| [1] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [2] |
SMOLDERS EJ, BURGER DM, FELD JJ, et al. Review article: Clinical pharmacology of current and investigational hepatitis B virus therapies[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 51(2): 231-243. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15581. |
| [3] |
HUI CK, LEUNG N, YUEN ST, et al. Natural history and disease progression in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients in immune-tolerant phase[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 46(2): 395-401. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21724. |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
SACKS LV, SHAMSUDDIN HH, YASINSKAYA YI, et al. Scientific and regulatory reasons for delay and denial of FDA approval of initial applications for new drugs, 2000-2012[J]. JAMA, 2014, 311(4): 378-384. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.282542. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
CORNBERG M, LOK AS, TERRAULT NA, et al. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B-Report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72(3): 539-557. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.11.003. |
| [8] |
RAJORIYA N, COMBET C, ZOULIM F, et al. How viral genetic variants and genotypes influence disease and treatment outcome of chronic hepatitis B. Time for an individualised approach?[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(6): 1281-1297. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.011. |
| [9] |
VERRIER ER, COLPITTS CC, SUREAU C, et al. Hepatitis B virus receptors and molecular drug targets[J]. Hepatol Int, 2016, 10(4): 567-573. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-016-9718-5. |
| [10] |
URBAN S, BARTENSCHLAGER R, KUBITZ R, et al. Strategies to inhibit entry of HBV and HDV into hepatocytes[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 147(1): 48-64. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.030. |
| [11] |
WEDEMEYER H, SCHÖNEWEIS K, BOGOMOLOV PO, et al. GS-13-Final results of a multicenter, open-label phase 2 clinical trial (MYR203) to assess safety and efficacy of myrcludex B in cwith PEG-interferon Alpha 2a in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(Suppl 1): e81. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0618827819301410 |
| [12] |
ZHANG M, ZHANG J, TAN Y, et al. SAT452-efficacy and safety of GLS4/ritonavir combined with entecavir in HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B: Interim results from phase 2b, multi-center study[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73: s878.
|
| [13] |
YUEN M, BERLIBA E, SUKEEPAISARNJAROEN W, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and antiviral activity of the capsid inhibitor (CI) AB-506 in healthy subjects (HS) and chronic hepatitis B (CHB) subjects[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(6): 1492A-1493A. http://hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/289899 |
| [14] |
BILLIOUD G, KRUSE RL, CARRILLO M, et al. In vivo reduction of hepatitis B virus antigenemia and viremia by antisense oligonucleotides[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(4): 781-789. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.032. |
| [15] |
PAN J, TONG S, KANG L, et al. New anti-hepatitis B virus drugs under development and evaluation[J]. Curr Opin Infect Dis, 2016, 29(6): 632-638. DOI: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000318. |
| [16] |
YUEN M, LOCARNINI S, GIVEN B, et al. First clinical experience with RNA interference[RNAi]-based triple combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B (CHB): JNJ-73763989(JNJ-3989), JNJ-56136379(JNJ-6379) and a nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA)[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(6): 1489A.
|
| [17] |
MENG Z, LU M. RNA Interference-induced innate immunity, off-target effect, or immune adjuvant?[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 331. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00331. |
| [18] |
NOORDEEN F, VAILLANT A, JILBERT AR. Nucleic acid polymers prevent the establishment of duck hepatitis B virus infection in vivo[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2013, 57(11): 5299-5306. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01005-13. |
| [19] |
VAILLANT A. Nucleic acid polymers: Broad spectrum antiviral activity, antiviral mechanisms and optimization for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection[J]. Antiviral Res, 2016, 133: 32-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.07.004. |
| [20] |
GOHIL V, MISNER D, CHANDA S, et al. The S-antigen transport-inhibiting polymer (STOPS (TM)) ALG-010133[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72: 508A.
|
| [21] |
BAZINET M, PÂNTEA V, PLACINTA G, et al. Safety and efficacy of 48 weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, tenofovir disoproxil, and pegylated interferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic HBV infection naïve to nucleos(t)ide therapy[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(8): 2180-2194. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.058. |
| [22] |
BARNES E. Therapeutic vaccines in HBV: Lessons from HCV[J]. Med Microbiol Immunol, 2015, 204(1): 79-86. DOI: 10.1007/s00430-014-0376-8. |
| [23] |
ZHANG E, KOSINSKA A, LU M, et al. Current status of immunomodulatory therapy in chronic hepatitis B, fifty years after discovery of the virus: Search for the "magic bullet" to kill cccDNA[J]. Antiviral Res, 2015, 123: 193-203. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.10.009. |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
GANE E, DUNBAR PR, BROOKS A, et al. AS071-efficacy and safety of 24 weeks treatment with oral TLR8 agonist, selgantolimod, in virally-suppressed adult patients with chronic hepatitis B: A phase 2 study[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73: s52.
|
| [26] |
BAUM P, ODEGARD V. ASGR1-TLR8. An ASGR1-directed TLR8 immunotac(TM) therapeutic, is a potent myeloid cell agonist with liver-localized activity for the treatment of chronic HBV[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72: 503A. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31039 |










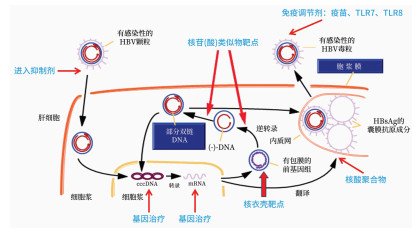




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: