| [1] |
SALEN G, STEINER RD. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX)[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2017, 40(6): 771-781. DOI: 10.1007/s10545-017-0093-8 |
| [2] |
LARSON A, WEISFELD-ADAMS JD, BENKE TA, et al. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis presenting with infantile spasms and intellectual disability[J]. JIMD Rep, 2017, 35: 1-5.
|
| [3] |
MIGNARRI A, GALLUS GN, DOTTI MT, et al. A suspicion index for early diagnosis and treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2014, 37(3): 421-429. DOI: 10.1007/s10545-013-9674-3 |
| [4] |
SEKIJIMA Y, KOYAMA S, YOSHINAGA T, et al. Nationwide survey on cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in Japan[J]. J Hum Genet, 2018, 63(3): 271-280. DOI: 10.1038/s10038-017-0389-4 |
| [5] |
DUELL PB, SALEN G, EICHLER FS, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and clinical outcomes in 43 cases with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2018, 12(5): 1169-1178. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2018.06.008 |
| [6] |
TIBREWAL S, DUELL PB, DEBARBER AE, et al. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Early diagnosis on the basis of juvenile cataracts[J]. J AAPOS, 2017, 21(6): 505-507. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2017.07.211 |
| [7] |
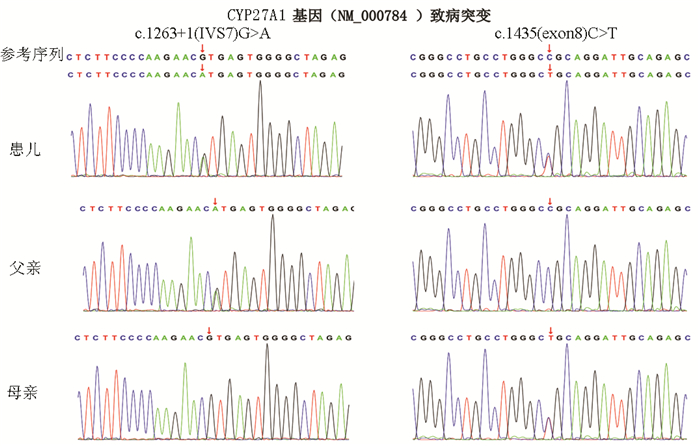
GUO HM, LI M, JIN Y, et al. A case report of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with novel mutations in CYP27A1 gene[J]. J Clin Pediatr, 2017, 35(11): 841-843. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3606.2017.11.010 |
| [8] |
ZHANG XY, LU Y. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A case report and literature review[J]. Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2016, 11(3): 210-214. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2016.03.010 |
| [9] |
DI TARANTO MD, GELZO M, GIACOBBE C, et al. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, a metabolic disease with different neurological signs: Two case reports[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2016, 31(5): 1185-1188. DOI: 10.1007/s11011-016-9841-y |
| [10] |
TAO QQ, ZHANG Y, LIN HX, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of Chinese patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2019, 14(1): 282. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-019-1252-9 |
| [11] |
RICHARDS S, AZIZ N, BALE S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology[J]. Genet Med, 2015, 17(5): 405-424. DOI: 10.1038/gim.2015.30 |
| [12] |
KLIEGMAN R, NELSON WE. Nelson textbook of pediatrics[M]. 19th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2011.
|
| [13] |
SHIGA K, FUKUYAMA R, KIMURA S, et al. Mutation of the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene (CYP27) results in truncation of mRNA expressed in leucocytes in a Japanese family with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 1999, 67(5): 675-677. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.67.5.675 |
| [14] |
WALLON D, GUYANT-MARÉCHAL L, LAQUERRIÈRE A, et al. Clinical imaging and neuropathological correlations in an unusual case of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis[J]. Clin Neuropathol, 2010, 29(6): 361-364.
|
| [15] |
FEDERICO A, DOTTI MT. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, pathogenesis, and therapy[J]. J Child Neurol, 2003, 18(9): 633-638. DOI: 10.1177/08830738030180091001 |
| [16] |
PIERRE G, SETCHELL K, BLYTH J, et al. Prospective treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with cholic acid therapy[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2008, 31(Suppl 2): s241-s245.
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: