, 34(1): 119-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2018.01.030. |
| [17] |
LUBBERS T, KOX M, DE HAAN JJ, et al. Continuous administration of enteral lipid- and protein-rich nutrition limits inflammation in a human endotoxemia model[J]. Crit Care Med, 2013, 41(5): 1258-1265. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827c0a17. |
| [18] |
ZHU X, PRIBIS JP, RODRIGUEZ PC, et al. The central role of arginine catabolism in T-cell dysfunction and increased susceptibility to infection after physical injury[J]. Ann Surg, 2014, 259(1): 171-178. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828611f8. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: