| [1] |
ZHANG J, WANG X, VIKASH V, et al. ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 4350965. DOI: 10.1155/2016/4350965. |
| [2] |
RAMÍREZ A, VÁZQUEZ-SÁNCHEZ AY, CARRIÓN-ROBALINO N, et al. Ion channels and oxidative stress as a potential link for the diagnosis or treatment of liver diseases[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 3928714. DOI: 10.1155/2016/3928714. |
| [3] |
HE F, GUO FC, LI Z, et al. Myeloid-specific disruption of recombination signal binding protein Jκ ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by attenuating inflammation through cylindromatosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(1): 303-314. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27394. |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
ZHENG RL, HUANG ZY. Free Radical Biology(The Third Edition)[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007: 201-203.
郑荣梁, 黄中洋. 自由基生物学(第三版)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007: 201-203.
|
| [6] |
NOGUEIRAS R, HABEGGER KM, CHAUDHARY N, et al. Sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3: physiological modulators of metabolism[J]. Physiol Rev, 2012, 92(3): 1479-1514. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2011. |
| [7] |
SÁNCHEZ-VALLE V, CHÁVEZ-TAPIA NC, URIBE M, et al. Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: a review[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2012, 19(28): 4850-4860. DOI: 10.2174/092986712803341520. |
| [8] |
WILLEMS PH, ROSSIGNOL R, DIETEREN CE, et al. Redox homeostasis and mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 22(2): 207-218. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.06.006. |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
LYU YH, WU SS, WANG ZC, et al. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine regulating reactive oxygen species(ROS) against liver fibrosis[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 39(6): 117-121. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717. |
| [11] |
GUO R, YAN M. Cellular and molecular mechanism of liver fibrosis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2012, 4(4): 57-62.
郭蓉, 阎明. 肝纤维化的细胞和分子机制研究进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2012, 4(4): 57-62.
|
| [12] |
ZHAO J, QI YF, YU YR. Research advances in the role of oxidative stress in the development and progression of liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(9): 2067-2071. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.040.
|
| [13] |
PAIK YH, KIM J, AOYAMA T, et al. Role of NADPH oxidases in liver fibrosis[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2014, 20(17): 2854-2872. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5619. |
| [14] |
URTASUN R, CONDE DE LA ROSA L, NIETO N. Oxidative and nitrosative stress and fibrogenic response[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2008, 12(4): 769-790, ⅷ. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2008.07.005. |
| [15] |
SCAMBLER T, JAROSZ-GRIFFITHS HH, LARA-REYNA S, et al. ENaC-mediated sodium influx exacerbates NLRP3-dependent inflammation in cystic fibrosis[J]. Elife, 2019, 8: e49248. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.49248. |
| [16] |
ZHANG K, LIN L, ZHU Y, et al. Saikosaponin d alleviates liver fibrosis by negatively regulating the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome through activating the ERβ pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 894981. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.894981. |
| [17] |
YI J, WU S, TAN S, et al. Berberine alleviates liver fibrosis through inducing ferrous redox to activate ROS-mediated hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 374. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00768-7. |
| [18] |
GAN D, ZHANG W, HUANG C, et al. Ursolic acid ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis through the NOXs/ROS pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(10): 6799-6813. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.26541. |
| [19] |
CHUNG HK, KIM YK, PARK JH, et al. The indole derivative NecroX-7 improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in ob/ob mice through suppression of mitochondrial ROS/RNS and inflammation[J]. Liver Int, 2015, 35(4): 1341-1353. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12741. |
| [20] |
LIU YY, LI L, LI XW, et al. Research progress of microRNAs in TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. World Latest Medicine Information, 2018, 18(A5): 115-116, 119. DOI: 10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2018.105.054. |
| [21] |
SU P, FENG SS, LI QW. Research progress of the structure and function of NF-κB and IκB in different animal groups[J]. Yi Chuan, 2016, 38(6): 523-531. DOI: 10.16288/j.yczz.15-509. |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
SHEN H, SHENG L, CHEN Z, et al. Mouse hepatocyte overexpression of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) triggers fatal macrophage-dependent liver injury and fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60(6): 2065-2076. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27348. |
| [24] |
ZHU H, PING J, XU LM. Role of the nuclear factor - kappa B signaling pathway on the progress of hepatic fibrosis and the anti-fibroticmechanism of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(4): 858-861. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.04.035. |
| [25] |
ABBAS N, GETACHEW A, YOU K, et al. Kupffer cells mediate the recruitment of hepatic stellate cells into the localized liver damage[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 529(2): 474-479. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.041. |
| [26] |
MA L, ZHAO Y, WU HY, et al. Expression of TLR4 /MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B virus and its clinical significance[J]. Chin J Mod Med, 2021, 31(2): 72-77. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2021.21.012. |
| [27] |
CUI DL. The roles of NF-κB in liver fibrosis[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2010.
崔东来. 抑制NF-κB诱导肝星状细胞凋亡[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2010.
|
| [28] |
CHEN JY, HAO FY, LIN JQ, et al. The effect of carvedilol on the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway in an animal model of liver fibrosis and its anti-liver fibrosis mechanism[J]. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 2021, 44(7): 771-776. DOI: 10.3639/j.issn.1009-5551.2021.07.002. |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
REEVES HL, FRIEDMAN SL. Activation of hepatic stellate cells—a key issue in liver fibrosis[J]. Front Biosci, 2002, 7: d808-d826. DOI: 10.2741/reeves. |
| [31] |
FENG XY, HE PL, ZHAO W, et al. Effects of Panax notoginseng total saponins on improving nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats and NO/iNOS/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Chin Tradit Patent Med, 2021, 43(1): 50-55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.01.010. |
| [32] |
TANG H, ZENG Q, REN N, et al. Kaempferide improves oxidative stress and inflammation by inhibiting the TLR4/IκBα/NF-κB pathway in obese mice[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2021, 24(4): 493-498. DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2021.52690.11892. |
| [33] |
LIU F, FENG M, XING J, et al. Timosaponin alleviates oxidative stress in rats with high fat diet-induced obesity via activating Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 909: 174377. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174377. |
| [34] |
LI J, WANG T, LIU P, et al. Hesperetin ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE pathway in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and a rat model of high-fat diet-induced NAFLD[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(9): 3898-3918. DOI: 10.1039/d0fo02736g. |
| [35] |
CHEN X, DING C, LIU W, et al. Abscisic acid ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis by regulating the NF-кB signaling pathway in mice[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 891: 173652. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173652. |
| [36] |
RODRÍGUEZ MJ, SABAJ M, TOLOSA G, et al. Maresin-1 prevents liver fibrosis by targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(12): 3406. DOI: 10.3390/cells10123406. |
| [37] |
ZAGHLOUL RA, ZAGHLOUL AM, EL-KASHEF DH. Hepatoprotective effect of Baicalin against thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis in rats: Targeting NOX4/NF-κ B/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 295: 120410. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120410. |
| [38] |
CHEN Y, ZHAO C, LIU X, et al. Plumbagin ameliorates liver fibrosis via a ROS-mediated NF-кB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 116: 108923. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108923. |
| [39] |
de SOUZA BASSO B, HAUTE GV, ORTEGA-RIBERA M, et al. Methoxyeugenol deactivates hepatic stellate cells and attenuates liver fibrosis and inflammation through a PPAR-γ and NF-kB mechanism[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 280: 114433. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114433. |
| [40] |
LIU Y, KUANG Q, DAI X, et al. Deficiency in Inactive Rhomboid Protein2 (iRhom2) alleviates alcoholic liver fibrosis by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(14): 7701. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23147701. |
| [41] |
YE L, CHEN T, CAO J, et al. Short hairpin RNA attenuates liver fibrosis by regulating the PPAR-γ and NF-κB pathways in HBV induced liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Int J Oncol, 2020, 57(5): 1116-1128. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5125. |
| [42] |
SUN X, HUANG X, ZHU X, et al. HBOA ameliorates CCl4-incuded liver fibrosis through inhibiting TGF-β1/Smads, NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 115: 108901. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108901. |



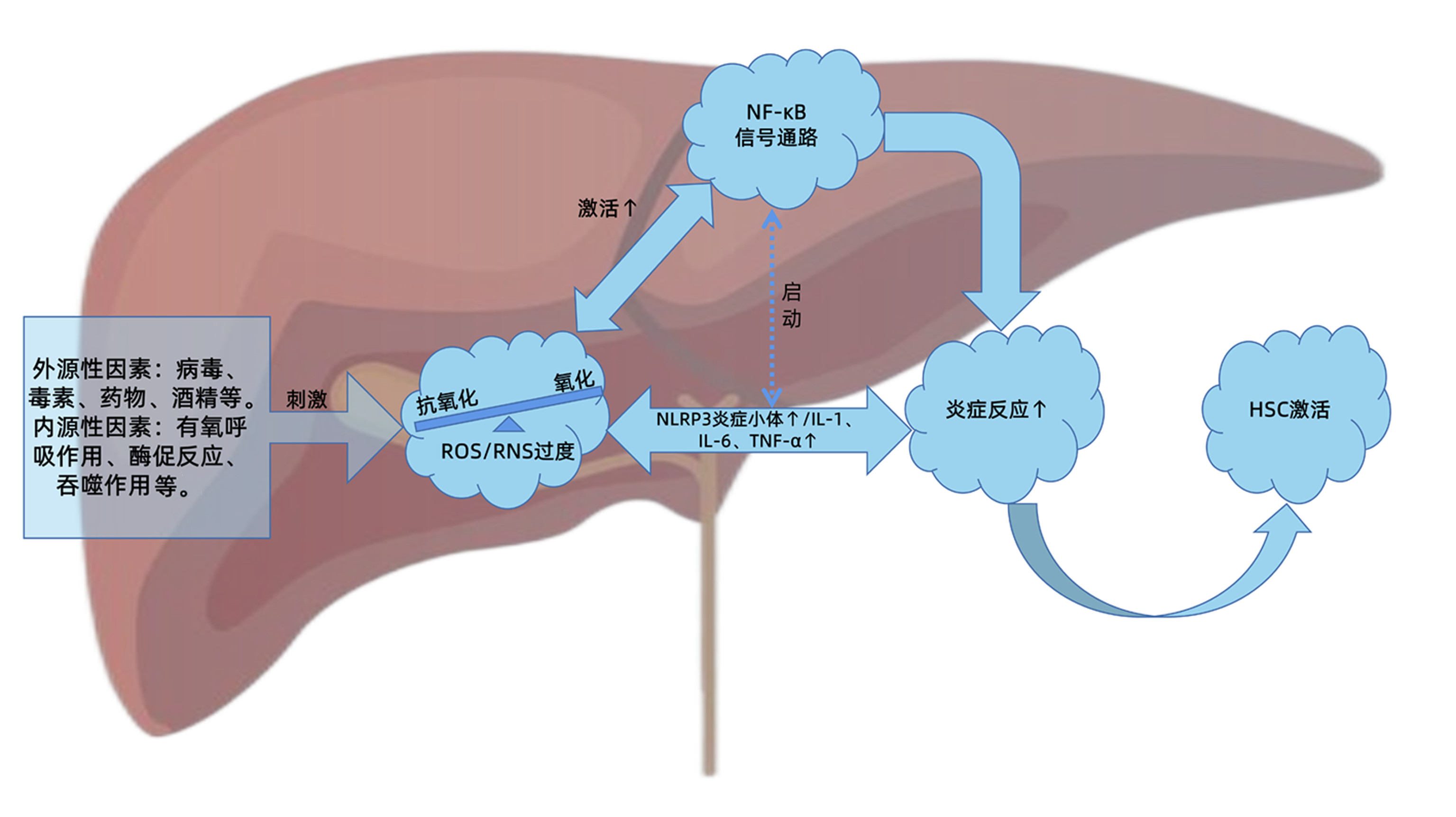




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: