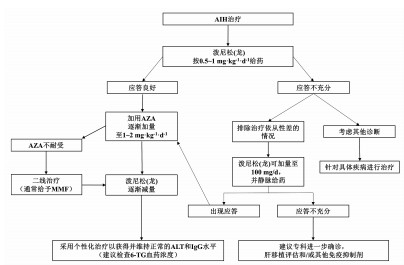
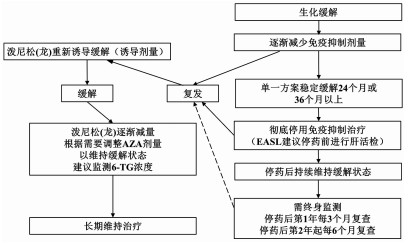
| [1] |
DANZIGER-ISAKOV L, KUMAR D, AST ID Community of Practice. Vaccination of solid organ transplant candidates and recipients: Guidelines from the American society of transplantation infectious diseases community of practice[J]. Clin Transplant, 2019, 33(9): e13563. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13563. |
| [2] |
LOOMBA R, LIANG TJ. Hepatitis B reactivation associated with immune suppressive and biological modifier therapies: Current concepts, management strategies, and future directions[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152(6): 1297-1309. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.009. |
| [3] |
TERRAULT NA, LOK A, McMAHON BJ, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(4): 1560-1599. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29800. |
| [4] |
REDDY KR, BEAVERS KL, HAMMOND SP, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(1): 215-219. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.039. |
| [5] |
PERRILLO RP, GISH R, FALCK-YTTER YT. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(1): 221-244. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.038. |
| [6] |
PATTULLO V. Prevention of hepatitis B reactivation in the setting of immunosuppression[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2016, 22(2): 219-237. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2016.0024. |
| [7] |
EBADI M, BHANJI RA, MAZURAK VC, et al. Severe vitamin D deficiency is a prognostic biomarker in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 49(2): 173-182. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15029. |
| [8] |
CZAJA AJ, MONTANO-LOZA AJ. Evolving role of vitamin D in immune-mediated disease and its implications in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2019, 64(2): 324-344. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-018-5351-6. |
| [9] |
American Gastroenterological Association. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: Osteoporosis in hepatic disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 125(3): 937-940. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)01060-6. |
| [10] |
JANIK MK, WUNSCH E, RASZEJA-WYSZOMIRSKA J, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis exerts a profound, negative effect on health-related quality of life: A prospective, single-centre study[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(1): 215-221. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13960. |
| [11] |
MIELI-VERGANI G, VERGANI D, CZAJA AJ, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4: 18017. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.17. |
| [12] |
WONG LL, FISHER HF, STOCKEN DD, et al. The impact of autoimmune hepatitis and its treatment on health utility[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(4): 1487-1497. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30031. |
| [13] |
SHEIKO MA, SUNDARAM SS, CAPOCELLI KE, et al. Outcomes in pediatric autoimmune hepatitis and significance of azathioprine metabolites[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2017, 65(1): 80-85. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001563. |
| [14] |
MANNS MP, WOYNAROWSKI M, KREISEL W, et al. Budesonide induces remission more effectively than prednisone in a controlled trial of patients with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 139(4): 1198-1206. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.046. |
| [15] |
HEMPFLING W, GRUNHAGE F, DILGER K, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic action of budesonide in early- and late-stage primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2003, 38(1): 196-202. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50266. |
| [16] |
PEISELER M, LIEBSCHER T, SEBODE M, et al. Efficacy and limitations of budesonide as a second-line treatment for patients with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16(2): 260-267. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.12.040. |
| [17] |
ZACHOU K, GATSELIS NK, ARVANITI P, et al. A real-world study focused on the long-term efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil as first-line treatment of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43(10): 1035-1047. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13584. |
| [18] |
NASTASIO S, SCIVERES M, MATARAZZO L, et al. Long-term follow-up of children and young adults with autoimmune hepatitis treated with cyclosporine[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51(5): 712-718. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.10.018. |
| [19] |
VAN THIEL DH, WRIGHT H, CARROLL P, et al. Tacrolimus: A potential new treatment for autoimmune chronic active hepatitis: Results of an open-label preliminary trial[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1995, 90(5): 771-776.
|
| [20] |
RAHIM MN, LIBERAL R, MIQUEL R, et al. Acute severe autoimmune hepatitis: Corticosteroids or liver transplantation?[J]. Liver Transpl, 2019, 25(6): 946-959. DOI: 10.1002/lt.25451. |
| [21] |
CZAJA AJ, CARPENTER HA. Autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndromes and liver pathology[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2017, 46(2): 345-364. DOI: 10.1016/j.gtc.2017.01.008. |
| [22] |
KUIPER EM, ZONDERVAN PE, van BUUREN HR. Paris criteria are effective in diagnosis of primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 8(6): 530-534. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.03.004. |
| [23] |
TRAN TT, AHN J, REAU NS. Corrigendum: ACG Clinical Guideline: Liver disease and pregnancy[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2016, 111(11): 1668. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2016.462. |
| [24] |
AKBARI M, SHAH S, VELAYOS FS, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the effects of thiopurines on birth outcomes from female and male patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2013, 19(1): 15-22. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.22948. |
| [25] |
COSCIA LA, ARMENTI DP, KING RW, et al. Update on the teratogenicity of maternal mycophenolate mofetil[J]. J Pediatr Genet, 2015, 4(2): 42-55. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1556743. |
| [26] |
TAUBERT R, HARDTKE-WOLENSKI M, NOYAN F, et al. Hyperferritinemia and hypergammaglobulinemia predict the treatment response to standard therapy in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(6): e0179074. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179074. |
| [27] |
HARTL J, EHLKEN H, WEILER-NORMANN C, et al. Patient selection based on treatment duration and liver biochemistry increases success rates after treatment withdrawal in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62(3): 642-646. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.018. |
| [28] |
GUIRGUIS J, ALONSO Y, LOPEZ R, et al. Well-controlled autoimmune hepatitis treatment withdrawal may be safely accomplished without liver-biopsy guidance[J]. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf), 2018, 6(4): 284-290. DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goy020. |
| [29] |
THAN NN, WIEGARD C, WEILER-NORMANN C, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with difficult to treat type 1 autoimmune hepatitis on Tacrolimus therapy[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2016, 51(3): 329-336. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2015.1095351. |
| [30] |
HVBENER S, OO YH, THAN NN, et al. Efficacy of 6-mercaptopurine as second-line treatment for patients with autoimmune hepatitis and azathioprine intolerance[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 14(3): 445-453. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.09.037. |
| [31] |
MACK CL, ADAMS D, ASSIS DN, et al. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis in adults and children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72(2): 671-722. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31065. |



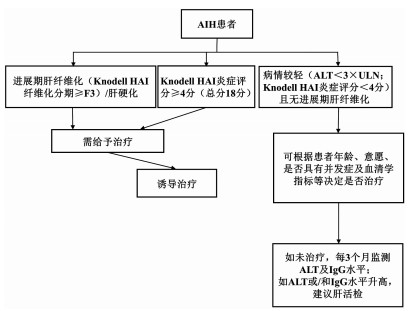




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: