| [1] |
DIEHL AM, DAY C. Cause, pathogenesis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(21): 2063-2072. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1503519 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
SHU JR, LI JQ, LIU Q. Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and related risk factors[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(9): 2085-2090. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.045 |
| [4] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, KOENIG AB, ABDELATIF D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(1): 73-84. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28431 |
| [5] |
AHMED A, WONG RJ, HARRISON SA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease review: Diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13(12): 2062-2070. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.029 |
| [6] |
TILG H, MOSCHEN AR. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52(5): 1836-1846. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24001 |
| [7] |
SCHAFFER JE. Lipotoxicity: Many roads to cell dysfunction and cell death: Introduction to a thematic review series[J]. J Lipid Res, 2016, 57(8): 1327-1328. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.E069880 |
| [8] |
ANGULO P, KLEINER DE, DAM-LARSEN S, et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 149(2): 389-397. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.043 |
| [9] |
MUSSO G, CASSADER M, PASCHETTA E, et al. Bioactive lipid species and metabolic pathways in progression and resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155(2): 282-302. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.031 |
| [10] |
CUSI K. Role of obesity and lipotoxicity in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Pathophysiology and clinical implications[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142(4): 711-725. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.02.003 |
| [11] |
MACHADO MV, DIEHL AM. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(8): 1769-1777. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.066 |
| [12] |
PARTHASARATHY G, REVELO X, MALHI H. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An overview[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2020, 4(4): 478-492. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1479 |
| [13] |
IBRAHIM SH, HIRSOVA P, GORES GJ. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis pathogenesis: Sublethal hepatocyte injury as a driver of liver inflammation[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(5): 963-972. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315691 |
| [14] |
LEBEAUPIN C, VALLÉE D, HAZARI Y, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(4): 927-947. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.06.008 |
| [15] |
ZHANG B, LI M, ZOU Y, et al. NFκB/Orai1 facilitates endoplasmic reticulum stress by oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2019, 7: 202. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00202 |
| [16] |
YANG MT, CHEN ZJ, XIAO CX, et al. Effects of sera of rats fed with Huganqingzhi tablets on endoplasmic reticulum stress in a HepG2 cell model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J South Med Univ, 2018, 38(11): 1277-1287. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJD201811002.htm |
| [17] |
WANG L, CHEN J, NING C, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress related molecular mechanisms in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2018, 19(9): 1087-1094. DOI: 10.2174/1389450118666180516122517 |
| [18] |
SANO R, REED JC. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1833(12): 3460-3470. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.028 |
| [19] |
WANG S, CHEN Z, LAM V, et al. IRE1α-XBP1s induces PDI expression to increase MTP activity for hepatic VLDL assembly and lipid homeostasis[J]. Cell Metab, 2012, 16(4): 473-486. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.09.003 |
| [20] |
ZHANG K, WANG S, MALHOTRA J, et al. The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1α prevents ER stress-induced hepatic steatosis[J]. EMBO J, 2011, 30(7): 1357-1375. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.52 |
| [21] |
YE D, LI FY, LAM KS, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates obesity-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through activation of X-box binding protein-1 in mice[J]. Gut, 2012, 61(7): 1058-1067. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300269 |
| [22] |
NING J, HONG T, WARD A, et al. Constitutive role for IRE1α-XBP1 signaling pathway in the insulin-mediated hepatic lipogenic program[J]. Endocrinology, 2011, 152(6): 2247-2255. DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-1036 |
| [23] |
DONNELLY N, GORMAN AM, GUPTA S, et al. The eIF2α kinases: Their structures and functions[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2013, 70(19): 3493-3511. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1252-6 |
| [24] |
LAKE AD, NOVAK P, HARDWICK RN, et al. The adaptive endoplasmic reticulum stress response to lipotoxicity in progressive human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2014, 137(1): 26-35. DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kft230 |
| [25] |
XIAO G, ZHANG T, YU S, et al. ATF4 protein deficiency protects against high fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia in mice[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(35): 25350-25361. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470526 |
| [26] |
LI H, MENG Q, XIAO F, et al. ATF4 deficiency protects mice from high-carbohydrate-diet-induced liver steatosis[J]. Biochem J, 2011, 438(2): 283-289. DOI: 10.1042/BJ20110263 |
| [27] |
DEZWAAN-MCCABE D, SHELDON RD, GORECKI MC, et al. ER stress inhibits liver fatty acid oxidation while unmitigated stress leads to anorexia-induced lipolysis and both liver and kidney steatosis[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 19(9): 1794-1806. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.020 |
| [28] |
CHEN X, ZHANG F, GONG Q, et al. Hepatic ATF6 increases fatty acid oxidation to attenuate hepatic steatosis in mice through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α[J]. Diabetes, 2016, 65(7): 1904-1915. DOI: 10.2337/db15-1637 |
| [29] |
ALKHOURI N, CARTER-KENT C, FELDSTEIN AE. Apoptosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 5(2): 201-212. DOI: 10.1586/egh.11.6 |
| [30] |
ZHANG J, ZHANG H, DENG X, et al. Baicalin attenuates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing key regulators of lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in mice[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 192: 46-54. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.027 |
| [31] |
CAZANAVE SC, MOTT JL, BRONK SF, et al. Death receptor 5 signaling promotes hepatocyte lipoapoptosis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(45): 39336-39348. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.280420 |
| [32] |
MA ZW, LIU DX. Humanin decreases mitochondrial membrane permeability by inhibiting the membrane association and oligomerization of Bax and Bid proteins[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2018, 39(6): 1012-1021. DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.169 |
| [33] |
CAZANAVE SC, ELMI NA, AKAZAWA Y, et al. CHOP and AP-1 cooperatively mediate PUMA expression during lipoapoptosis[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2010, 299(1): g236-g243. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00091.2010 |
| [34] |
IURLARO R, MUÑOZ-PINEDO C. Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. FEBS J, 2016, 283(14): 2640-2652. DOI: 10.1111/febs.13598 |
| [35] |
SHEN X, LI LP. Progress in the relationship between apoptosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Dig Dis, 2014, 34(4): 245-248, 252. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2014.04.006 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
HIRSOVA P, GORES GJ. Death receptor-mediated cell death and proinflammatory signaling in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 1(1): 17-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2014.11.005 |
| [38] |
KAHRAMAN A, SCHLATTJAN M, KOCABAYOGLU P, et al. Major histocompatibility complex class I-related chains A and B (MIC A/B): A novel role in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(1): 92-102. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23253 |
| [39] |
PAN J, OU Z, CAI C, et al. Fatty acid activates NLRP3 inflammasomes in mouse Kupffer cells through mitochondrial DNA release[J]. Cell Immunol, 2018, 332: 111-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.08.006 |
| [40] |
REID DT, REYES JL, MCDONALD BA, et al. Kupffer cells undergo fundamental changes during the development of experimental NASH and are critical in initiating liver damage and inflammation[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(7): e0159524. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159524 |
| [41] |
BAECK C, WEHR A, KARLMARK KR, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury[J]. Gut, 2012, 61(3): 416-426. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300304 |
| [42] |
CASTANHEIRA F, KUBES P. Neutrophils and NETs in modulating acute and chronic inflammation[J]. Blood, 2019, 133(20): 2178-2185. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-11-844530 |
| [43] |
van der WINDT DJ, SUD V, ZHANG H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote inflammation and development of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(4): 1347-1360. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29914 |
| [44] |
IBUSUKI R, UTO H, ARIMA S, et al. Transgenic expression of human neutrophil peptide-1 enhances hepatic fibrosis in mice fed a choline-deficient, L-amino acid-defined diet[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33(10): 1549-1556. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12203 |
| [45] |
GOMEZ-SANTOS L, LUKA Z, WAGNER C, et al. Inhibition of natural killer cells protects the liver against acute injury in the absence of glycine N-methyltransferase[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56(2): 747-759. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25694 |
| [46] |
HIRSOVA P, IBRAHIM SH, KRISHNAN A, et al. Lipid-induced signaling causes release of inflammatory extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(4): 956-967. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.12.037 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
DENG ZB, LIU Y, LIU C, et al. Immature myeloid cells induced by a high-fat diet contribute to liver inflammation[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(5): 1412-1420. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23148 |
| [49] |
JIN J, LIU JX, YI M. Protective effect of berberine against hepatic lipid toxicity induced by high-fat diet in NAFLD mice and its related mechanism[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2019, 18(11): 1124-1128. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2019.11.002 |
| [50] |
IBRAHIM SH, HIRSOVA P, TOMITA K, et al. Mixed lineage kinase 3 mediates release of C-X-C motif ligand 10-bearing chemotactic extracellular vesicles from lipotoxic hepatocytes[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63(3): 731-744. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28252 |
| [51] |
KAKAZU E, MAUER AS, YIN M, et al. Hepatocytes release ceramide-enriched pro-inflammatory extracellular vesicles in an IRE1α-dependent manner[J]. J Lipid Res, 2016, 57(2): 233-245. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M063412 |



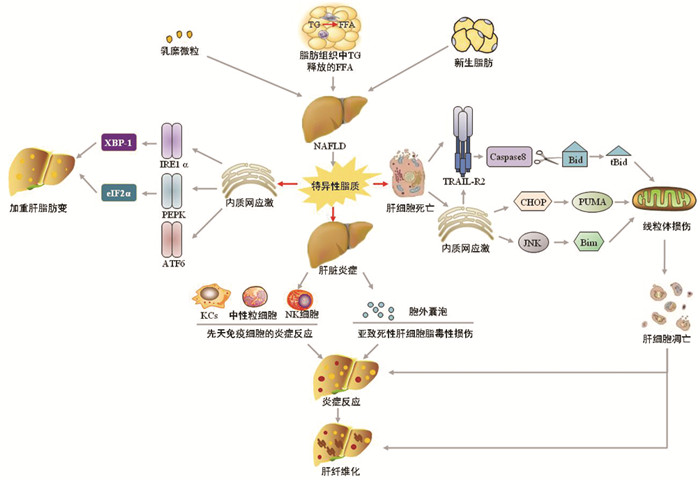




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: