| [1] |
THANDRA KC, BARSOUK A, SAGINALA K, et al. Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2020, 6(4): 289-294. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2020.102153. |
| [2] |
CHEN J, DENG X, LIU Y, et al. Kupffer cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Friend or foe?[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2020, 16(13): 2367-2378. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.47143. |
| [3] |
TACKE F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(6): 1300-1312. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026. |
| [4] |
YANG YM, KIM SY, SEKI E. Inflammation and liver cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2019, 39(1): 26-42. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1676806. |
| [5] |
FU XT, DAI Z, SONG K, et al. Macrophage-secreted IL-8 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3/Snail pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2015, 46(2): 587-596. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2761. |
| [6] |
ABDULLAH Z, KNOLLE PA. Liver macrophages in healthy and diseased liver[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2017, 469(3-4): 553-560. DOI: 10.1007/s00424-017-1954-6. |
| [7] |
LI P, HE K, LI J, et al. The role of Kupffer cells in hepatic diseases[J]. Mol Immunol, 2017, 85: 222-229. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.02.018. |
| [8] |
WANG Z, DABROSIN C, YIN X, et al. Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer prevention and therapy[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2015, 35(Suppl): s224-s243. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.01.001. |
| [9] |
MURAKAMI K, KASAJIMA A, KAWAGISHI N, et al. The prognostic significance of vasohibin 1-associated angiogenesis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol, 2014, 45(3): 589-597. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.10.028. |
| [10] |
XUE X, GAO W, SUN B, et al. Vasohibin 2 is transcriptionally activated and promotes angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(13): 1724-1734. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.177. |
| [11] |
LI XY, WU L, LI SW, et al. Effect of CD16a, the surface receptor of Kupffer cells, on the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37(6): 1465-1474. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2561. |
| [12] |
AKIBA J, YANO H, OGASAWARA S, et al. Expression and function of interleukin-8 in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Oncol, 2001, 18(2): 257-264. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.18.2.257. |
| [13] |
CHEN JA, SHI M, LI JQ, et al. Angiogenesis: Multiple masks in hepatocellular carcinoma and liver regeneration[J]. Hepatol Int, 2010, 4(3): 537-547. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-010-9192-4. |
| [14] |
JOO YY, JANG JW, LEE SW, et al. Circulating pro- and anti-angiogenic factors in multi-stage liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 9137. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-45537-w. |
| [15] |
MONNIER J, PIQUET-PELLORCE C, FEIGE JJ, et al. Prokineticin 2/Bv8 is expressed in Kupffer cells in liver and is down regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(8): 1182-1191. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1182. |
| [16] |
AKAZAWA Y, KONO H, HARA M, et al. M-CSF receptor antagonists inhibit the initiation and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(9): 4787-4794. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.13663. |
| [17] |
MALEHMIR M, PFISTER D, GALLAGE S, et al. Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(4): 641-655. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0379-5. |
| [18] |
YAN L, XU F, DAI CL. Relationship between epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and the inflammatory microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 203. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0887-z. |
| [19] |
WANG D, LUO L, CHEN W, et al. Significance of the vascular endothelial growth factor and the macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014, 31(3): 1199-1204. DOI: 10.3892/or.2013.2946. |
| [20] |
KLEMKE L, DE OLIVEIRA T, WITT D, et al. Hsp90-stabilized MIF supports tumor progression via macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(2): 155. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03426-z. |
| [21] |
BRODT P. Role of the microenvironment in liver metastasis: From pre- to prometastatic niches[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2016, 22(24): 5971-5982. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0460. |
| [22] |
MIYAZOE Y, MIUMA S, MIYAAKI H, et al. Extracellular vesicles from senescent hepatic stellate cells promote cell viability of hepatoma cells through increasing EGF secretion from differentiated THP-1 cells[J]. Biomed Rep, 2020, 12(4): 163-170. DOI: 10.3892/br.2020.1279. |
| [23] |
LI H, ZHOU Y, WANG H, et al. Crosstalk between liver macrophages and surrounding cells in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1169. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01169. |
| [24] |
RAMIREZ-PEDRAZA M, FERNÁNDEZ M. Interplay between macrophages and angiogenesis: A double-edged sword in liver disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2882. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02882. |
| [25] |
POISSON J, LEMOINNE S, BOULANGER C, et al. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(1): 212-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.009. |
| [26] |
MANZI M, BACIGALUPO ML, CARABIAS P, et al. Galectin-1 controls the proliferation and migration of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and their interaction with hepatocarcinoma cells[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2016, 231(7): 1522-1533. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25244. |
| [27] |
DAI S, LIU F, QIN Z, et al. Kupffer cells promote T-cell hepatitis by producing CXCL10 and limiting liver sinusoidal endothelial cell permeability[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(16): 7163-7177. DOI: 10.7150/thno.44960. |
| [28] |
UWATOKU R, SUEMATSU M, EZAKI T, et al. Kupffer cell-mediated recruitment of rat dendritic cells to the liver: Roles of N-acetylgalactosamine-specific sugar receptors[J]. Gastroenterology, 2001, 121(6): 1460-1472. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2001.29594. |
| [29] |
LO TH, SILVEIRA PA, FROMM PD, et al. Characterization of the expression and function of the C-type lectin receptor CD302 in mice and humans reveals a role in dendritic cell migration[J]. J Immunol, 2016, 197(3): 885-898. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600259. |
| [30] |
DI ROSA M, TIBULLO D, SACCONE S, et al. CHI3L1 nuclear localization in monocyte derived dendritic cells[J]. Immunobiology, 2016, 221(2): 347-356. DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.09.023. |
| [31] |
BAMBOAT ZM, OCUIN LM, BALACHANDRAN VP, et al. Conventional DCs reduce liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via IL-10 secretion[J]. J Clin Invest, 2010, 120(2): 559-69. DOI: 10.1172/JCI40008. |
| [32] |
HEFETZ-SELA S, STEIN I, KLIEGER Y, et al. Acquisition of an immunosuppressive protumorigenic macrophage phenotype depending on c-Jun phosphorylation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014, 111(49): 17582-17587. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1409700111. |
| [33] |
DOU L, SHI X, HE X, et al. Macrophage phenotype and function in liver disorder[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 3112. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03112. |
| [34] |
NOONAN A, PAWLIK TM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: An update on investigational drugs in phase I and Ⅱ clinical trials[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2019, 28(11): 941-949. DOI: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1677606. |
| [35] |
HUANG A, YANG XR, CHUNG WY, et al. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 146. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00264-x. |
| [36] |
RIZZO A, RICCI AD, BRANDI G. Immune-based combinations for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Shaping the direction of first-line therapy[J]. Future Oncol, 2021, 17(7): 755-757. DOI: 10.2217/fon-2020-0986. |
| [37] |
ABDELGALIL AA, ALKAHTANI HM, AL-JENOOBI FI. Sorafenib[J]. Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol, 2019, 44: 239-266. DOI: 10.1016/bs.podrm.2018.11.003. |
| [38] |
PICCIONI F, FIORE E, BAYO J, et al. 4-methylumbelliferone inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by decreasing IL-6 production and angiogenesis[J]. Glycobiology, 2015, 25(8): 825-835. DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwv023. |
| [39] |
FUKUMURA D, KLOEPPER J, AMOOZGAR Z, et al. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2018, 15(5): 325-340. DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.29. |
| [40] |
KIM CG, JANG M, KIM Y, et al. VEGF-A drives TOX-dependent T cell exhaustion in anti-PD-1-resistant microsatellite stable colorectal cancers[J]. Sci Immunol, 2019, 4(41): eaay0555. DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aay0555. |
| [41] |
DE GRAMONT A, FAIVRE S, RAYMOND E. Novel TGF-β inhibitors ready for prime time in onco-immunology[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2017, 6(1): e1257453. DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1257453. |
| [42] |
GRETEN TF, LAI CW, LI G, et al. Targeted and immune-based therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(2): 510-524. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.09.051. |



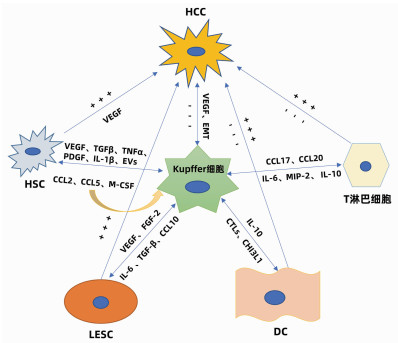




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: