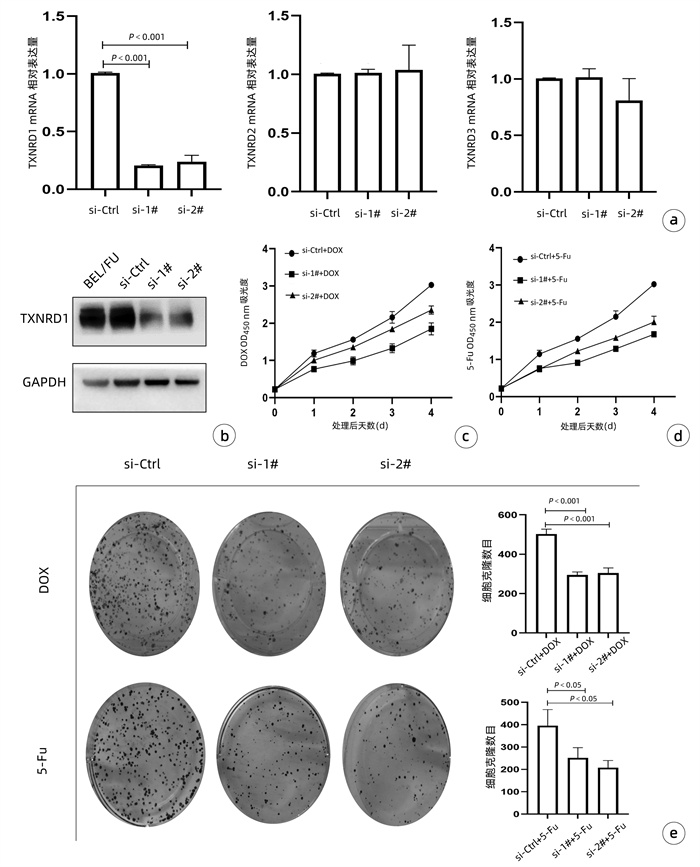
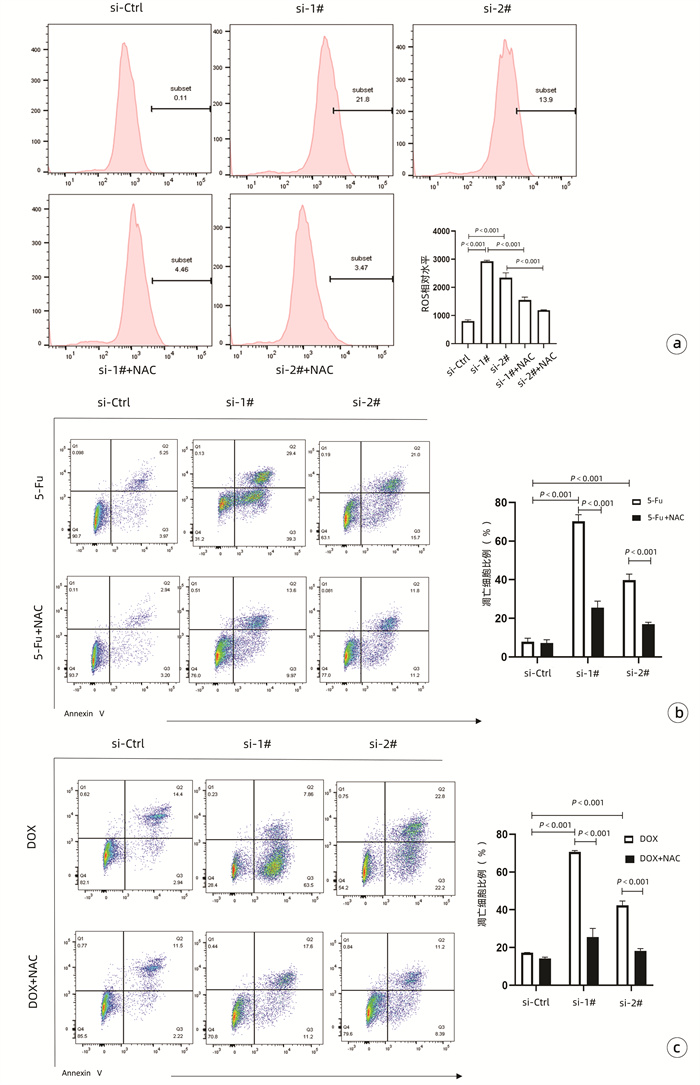
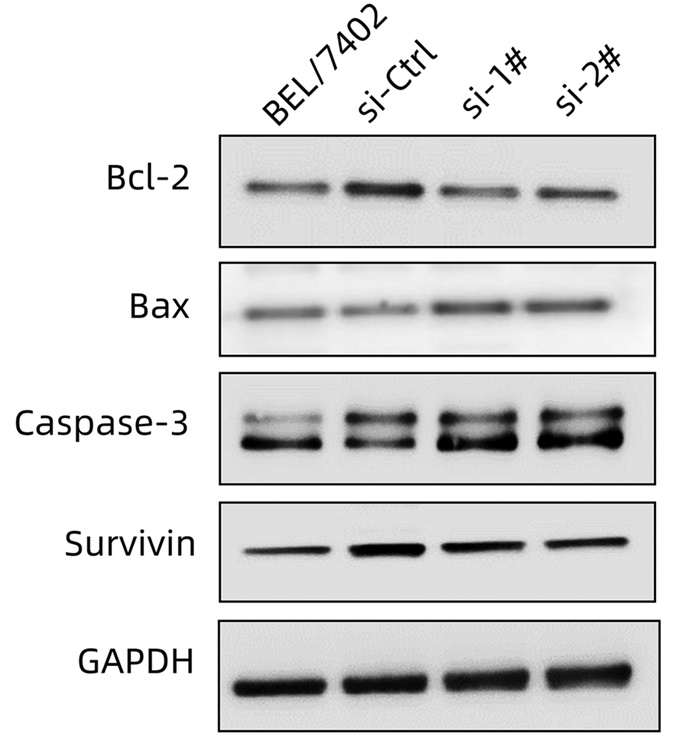
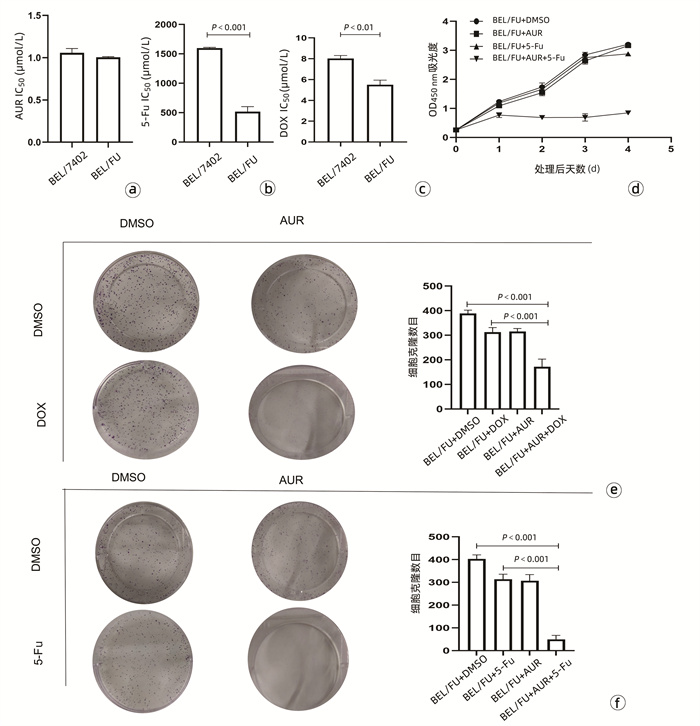
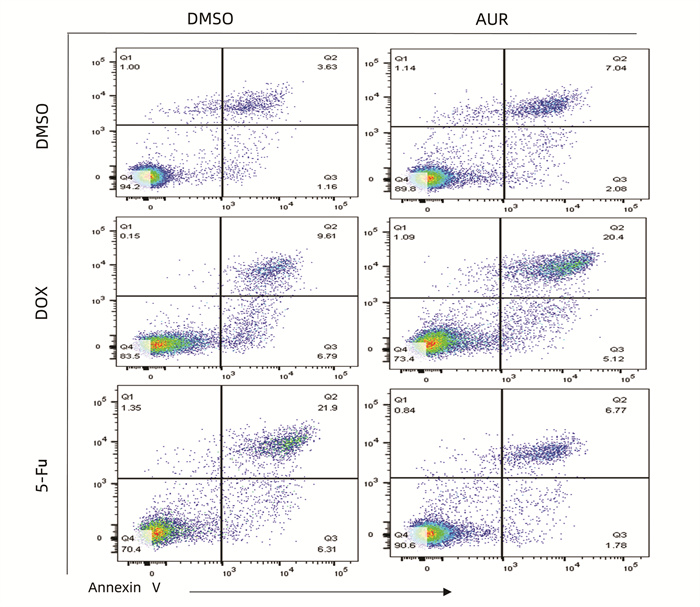
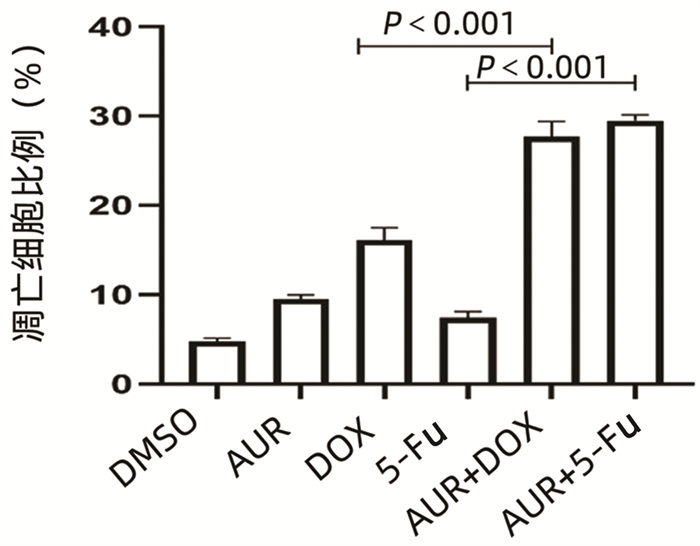
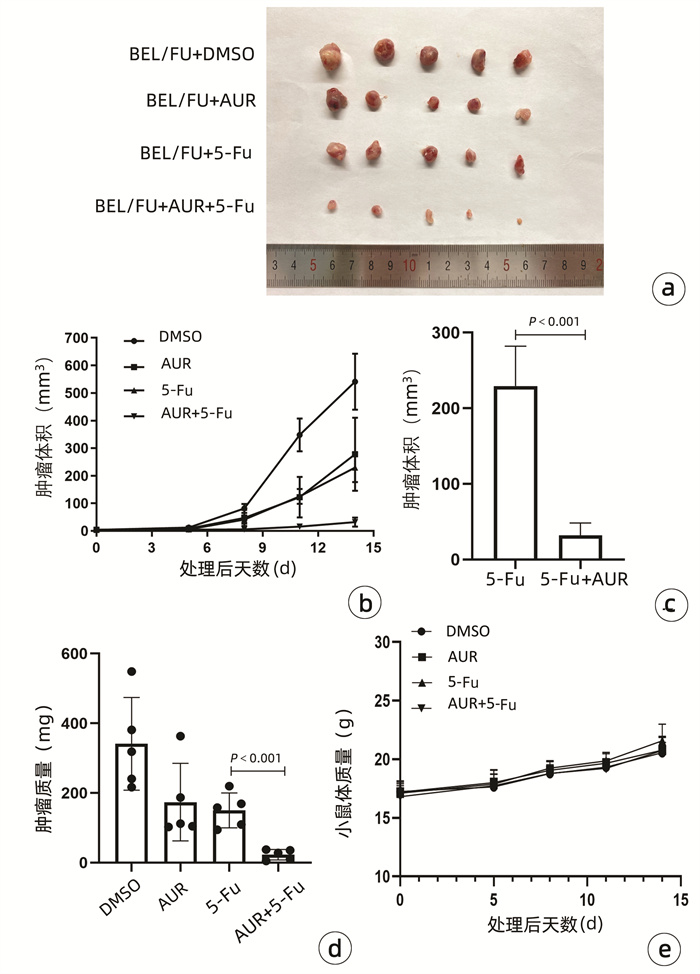
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
CHEN Z, XIE H, HU M, et al. Recent progress in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(9): 2993-3036.
|
| [3] |
SZAKÁCS G, PATERSON JK, LUDWIG JA, et al. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2006, 5(3): 219-234. DOI: 10.1038/nrd1984. |
| [4] |
BUKOWSKI K, KCIUK M, KONTEK R. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(9): 3233. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21093233. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
KUDRYAVTSEVA AV, KRASNOV GS, DMITRIEV AA, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in aging and cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(29): 44879-44905. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9821. |
| [7] |
JAKUBCZYK K, DEC K, KAŁDUŃSKA J, et al. Reactive oxygen species-sources, functions, oxidative damage[J]. Pol Merkur Lekarski, 2020, 48(284): 124-127.
|
| [8] |
AK IN-BAL I DF, AL-KHAFAJI K, AKTAS SH, et al. Bioinformatic and computational analysis for predominant mutations of the Nrf2/Keap1 complex in pediatric leukemia[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2021, 39(12): 4290-4303. DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1775702. |
| [9] |
GAO Q, ZHANG G, ZHENG Y, et al. SLC27A5 deficiency activates NRF2/TXNRD1 pathway by increased lipid peroxidation in HCC[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(3): 1086-1104. DOI: 10.1038/s41418-019-0399-1. |
| [10] |
HUANG S, ZHU X, KE Y, et al. LncRNA FTX inhibition restrains osteosarcoma proliferation and migration via modulating miR-320a/TXNRD1[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, 21(4): 379-387. DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1702405. |
| [11] |
PARK N, CHUN YJ. Auranofin promotes mitochondrial apoptosis by inducing annexin A5 expression and translocation in human prostate cancer cells[J]. J Toxicol Environ Health A, 2014, 77(22-24): 1467-1476. DOI: 10.1080/15287394.2014.955834. |
| [12] |
FU B, MENG W, ZENG X, et al. TXNRD1 is an unfavorable prognostic factor for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 4698167. DOI: 10.1155/2017/4698167. |
| [13] |
PRASAD S, GUPTA SC, TYAGI AK. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative nutraceuticals[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 387: 95-105. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.03.042. |
| [14] |
LIU N, GUO Z, XIA X, et al. Auranofin lethality to prostate cancer includes inhibition of proteasomal deubiquitinases and disrupted androgen receptor signaling[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 846: 1-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.01.004. |
| [15] |
LIOU GY, STORZ P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer[J]. Free Radic Res, 2010, 44(5): 479-496. DOI: 10.3109/10715761003667554. |
| [16] |
SEIFRIED HE, ANDERSON DE, SORKIN BC, et al. Free radicals: The pros and cons of antioxidants. Executive summary report[J]. J Nutr, 2004, 134(11): 3143S-3163S. DOI: 10.1093/jn/134.11.3143S. |
| [17] |
SUN C, ZHANG H, MA XF, et al. Isoliquiritigenin enhances radiosensitivity of HepG2 cells via disturbance of redox status[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2013, 65(3): 433-444. DOI: 10.1007/s12013-012-9447-x. |
| [18] |
LING S, LI J, SHAN Q, et al. USP22 mediates the multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma via the SIRT1/AKT/MRP1 signaling pathway[J]. Mol Oncol, 2017, 11(6): 682-695. DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12067. |
| [19] |
ZHOU Y, WANG Y, ZHOU W, et al. YAP promotes multi-drug resistance and inhibits autophagy-related cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma via the RAC1-ROS-mTOR pathway[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 179. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-0898-7. |
| [20] |
KIM NH, PARK HJ, OH MK, et al. Antiproliferative effect of gold(I) compound auranofin through inhibition of STAT3 and telomerase activity in MDA-MB 231 human breast cancer cells[J]. BMB Rep, 2013, 46(1): 59-64. DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.1.123. |
| [21] |
HWANG-BO H, JEONG JW, HAN MH, et al. Auranofin, an inhibitor of thioredoxin reductase, induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells by generation of reactive oxygen species[J]. Gen Physiol Biophys, 2017, 36(2): 117-128. DOI: 10.4149/gpb_2016043. |
| [22] |
LIU JJ, LIU Q, WEI HL, et al. Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase by auranofin induces apoptosis in adriamycin-resistant human K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells[J]. Pharmazie, 2011, 66(6): 440-444.
|
| [23] |
ZHENG Y, LIU Y, ZHAO S, et al. Large-scale analysis reveals a novel risk score to predict overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 6079-6096. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S181396. |
| [24] |
CARLSON BA, YOO MH, TOBE R, et al. Thioredoxin reductase 1 protects against chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis via control of cellular redox homeostasis[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2012, 33(9): 1806-1813. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs230. |
| [25] |
OZBEN T. Antioxidant supplementation on cancer risk and during cancer therapy: An update[J]. Curr Top Med Chem, 2015, 15(2): 170-178. DOI: 10.2174/1568026615666141209160918 |
| [26] |
CALAF GM, AGUAYO F, SERGI CM, et al. Antioxidants and cancer: Theories, techniques, and trials in preventing cancer[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 5363064. DOI: 10.1155/2018/5363064. |
| [27] |
KLEIN EA, THOMPSON IM Jr, TANGEN CM, et al. Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: The selenium and vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT)[J]. JAMA, 2011, 306(14): 1549-1556. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2011.1437. |
| [28] |
ARNÉR E. Targeting the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1 for anticancer therapy[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2017, 136: 139-151. DOI: 10.1016/bs.acr.2017.07.005. |



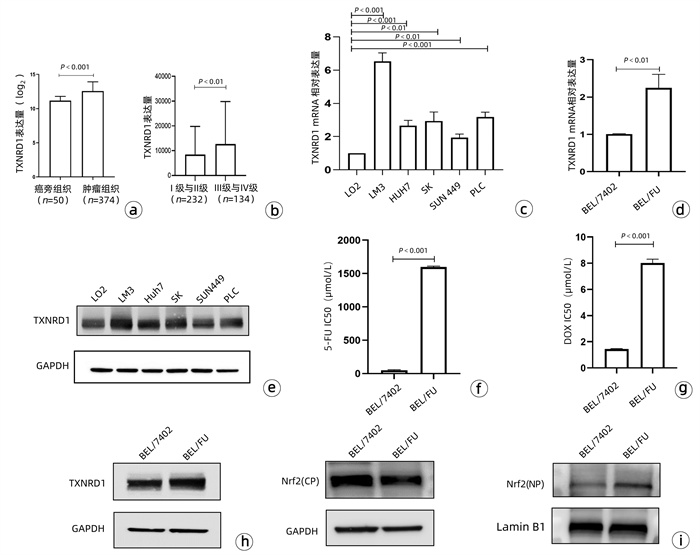




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: