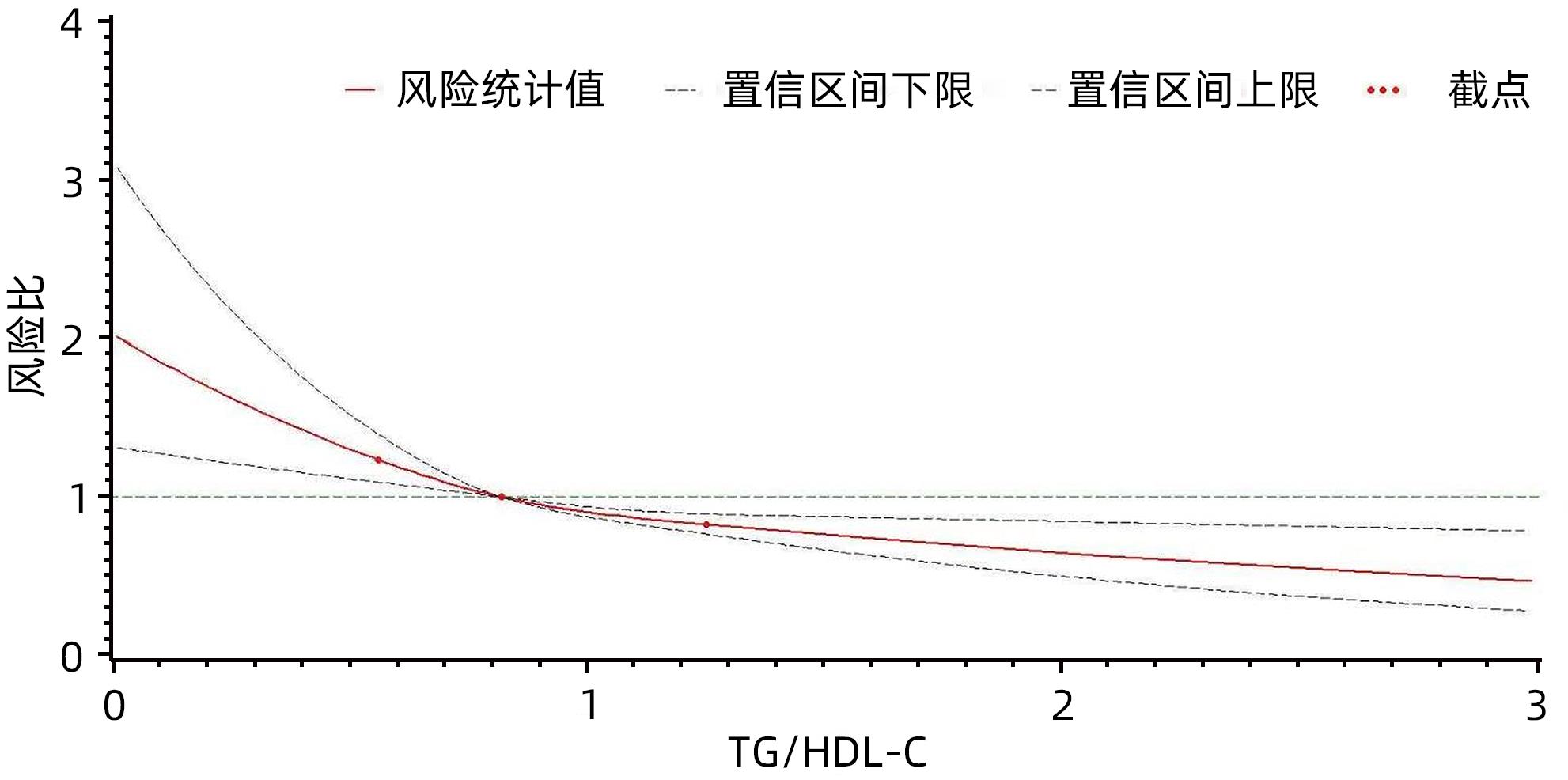
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
MCGLYNN KA, PETRICK JL, EL-SERAG HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( Suppl 1): 4- 13. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31288. |
| [4] |
HUANG DQ, EL-SERAG HB, LOOMBA R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18( 4): 223- 238. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00381-6. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
BOROUGHS LK, DEBERARDINIS RJ. Metabolic pathways promoting cancer cell survival and growth[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2015, 17( 4): 351- 359. DOI: 10.1038/ncb3124. |
| [7] |
GANJALI S, BANACH M, PIRRO M, et al. HDL and cancer-causality still needs to be confirmed? Update 2020[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2021, 73: 169- 177. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.10.007. |
| [8] |
GIANNINI C, SANTORO N, CAPRIO S, et al. The triglyceride-to-HDL cholesterol ratio: Association with insulin resistance in obese youths of different ethnic backgrounds[J]. Diabetes Care, 2011, 34( 8): 1869- 1874. DOI: 10.2337/dc10-2234. |
| [9] |
GASEVIC D, FROHLICH J, JOHN MANCINI GB, et al. The association between triglyceride to high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance in a multiethnic primary prevention cohort[J]. Metabolism, 2012, 61( 4): 583- 589. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.09.009. |
| [10] |
TURAK O, AFŞAR B, OZCAN F, et al. The role of plasma triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio to predict new cardiovascular events in essential hypertensive patients[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich), 2016, 18( 8): 772- 777. DOI: 10.1111/jch.12758. |
| [11] |
MILLER M, STONE NJ, BALLANTYNE C, et al. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2011, 123( 20): 2292- 2333. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182160726. |
| [12] |
HE S, WANG S, CHEN XP, et al. Higher ratio of triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol may predispose to diabetes mellitus: 15-year prospective study in a general population[J]. Metabolism, 2012, 61( 1): 30- 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.05.007. |
| [13] |
FAN NG, PENG L, XIA ZH, et al. Triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as a surrogate for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2019, 18( 1): 39. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-0986-7. |
| [14] |
WU SL, HUANG ZR, YANG XC, et al. Prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health and its relationship with the 4-year cardiovascular events in a northern Chinese industrial city[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes, 2012, 5( 4): 487- 493. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.111.963694. |
| [15] |
CHEW NWS, NG CH, TAN DJH, et al. The global burden of metabolic disease: Data from 2000 to 2019[J]. Cell Metab, 2023, 35( 3): 414- 428. e 3. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.02.003. |
| [16] |
LI J, ZOU BY, YEO YH, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4( 5): 389- 398. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1. |
| [17] |
NDERITU P, BOSCO C, GARMO H, et al. The association between individual metabolic syndrome components, primary liver cancer and cirrhosis: A study in the Swedish AMORIS cohort[J]. Int J Cancer, 2017, 141( 6): 1148- 1160. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.30818. |
| [18] |
WELZEL TM, GRAUBARD BI, ZEUZEM S, et al. Metabolic syndrome increases the risk of primary liver cancer in the United States: A study in the SEER-Medicare database[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54( 2): 463- 471. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24397. |
| [19] |
XIA B, PENG JJ, ENRICO DT, et al. Metabolic syndrome and its component traits present gender-specific association with liver cancer risk: A prospective cohort study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21( 1): 1084. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08760-1. |
| [20] |
CHO Y, CHO EJ, YOO JJ, et al. Association between lipid profiles and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide population-based study[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2021, 13( 7): 1599. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13071599. |
| [21] |
BORENA W, STROHMAIER S, LUKANOVA A, et al. Metabolic risk factors and primary liver cancer in a prospective study of 578, 700 adults[J]. Int J Cancer, 2012, 131( 1): 193- 200. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.26338. |
| [22] |
KASMARI AJ, WELCH A, LIU GD, et al. Independent of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma risk is increased with diabetes and metabolic syndrome[J]. Am J Med, 2017, 130( 6): 746. e1- 746. e 7. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.12.029. |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
HALSTED CH. Nutrition and alcoholic liver disease[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2004, 24( 3): 289- 304. DOI: 10.1055/s-2004-832941. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
GHADIR MR, RIAHIN AA, HAVASPOUR A, et al. The relationship between lipid profile and severity of liver damage in cirrhotic patients[J]. Hepat Mon, 2010, 10( 4): 285- 288.
|
| [27] |
PEREZ-MATOS MC, SANDHU B, BONDER A, et al. Lipoprotein metabolism in liver diseases[J]. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2019, 30( 1): 30- 36. DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000569. |
| [28] |
LONG J, ZHANG CJ, ZHU N, et al. Lipid metabolism and carcinogenesis, cancer development[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2018, 8( 5): 778- 791.
|
| [29] |
MICHIEL DF, OPPENHEIM JJ. Cytokines as positive and negative regulators of tumor promotion and progression[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 1992, 3( 1): 3- 15.
|
| [30] |
MOTTA M, GIUGNO I, RUELLO P, et al. Lipoprotein(a) behaviour in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Minerva Med, 2001, 92( 5): 301- 305.
|



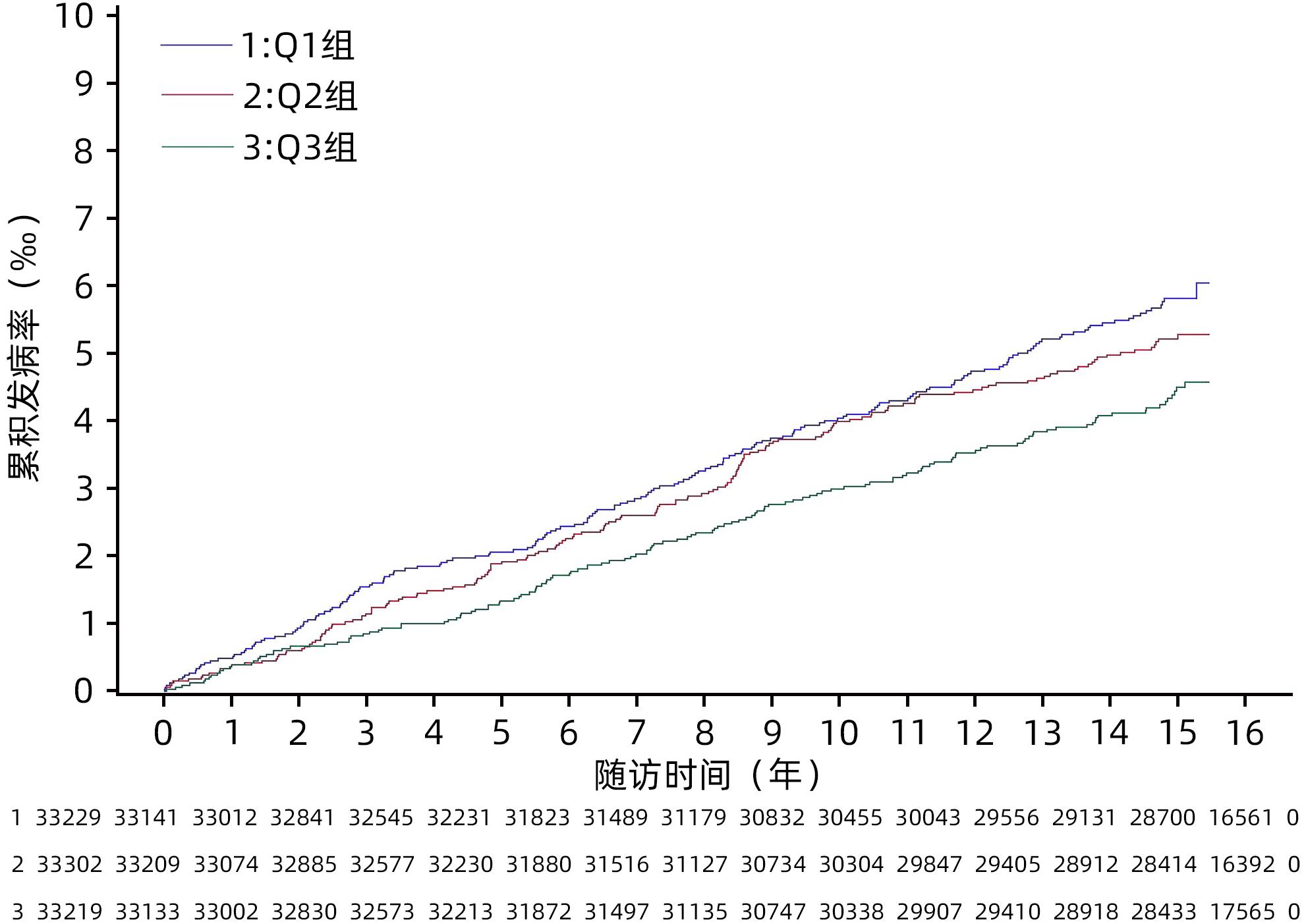




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: