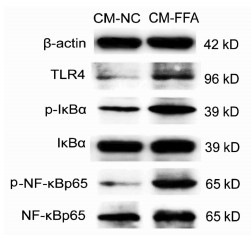
| [1] |
YOUNOSSI ZM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - A global public health perspective[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(3): 531-544. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.033 |
| [2] |
TACKE F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(6): 1300-1312. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026 |
| [3] |
WANG Q, XU QY, WU HM, et al. Effect of lipid-induced macrophage M1/M2 polarization on lipid metabolism in hepatocytes[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2018, 26(4): 276-281. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.009 |
| [4] |
GÓMEZ-LECHÓN MJ, DONATO MT, MARTÍNEZ-ROMERO A, et al. A human hepatocellular in vitro model to investigate steatosis[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2007, 165(2): 106-116. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2006.11.004 |
| [5] |
XIAO WS, LE YY, ZENG SL, et al. Research advances in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(8): 1874-1879. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.08.043 |
| [6] |
HOLLAND WL, BIKMAN BT, WANG LP, et al. Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor TLR4 requires saturated fatty acid-induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011, 121(5): 1858-1870. DOI: 10.1172/JCI43378 |
| [7] |
KAZANKOV K, JØRGENSEN S, THOMSEN KL, et al. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(3): 145-159. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0082-x |
| [8] |
TOSELLO-TRAMPONT AC, LANDES SG, NGUYEN V, et al. Kuppfer cells trigger nonalcoholic steatohepatitis development in diet-induced mouse model through tumor necrosis factor-α production[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(48): 40161-40172. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417014 |
| [9] |
WU HM, NI XX, XU QY, et al. Regulation of lipid-induced macrophage polarization through modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activity affects hepatic lipid metabolism via a Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 35(11): 1998-2008. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15025 |
| [10] |
KOU XN, XIE XK, HAO MX, et al. Effects and mechanism of microRNA-140 inhibition on the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2020, 12(3): 34-40. (in Chinese)
寇小妮, 解新科, 郝明霞, 等.微小RNA-140抑制对小鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病进展的影响及机制[J/CD].中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2020, 12(3): 34-40.
|
| [11] |
ZHENG Y, WANG JR, LIU LL, et al. Molecular mechanism of the anti -liver fibrosis effect of curcumol: An analysis based on the TLR4 /NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(7): 1508-1513. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.07.013 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
GORDON S, MARTINEZ F O. Alternative activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions[J]. Immunity, 2010, 32(5): 593-604. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.007 |



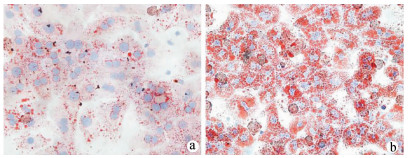




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: