| [1] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of primary sclerosing cholangitis(2021)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 50- 61. DOI: 10.3760/cma. j. cnl12138-20211109-0078.
中华医学会肝病学分会. 原发性硬化性胆管炎诊断及治疗指南(2021)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 1): 50- 61. DOI: 10.3760/ cma. j. cnl12138-20211109-00786.
|
| [2] |
POCH T, KRAUSE J, CASAR C, et al. Single-cell atlas of hepatic T cells reveals expansion of liver-resident naive-like CD4 + T cells in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 2): 414- 423. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.016. |
| [3] |
CHEN Y, TIAN Z. Innate lymphocytes: pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of liver diseases and cancer[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 1): 57- 72. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-00561-z. |
| [4] |
BERINGER A, MIOSSEC P. IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells and liver diseases, with focus on autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2018, 17( 12): 1176- 1185. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.06.008. |
| [5] |
KUNZMANN LK, SCHOKNECHT T, POCH T, et al. Monocytes as potential mediators of pathogen-induced T-helper 17 differentiation in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis(PSC)[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 4): 1310- 1326. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31140. |
| [6] |
JEFFERY HC, HUNTER S, HUMPHREYS EH, et al. Bidirectional cross-talk between biliary epithelium and Th17 cells promotes local Th17 expansion and bile duct proliferation in biliary liver diseases[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 203( 5): 1151- 1159. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800455. |
| [7] |
NAKAMOTO N, SASAKI N, AOKI R, et al. Gut pathobionts underlie intestinal barrier dysfunction and liver T helper 17 cell immune response in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Nat Microbiol, 2019, 4( 3): 492- 503. DOI: 10.1038/s41564-018-0333-1. |
| [8] |
LONGHI MS, MIELI-VERGANI G, VERGANI D. Regulatory T cells in autoimmune hepatitis: an updated overview[J]. J Autoimmun, 2021, 119: 102619. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102619. |
| [9] |
TAYLOR AE, CAREY AN, KUDIRA R, et al. Interleukin 2 promotes hepatic regulatory T cell responses and protects from biliary fibrosis in murine sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68( 5): 1905- 1921. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30061. |
| [10] |
SCHWINGE D, VON HAXTHAUSEN F, QUAAS A, et al. Dysfunction of hepatic regulatory T cells in experimental sclerosing cholangitis is related to IL-12 signaling[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 4): 798- 805. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.12.001. |
| [11] |
HELMIN KA, MORALES-NEBREDA L, TORRES ACOSTA MA, et al. Maintenance DNA methylation is essential for regulatory T cell development and stability of suppressive function[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130( 12): 6571- 6587. DOI: 10.1172/JCI137712. |
| [12] |
VOSKENS C, STOICA D, ROSENBERG M, et al. Autologous regulatory T-cell transfer in refractory ulcerative colitis with concomitant primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gut, 2023, 72( 1): 49- 53. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327075. |
| [13] |
JIANG T, ZHANG HW, WEN YP, et al. 5-Aza-2-deoxycytidine alleviates the progression of primary biliary cholangitis by suppressing the FoxP3 methylation and promoting the Treg/Th17 balance[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 96: 107820. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107820. |
| [14] |
ZIMMER CL, VON SETH E, BUGGERT M, et al. A biliary immune landscape map of primary sclerosing cholangitis reveals a dominant network of neutrophils and tissue-resident T cells[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2021, 13( 599): eabb3107. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb3107. |
| [15] |
RAVICHANDRAN G, NEUMANN K, BERKHOUT LK, et al. Interferon-γ-dependent immune responses contribute to the pathogenesis of sclerosing cholangitis in mice[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 4): 773- 782. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.05.023. |
| [16] |
LUO P, LIU L, HOU W, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis detected immune cell-related pathways associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 2371347. DOI: 10.1155/2022/2371347. |
| [17] |
LIASKOU E, JEFFERY LE, TRIVEDI PJ, et al. Loss of CD28 expression by liver-infiltrating T cells contributes to pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 147( 1): 221- 232.e7. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.003. |
| [18] |
TEDESCO D, THAPA M, CHIN CY, et al. Alterations in intestinal microbiota lead to production of interleukin 17 by Intrahepatic γδ T-cell receptor-positive cells and pathogenesis of cholestatic liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154( 8): 2178- 2193. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.02.019. |
| [19] |
VALESTRAND L, BERNTSEN NL, ZHENG F, et al. Lipid antigens in bile from patients with chronic liver diseases activate natural killer T cells[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2021, 203( 2): 304- 314. DOI: 10.1111/cei.13541. |
| [20] |
BERNTSEN NL, FOSBY B, TAN C, et al. Natural killer T cells mediate inflammation in the bile ducts[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2018, 11( 6): 1582- 1590. DOI: 10.1038/s41385-018-0066-8. |
| [21] |
VALESTRAND L, ZHENG F, HANSEN SH, et al. Bile from patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis contains mucosal-associated invariant T-cell antigens[J]. Am J Pathol, 2022, 192( 4): 629- 641. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.12.008. |
| [22] |
VON SETH E, ZIMMER CL, REUTERWALL-HANSSON M, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis leads to dysfunction and loss of MAIT cells[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2018, 48( 12): 1997- 2004. DOI: 10.1002/eji.201847608. |
| [23] |
BÖTTCHER K, ROMBOUTS K, SAFFIOTI F, et al. MAIT cells are chronically activated in patients with autoimmune liver disease and promote profibrogenic hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68( 1): 172- 186. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29782. |
| [24] |
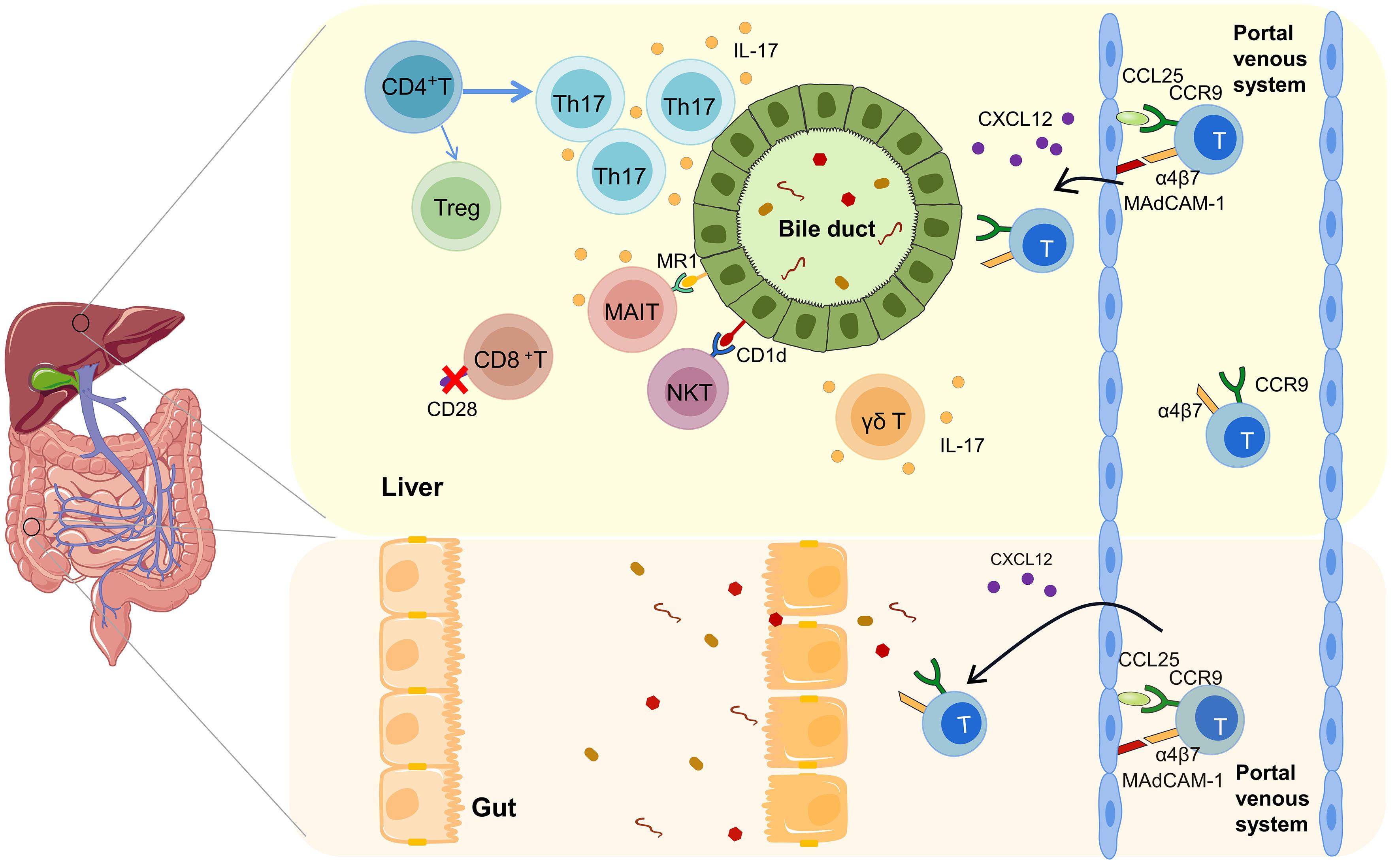
de KRIJGER M, WILDENBERG ME, de JONGE WJ, et al. Return to sender: Lymphocyte trafficking mechanisms as contributors to primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 3): 603- 615. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.05.006. |
| [25] |
GRAHAM JJ, MUKHERJEE S, YUKSEL M, et al. Aberrant hepatic trafficking of gut-derived T cells is not specific to primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 75( 3): 518- 530. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32193. |
| [26] |
CHRISTENSEN B, MICIC D, GIBSON PR, et al. Vedolizumab in patients with concurrent primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease does not improve liver biochemistry but is safe and effective for the bowel disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 47( 6): 753- 762. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14525. |
| [27] |
RAI RP, LIU Y, IYER SS, et al. Blocking integrin α4β7-mediated CD4 T cell recruitment to the intestine and liver protects mice from western diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 5): 1013- 1022. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.047. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: