| [1] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Hepatology Group, Infectious Diseases Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Hepatology Group, Hepatology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [2] |
Pancreatic Surgery Group, Surgery Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis in China(2021)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20( 7): 730- 739. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210622-00297. |
| [3] |
PANIC N, MIHAJLOVIC S, VUJASINOVIC M, et al. Pancreatitis associated with viral hepatitis: Systematic review[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9( 10): 3309. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9103309. |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
ALANAZI A, NAGI MN, ALHARETH DY, et al. Crosstalk of TNF-α, IFN-γ, NF-κB, STAT1 and redox signaling in lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine/dimethylsulfoxide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice[J]. Saudi Pharm J, 2023, 31( 3): 370- 381. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.01.005. |
| [6] |
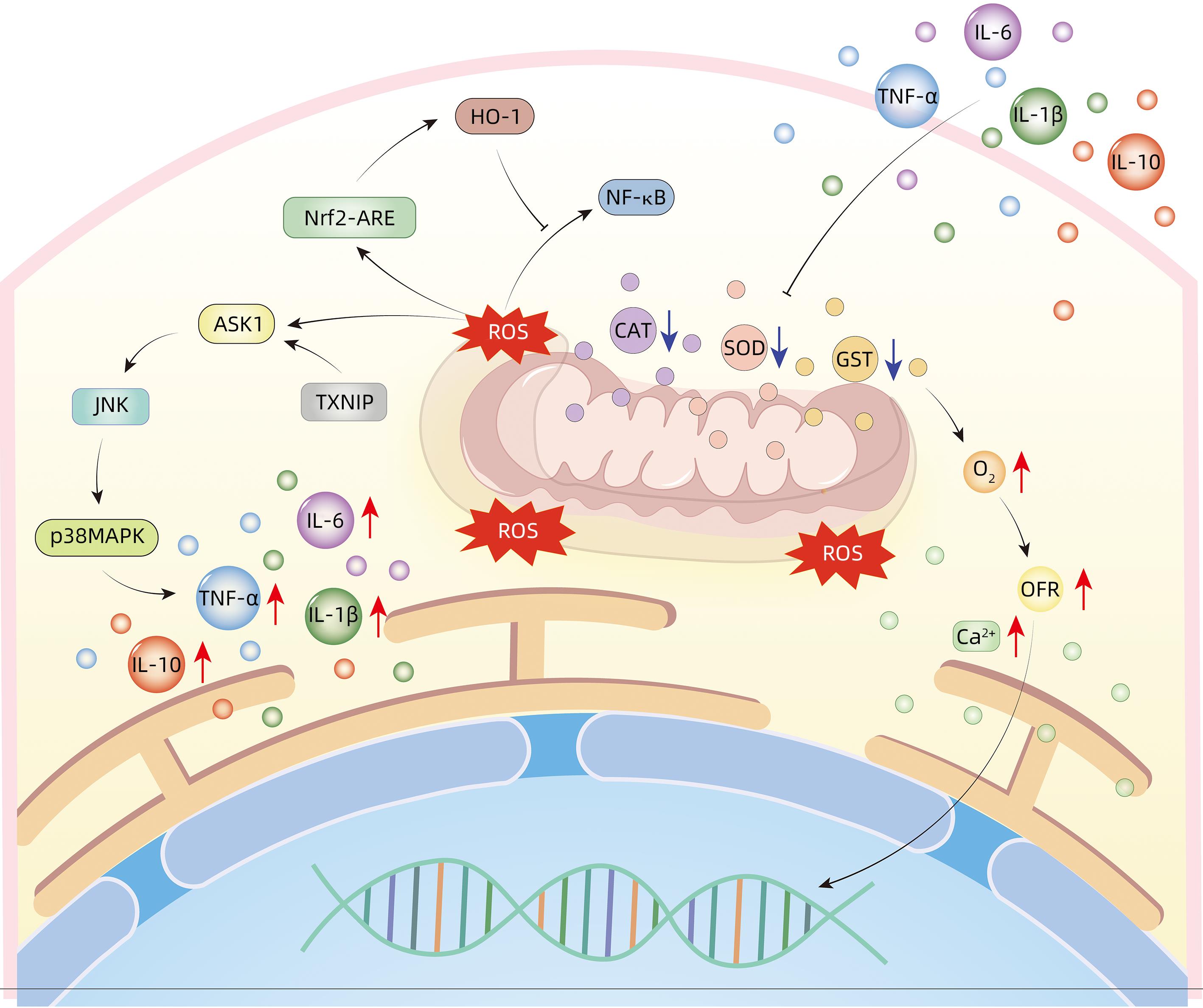
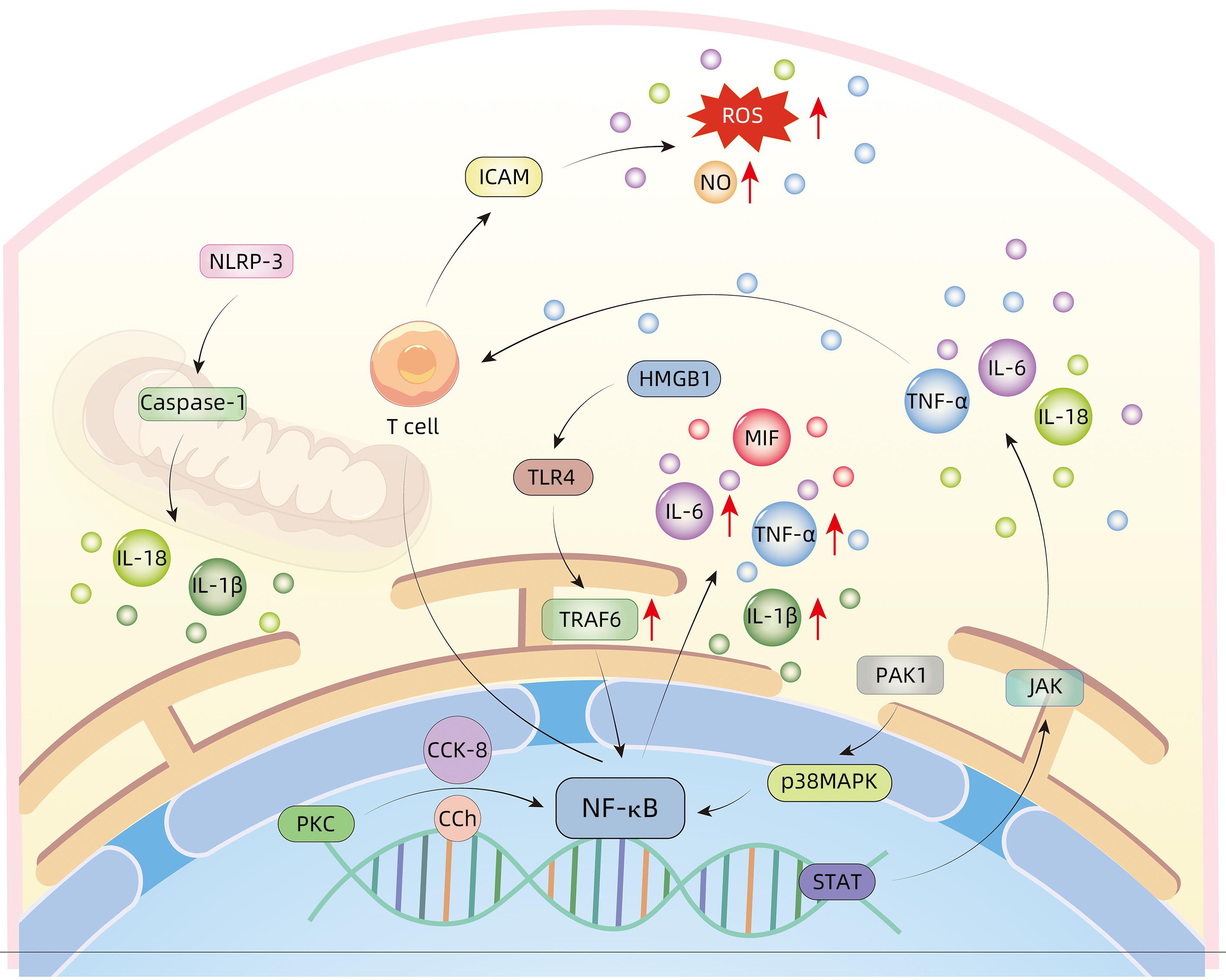
XU B, BAI B, SHA SM, et al. Interleukin-1β induces autophagy by affecting calcium homeostasis and trypsinogen activation in pancreatic acinar cells[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7( 7): 3620- 3631.
|
| [7] |
KANY S, VOLLRATH JT, RELJA B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20( 23): 6008. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20236008. |
| [8] |
LESINA M, WÖRMANN SM, NEUHÖFER P, et al. Interleukin-6 in inflammatory and malignant diseases of the pancreas[J]. Semin Immunol, 2014, 26( 1): 80- 87. DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.01.002. |
| [9] |
REX DAB, AGARWAL N, PRASAD TSK, et al. A comprehensive pathway map of IL-18-mediated signalling[J]. J Cell Commun Signal, 2020, 14( 2): 257- 266. DOI: 10.1007/s12079-019-00544-4. |
| [10] |
KURIMOTO M, WATANABE T, KAMATA K, et al. IL-33 as a critical cytokine for inflammation and fibrosis in inflammatory bowel diseases and pancreatitis[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 781012. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.781012. |
| [11] |
MALLEO G, MAZZON E, SIRIWARDENA AK, et al. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in acute pancreatitis: From biological basis to clinical evidence[J]. Shock Augusta Ga, 2007, 28( 2): 130- 140. DOI: 10.1097/shk.0b013e3180487ba1. |
| [12] |
TIEGS G, HORST AK. TNF in the liver: Targeting a central player in inflammation[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2022, 44( 4): 445- 459. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-022-00910-2. |
| [13] |
ISHIBASHI T, ZHAO HF, KAWABE K, et al. Blocking of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1(MCP-1) activity attenuates the severity of acute pancreatitis in rats[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2008, 43( 1): 79- 85. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-007-2126-9. |
| [14] |
ZHU CJ, LIU YN, SONG YD, et al. Deletion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor ameliorates inflammation in mice model severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 125: 109919. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109919. |
| [15] |
AMPOFO E, BERG JJ, MENGER MD, et al. Maslinic acid alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammation by downregulation of NFκB-mediated adhesion molecule expression[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 6119. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42465-7. |
| [16] |
LI Z, LIU T, FENG Y, et al. PPARγ alleviates sepsis-induced liver injury by inhibiting hepatocyte pyroptosis via inhibition of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 1269747. DOI: 10.1155/2022/1269747. |
| [17] |
SATOH A, GUKOVSKAYA AS, NIETO JM, et al. PKC-δ and-ε regulate NF-κB activation induced by cholecystokinin and TNF-α in pancreatic acinar cells[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2004, 287( 3): G582- G591. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00087.2004. |
| [18] |
ZHANG XP, ZHANG J, MA ML, et al. Pathological changes at early stage of multiple organ injury in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2010, 9( 1): 83- 87.
|
| [19] |
ZHU MH, XU Y, ZHANG WB, et al. Inhibition of PAK1 alleviates cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis via p38 and NF-κB pathways[J]. Biosci Rep, 2019, 39( 3): BSR20182221. DOI: 10.1042/bsr20182221. |
| [20] |
CHEN Z, DONG WH, WU Q, et al. Two-layer regulation of TRAF6 mediated by both TLR4/NF-kB signaling and miR-589-5p increases proinflammatory cytokines in the pathology of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2020, 12( 6): 2379- 2395.
|
| [21] |
LI G, WU XJ, YANG L, et al. TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway mediates HMGB1-induced pancreatic injury in mice with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37( 1): 99- 107. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2410. |
| [22] |
SENDLER M, VAN DEN BRANDT C, GLAUBITZ J, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome regulates development of systemic inflammatory response and compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndromes in mice with acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158( 1): 253- 269. e 14. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.040. |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
COUCKE EM, AKBAR H, KAHLOON A, et al. Biliary obstruction[M]. Treasure Island(FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
|
| [25] |
WANG GJ, GAO CF, WEI D, et al. Acute pancreatitis: Etiology and common pathogenesis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15( 12): 1427- 1430. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.1427. |
| [26] |
ZHAN XB, WAN JH, ZHANG GW, et al. Elevated intracellular trypsin exacerbates acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2019, 316( 6): G816- G825. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00004.2019. |
| [27] |
ZHENG Q, LIU JS, ZHENG BF, et al. The role of pancreatic duct in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2020, 33( 11): 1598- 1600. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2020.11.038. |
| [28] |
MEI QX, FU Y, HUANG ZH, et al. Intestinal TLR4 deletion exacerbates acute pancreatitis through gut microbiota dysbiosis and Paneth cells deficiency[J]. Gut Microbes, 2022, 14( 1): 2112882. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2112882. |
| [29] |
ZHANG ZW, TANAKA I, PAN Z, et al. Intestinal homeostasis and inflammation: Gut microbiota at the crossroads of pancreas-intestinal barrier axis[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2022, 52( 7): 1035- 1046. DOI: 10.1002/eji.202149532. |
| [30] |
PATEL BK, PATEL KH, BHATIA M, et al. Gut microbiome in acute pancreatitis: A review based on current literature[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27( 30): 5019- 5036. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5019. |
| [31] |
LIU XQ, HUSSAIN R, MEHMOOD K, et al. Mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum communication-mediated oxidative stress and autophagy[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 6459585. DOI: 10.1155/2022/6459585. |
| [32] |
RAMUDO L, MANSO MA. N-acetylcysteine in acute pancreatitis[J]. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 1( 1): 21- 26. DOI: 10.4292/wjgpt.v1.i1.21. |
| [33] |
BICZO G, VEGH ET, SHALBUEVA N, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction, through impaired autophagy, leads to endoplasmic reticulum stress, deregulated lipid metabolism, and pancreatitis in animal models[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154( 3): 689- 703. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.012. |
| [34] |
LIU YN, LI MK, MEI CP, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein deficiency protects against severe acute pancreatitis by suppressing apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13( 10): 914. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05355-x. |
| [35] |
XIONG J, WANG KZ, YUAN CX, et al. Luteolin protects mice from severe acute pancreatitis by exerting HO-1-mediated anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2017, 39( 1): 113- 125. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2809. |
| [36] |
LIU XN, ZHU QT, ZHANG M, et al. Isoliquiritigenin ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice via inhibition of oxidative stress and modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 7161592. DOI: 10.1155/2018/7161592. |
| [37] |
PLUSCZYK T, BERSAL B, WESTERMANN S, et al. ET-1 induces pancreatitis-like microvascular deterioration and acinar cell injury[J]. J Surg Res, 1999, 85( 2): 301- 310. DOI: 10.1006/jsre.1999.5610. |
| [38] |
AMBUDKAR IS. Polarization of calcium signaling and fluid secretion in salivary gland cells[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2012, 19( 34): 5774- 5781. DOI: 10.2174/092986712804143321. |
| [39] |
KABBANI AR, TERGAST TL, MANNS MP, et al. Behandlungsstrategien des akut-auf-chronischen leberversagens[J]. Med Klin Intensivmedizin Und Notfallmedizin, 2021, 116( 1): 3- 16. DOI: 10.1007/s00063-019-00613-x. |
| [40] |
KHANAM A, KOTTILIL S. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Pathophysiological mechanisms and management[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2021, 8: 752875. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.752875. |
| [41] |
YE C, LI WY, LI L, et al. Glucocorticoid treatment strategies in liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 846091. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.846091. |
| [42] |
ZHANG XF, WANG LY, ZHANG Y, et al. Etiological characteristics, laboratory test indexes and prognosis of hepatic failure patients with secondary infection[J]. Chin J Nosocomiology, 2023, 9( 17): 2590- 2594.
张晓芳, 汪陆叶, 章颖, 等. 肝衰竭继发感染病原学和实验室指标水平变化及预后[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2023, 9( 17): 2590- 2594.
|
| [43] |
WANG XM. Diagnostic value of inflammation index in hepatitis B virus-associated chronic and acute liver failure complicated with infection[J]. China Mod Med, 2020, 27( 32): 86- 89. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2020.32.026. |
| [44] |
XIE SA. Clinical study of ERCP in the treatment of acute biliary pancreatitis[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Medical University, 2022.
谢水安. ERCP治疗急性胆源性胰腺炎的临床研究[D]. 广州: 广州医科大学, 2022.
|
| [45] |
Expert Committee on Diagnosis and Treatment of Intrahepatic Cholestasis. Expert consensus for diagnosis and treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2015, 8( 5): 402- 406. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2015.05.002. |
| [46] |
YU BJ. Protective effect of rifaximin on severe acute pancreatitis and its mechanism[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2021.
喻冰君. 利福昔明对重症急性胰腺炎的保护作用及机制初探[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2021.
|
| [47] |
HAN H, LIU X. Current application status of probiotics in the treatment of acute pancreatitis[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2021, 49( 4): 374- 375, 379. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2021.04.05. |
| [48] |
LU WW, CHEN X, NI JL, et al. The role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute pancreatitis: A narrative review[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10( 3): 3445- 3451. DOI: 10.21037/apm-21-429. |
| [49] |
LUO YY, LIU X. Research progress in probiotic assisted treatment of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Trauma and Crit Medicine, 2021, 9( 2): 161- 164. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2021.02.22. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: