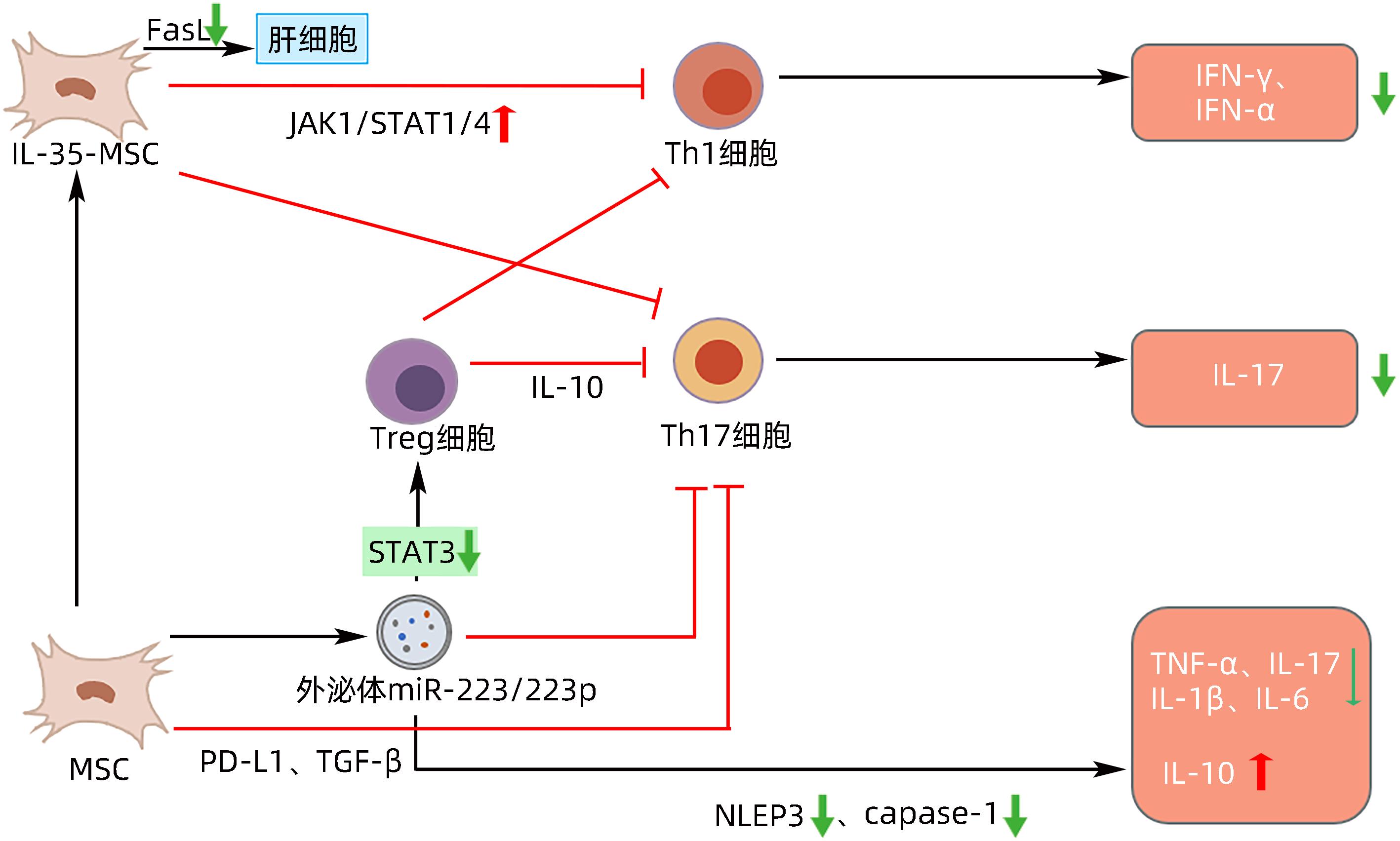
| [1] |
CARDON A, CONCHON S, RENAND A. Mechanisms of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2021, 37( 2): 79- 85. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000704. |
| [2] |
DALEKOS GN, SAMAKIDOU A, LYBEROPOULOU A, et al. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Pol Arch Intern Med, 2022, 132( 9): 16334. DOI: 10.20452/pamw.16334. |
| [3] |
OLIVAS I, RODRÍGUEZ-TAJES S, LONDOÑO MC. Autoimmune hepatitis: Challenges and novelties[J]. Med Clin, 2022, 159( 6): 289- 298. DOI: 10.1016/j.medcli.2022.04.004. |
| [4] |
HU CX, WU ZW, LI LJ. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote liver regeneration through regulation of immune cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2020, 16( 5): 893- 903. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.39725. |
| [5] |
HADE MD, SUIRE CN, SUO ZC. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Applications in regenerative medicine[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 8): 1959. DOI: 10.3390/cells10081959. |
| [6] |
CAI H, GUO HD. Mesenchymal stem cells and their exocytotic vesicles[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 3): 2085. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032085. |
| [7] |
JIANG W, XU JY. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Cell Prolif, 2020, 53( 1): e12712. DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12712. |
| [8] |
MISHRA VK, SHIH HH, PARVEEN F, et al. Identifying the therapeutic significance of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 5): 1145. DOI: 10.3390/cells9051145. |
| [9] |
HARRELL CR, DJONOV V, VOLAREVIC V. The cross-talk between mesenchymal stem cells and immune cells in tissue repair and regeneration[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 5): 2472. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052472. |
| [10] |
LIU JX, GAO JF, LIANG ZX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their microenvironment[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13( 1): 429. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02985-y. |
| [11] |
KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology , function , and biomedical applications of exosomes[J]. Science, 2020, 367( 6478): eaau6977. DOI: 10.1126/science.aau6977. |
| [12] |
LAKSHMI KAVYA ANV, SUBRAMANIAN S, RAMAKRISHNA S. Therapeutic applications of exosomes in various diseases: A review[J]. Biomater Adv, 2022, 134: 112579. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112579. |
| [13] |
ZHOU XN, KALLURI R. Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes[J]. Cancer Sci, 2020, 111( 9): 3100- 3110. DOI: 10.1111/cas.14563. |
| [14] |
LEI YG, YAO J, ZHENG J, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cel-derived extracellular vesicles enhance the recenerative capability of fibrotic liver[J]. Organ Transplant, 2023, 14( 3): 379- 388. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2023.03.009. |
| [15] |
JIANG LR, ZHANG SQ, HU HZ, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute liver failure by reducing the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 508( 3): 735- 741. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.189. |
| [16] |
RONG XL, LIU JZ, YAO X, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10( 1): 98. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1204-2. |
| [17] |
TERZIROLI BERETTA-PICCOLI B, MIELI-VERGANI G, VERGANI D. Autoimmmune hepatitis[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19( 2): 158- 176. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00768-8. |
| [18] |
BOVENSIEPEN CS, SCHAKAT M, SEBODE M, et al. TNF-producing Th1 cells are selectively expanded in liver infiltrates of patients with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 203( 12): 3148- 3156. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900124. |
| [19] |
DI GIORGIO A, VERGANI D, MIELI-VERGANI G. Cutting edge issues in juvenile sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2022, 54( 4): 417- 427. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.06.028. |
| [20] |
HE Y, HWANG S, AHMED YA, et al. Immunopathobiology and therapeutic targets related to cytokines in liver diseases[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 1): 18- 37. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-00580-w. |
| [21] |
EGGENHUIZEN PJ, NG BH, OOI JD. Treg enhancing therapies to treat autoimmune diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 19): 7015. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197015. |
| [22] |
ZHANG WQ, LIU X, ZHU YC, et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of Th17/Treg balance in health and disease[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2021, 51( 9): 2137- 2150. DOI: 10.1002/eji.202048794. |
| [23] |
BEHAIRY BE, EL-ARABY HA, KADER HH ABD EL, et al. Assessment of intrahepatic regulatory T cells in children with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2016, 15( 5): 682- 690. DOI: 10.5604/16652681.1212319. |
| [24] |
DIESTELHORST J, JUNGE N, SCHLUE J, et al. Pediatric autoimmune hepatitis shows a disproportionate decline of regulatory T cells in the liver and of IL-2 in the blood of patients undergoing therapy[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12( 7): e0181107. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181107. |
| [25] |
KIMURA N, YAMAGIWA S, SUGANO T, et al. Possible involvement of chemokine C-C receptor 7 - programmed cell death-1 + follicular helper T-cell subset in the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33( 1): 298- 306. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13844. |
| [26] |
HE CM, YANG YL, ZHENG KY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based treatment in autoimmune liver diseases: Underlying roles, advantages and challenges[J]. Ther Adv Chronic Dis, 2021, 12: 2040622321993442. DOI: 10.1177/2040622321993442. |
| [27] |
CHEN Y, CHEN S, LIU LY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune hepatitis by activation of the programmed death 1 pathway[J]. Immunol Lett, 2014, 162( 2 Pt B): 222- 228. DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.10.021. |
| [28] |
KIM JY, PARK M, KIM YH, et al. Tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells(T-MSCs) prevent Th17-mediated autoimmune response via regulation of the programmed death-1/programmed death ligand-1(PD-1/PD-L1) pathway[J]. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2018, 12( 2): e1022- e1033. DOI: 10.1002/term.2423. |
| [29] |
XU F, FEI ZY, DAI HX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles with high PD-L1 expression for autoimmune diseases treatment[J]. Adv Mater, 2022, 34( 1): e2106265. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202106265. |
| [30] |
GU YZ, XUE Q, CHEN YJ, et al. Different roles of PD-L1 and FasL in immunomodulation mediated by human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Hum Immunol, 2013, 74( 3): 267- 276. DOI: 10.1016/j.humimm.2012.12.011. |
| [31] |
YANG LL, JIA SN, SHAO X, et al. Interleukin-35 modulates the balance between viral specific CD4 +CD25 +CD127 dim/- regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Virol J, 2019, 16( 1): 48. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-019-1158-0. |
| [32] |
WANG W, GUO H, LI HY, et al. Interleukin-35 gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells protect concanavalin A-induced fulminant hepatitis by decreasing the interferon gamma level[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2018, 29( 2): 234- 241. DOI: 10.1089/hum.2017.171. |
| [33] |
WANG K, SHI YJ, SONG ZL, et al. Regulatory effect of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on Treg/Th17 immune balance in vitro[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 21( 5): 2123- 2130. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11019. |
| [34] |
CHEN QH, WU F, LIU L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells regulate the Th17/Treg cell balance partly through hepatocyte growth factor in vitro[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11( 1): 91. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-01612-y. |
| [35] |
LIU XX, REN SD, QU XB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit Th17 cells differentiation via IFN-γ-mediated SOCS 3 activation[J]. Immunol Res, 2015, 61( 3): 219- 229. DOI: 10.1007/s12026-014-8612-2. |
| [36] |
KIM SH, JUNG J, CHO KJ, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells on T cells by regulation of FoxP3 expression[J]. Int J Stem Cells, 2018, 11( 2): 196- 204. DOI: 10.15283/ijsc18031. |
| [37] |
MELIEF SM, SCHRAMA E, BRUGMAN MH, et al. Multipotent stromal cells induce human regulatory T cells through a novel pathway involving skewing of monocytes toward anti-inflammatory macrophages[J]. Stem Cells, 2013, 31( 9): 1980- 1991. DOI: 10.1002/stem.1432. |
| [38] |
HEIDARI M, POUYA S, BAGHAEI K, et al. The immunomodulatory effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned medium in chronic colitis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233( 11): 8754- 8766. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.26765. |
| [39] |
SHEN ZW, HUANG W, LIU J, et al. Effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on autoimmune diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 749192. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.749192. |
| [40] |
LU FB, CHEN DZ, CHEN L, et al. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice with bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-223-3p[J]. Mol Cells, 2019, 42( 12): 906- 918. DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2019.2283. |
| [41] |
ZHAO JW, LI Y, JIA RR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as dexamethasone delivery vehicles for autoimmune hepatitis therapy[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2021, 9: 650376. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.650376. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: