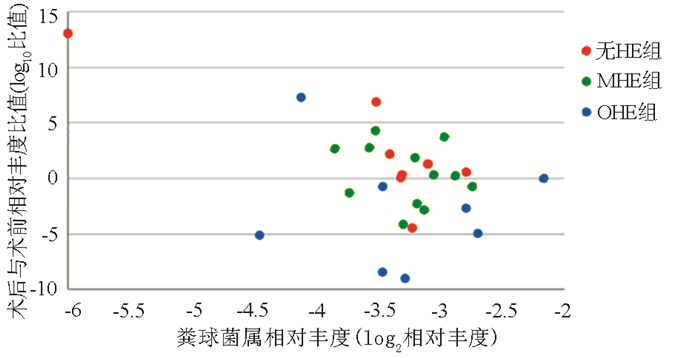
| [1] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(2): 406-460. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024 |
| [2] |
ZHANG JC, WANG YG, LIN F, et al. Recent advances on the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2019, 11(1): 6-11. (in Chinese)
张军昌, 王永刚, 林芳, 等. 肝性脑病发病机制新进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(1): 6-11.
|
| [3] |
RIDOLA L, CARDINALE V, RIGGIO O. The burden of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: From diagnosis to therapeutic strategies[J]. Ann Gastroenterol, 2018, 31(2): 151-164.
|
| [4] |
WANG JY, ZHANG NP, CHI BR, et al. Prevalence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy and quality of life evaluations in hospitalized cirrhotic patients in China[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(30): 4984-4991. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4984 |
| [5] |
QIN N, YANG F, LI A, et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7516): 59-64. DOI: 10.1038/nature13568 |
| [6] |
TANG SH, CHEN H, HAN GH. Association between gut microbiota and hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(5): 1109-1113. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.05.041 |
| [7] |
LU BJ, ZHAO YH, AN YT, et al. Research advances in gut microbiota in liver cirrhosis and related complications[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(11): 2433-2437. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.11.037 |
| [8] |
BAJAJ JS, HEUMAN DM, HYLEMON PB, et al. Altered profile of human gut microbiome is associated with cirrhosis and its complications[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60(5): 940-947. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.019 |
| [9] |
BAJAJ JS. The role of microbiota in hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Gut Microbes, 2014, 5(3): 397-403. DOI: 10.4161/gmic.28684 |
| [10] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(10): 2076-2089. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.007 |
| [11] |
FERENCI P. Hepatic encephalopathy-Definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: Final report of the Working Party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998[J]. Hepatology, 2002, 35(3): 716-721. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31250 |
| [12] |
ZOETENDAL EG, BEN-AMOR K, HARMSEN HJ, et al. Quantification of uncultured Ruminococcus obeum-like bacteria in human fecal samples by fluorescent in situ hybridization and flow cytometry using 16S rRNA-targeted probes[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2002, 68(9): 4225-4232. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.9.4225-4232.2002 |
| [13] |
DABARD J, BRIDONNEAU C, PHILLIPE C, et al. Ruminococcin A, a new lantibiotic produced by a Ruminococcus gnavus strain isolated from human feces[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2001, 67(9): 4111-4118. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.4111-4118.2001 |
| [14] |
DUNCAN SH, LOUIS P, FLINT HJ. Cultivable bacterial diversity from the human colon[J]. Lett Appl Microbiol, 2007, 44(4): 343-350. DOI: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02129.x |
| [15] |
WONG JM, de SOUZA R, KENDALL CW, et al. Colonic health: Fermentation and short chain fatty acids[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2006, 40(3): 235-243. DOI: 10.1097/00004836-200603000-00015 |
| [16] |
NAVA GM, STAPPENBECK TS. Diversity of the autochthonous colonic microbiota[J]. Gut Microbes, 2011, 2(2): 99-104. DOI: 10.4161/gmic.2.2.15416 |
| [17] |
SOKOL H, PIGNEUR B, WATTERLOT L, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008, 105(43): 16731-16736. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0804812105 |
| [18] |
SOKOL H, LAY C, SEKSIK P, et al. Analysis of bacterial bowel communities of IBD patients: What has it revealed?[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2008, 14(6): 858-867. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.20392 |
| [19] |
BAJAJ JS, BETRAPALLY NS, HYLEMON PB, et al. Salivary microbiota reflects changes in gut microbiota in cirrhosis with hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62(4): 1260-1271. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27819 |
| [20] |
BAJAJ JS, RIDLON JM, HYLEMON PB, et al. Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2012, 302(1): g168-g175. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00190.2011 |
| [21] |
de CRUZ P, KANG S, WAGNER J, et al. Association between specific mucosa-associated microbiota in Crohn's disease at the time of resection and subsequent disease recurrence: A pilot study[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(2): 268-278. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12694 |
| [22] |
BONGAERTS GP, SCHREURS BW, LUNEL FV, et al. Was isolation of Veillonella from spinal osteomyelitis possible due to poor tissue perfusion?[J]. Med Hypotheses, 2004, 63(4): 659-661. DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2004.02.052 |
| [23] |
ROVERY C, ETIENNE A, FOUCAULT C, et al. Veillonella montpellierensis endocarditis[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2005, 11(7): 1112-1114. DOI: 10.3201/eid1107.041361 |



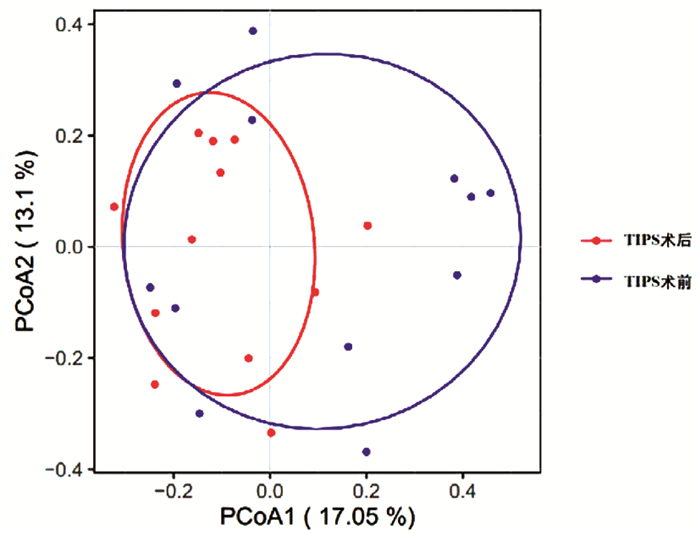




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: