| [1] |
ACHOUITAR S, GOLDSTEIN JL, MOHAMED M, et al. Common mutation in the PHKA2 gene with variable phenotype Ⅰn patients with liver phosphorylase b kinase deficiency[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2011, 104(4): 691-694. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.08.021 |
| [2] |
MAICHELE AJ, BURWINKEL B, MAIRE I, et al. Mutations in the testis/liver isoform of the phosphorylase kinase gamma subunit (PHKG2) cause autosomal liver glycogenosis in the gsd rat and in humans[J]. Nat Genet, 1996, 14(3): 337-340. DOI: 10.1038/ng1196-337 |
| [3] |
BRUSHIA RJ, WALSH DA. Phosphorylase kinase: The complexity of its regulation is reflected in the complexity of its structure[J]. Front Biosci, 1999, 4: d618-d641.
|
| [4] |
DAVIDSON JJ, OZÇELIK T, HAMACHER C, et al. cDNA cloning of a liver isoform of the phosphorylase kinase alpha subunit and mapping of the gene to Xp22.2-p22.1, the region of human X-linked liver glycogenosis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1992, 89(6): 2096-2100. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2096 |
| [5] |
FU J, WANG T, XIAO X. A novel PHKA2 mutation in a Chinese child with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸa: A case report and literature review[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2019, 20(1): 56. DOI: 10.1186/s12881-019-0789-8 |
| [6] |
LIU J, ZHANG MH, GONG JY, et al. Report of 7 cases of glycogen storage disease type Ⅵ and type Ⅸa[J]. Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2017, 12(4): 284-288. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2017.04.009 |
| [7] |
KISHNANI PS, GOLDSTEIN J, AUSTIN SL, et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage diseases type Ⅵ and Ⅸ: A clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG)[J]. Genet Med, 2019, 21(4): 772-789. DOI: 10.1038/s41436-018-0364-2 |
| [8] |
FERNANDES J, PIKAAR NA. Ketosis in hepatic glycogenosis[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1972, 47(251): 41-46. DOI: 10.1136/adc.47.251.41 |
| [9] |
ZHANG J, YUAN Y, MA M, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of 17 Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸa[J]. Gene, 2017, 627: 149-156. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.026 |
| [10] |
BEAUCHAMP NJ, DALTON A, RAMASWAMI U, et al. Glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ: High variability in clinical phenotype[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2007, 92(1-2): 88-99. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2007.06.007 |
| [11] |
HIRONO H, SHOJI Y, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Mutational analyses in four Japanese families with X-linked liver phosphorylase kinase deficiency type 1[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 1998, 21(8): 846-852. DOI: 10.1023/A:1005422819207 |
| [12] |
ROSCHER A, PATEL J, HEWSON S, et al. The natural history of glycogen storage disease types Ⅵ and Ⅸ: Long-term outcome from the largest metabolic center in Canada[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2014, 113(3): 171-176. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.09.005 |
| [13] |
BURWINKEL B, AMAT L, GRAY RG, et al. Variability of biochemical and clinical phenotype Ⅰn X-linked liver glycogenosis with mutations in the phosphorylase kinase PHKA2 gene[J]. Hum Genet, 1998, 102(4): 423-429. DOI: 10.1007/s004390050715 |
| [14] |
KISHNANI PS, AUSTIN SL, ABDENUR JE, et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage disease type Ⅰ: A practice guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics[J]. Genet Med, 2014, 16(11): e1. DOI: 10.1038/gim.2014.128 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
TSILIANIDIS LA, FISKE LM, SIEGEL S, et al. Aggressive therapy improves cirrhosis in glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2013, 109(2): 179-182. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.03.009 |
| [17] |
JOHNSON AO, GOLDSTEIN JL, BALI D. Glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ: Novel PHKA2 missense mutation and cirrhosis[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2012, 55(1): 90-92. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31823276ea |
| [18] |
LAU CK, HUI J, FONG FN, et al. Novel mutations in PHKA2 gene in glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ patients from Hong Kong, China[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2011, 102(2): 222-225. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.11.004 |
| [19] |
CHEN ST, CHEN HL, NI YH, et al. X-linked liver glycogenosis in a Taiwanese family: Transmission from undiagnosed males[J]. Pediatr Neonatol, 2009, 50(5): 230-233. DOI: 10.1016/S1875-9572(09)60068-1 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
YANG F, XU Y, FANG C, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of three Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸα[J]. Pediatr Neonatol, 2019, 60(4): 463-466. DOI: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2019.05.007 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
CHO SY, LAM CW, TONG SF, et al. X-linked glycogen storage disease IXa manifested in a female carrier due to skewed X chromosome inactivation[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2013, 426: 75-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.08.026 |
| [24] |
van den BERG IE, van BEURDEN EA, MALINGRÉ HE, et al. X-linked liver phosphorylase kinase deficiency is associated with mutations in the human liver phosphorylase kinase alpha subunit[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 1995, 56(2): 381-387. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1801119/ |
| [25] |
HENDRICKX J, LEE P, KEATING JP, et al. Complete genomic structure and mutational spectrum of PHKA2 in patients with x-linked liver glycogenosis type Ⅰ and Ⅱ[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 1999, 64(6): 1541-1549. DOI: 10.1086/302399 |
| [26] |
BURWINKEL B, MOSES SW, KILIMANN MW. Phosphorylase-kinase-deficient liver glycogenosis with an unusual biochemical phenotype Ⅰn blood cells associated with a missense mutation in the beta subunit gene (PHKB)[J]. Hum Genet, 1997, 101(2): 170-174. DOI: 10.1007/s004390050608 |
| [27] |
WILLEMS PJ, GERVER WJ, BERGER R, et al. The natural history of liver glycogenosis due to phosphorylase kinase deficiency: A longitudinal study of 41 patients[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 1990, 149(4): 268-271. DOI: 10.1007/BF02106291 |










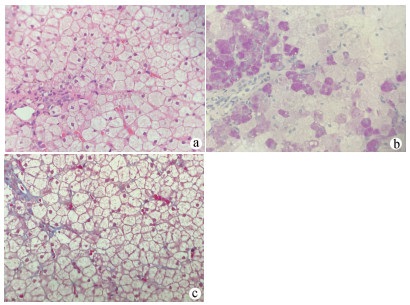




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: