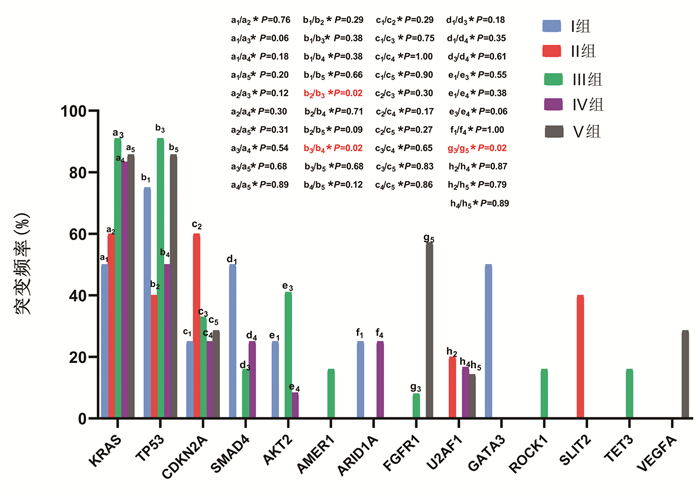
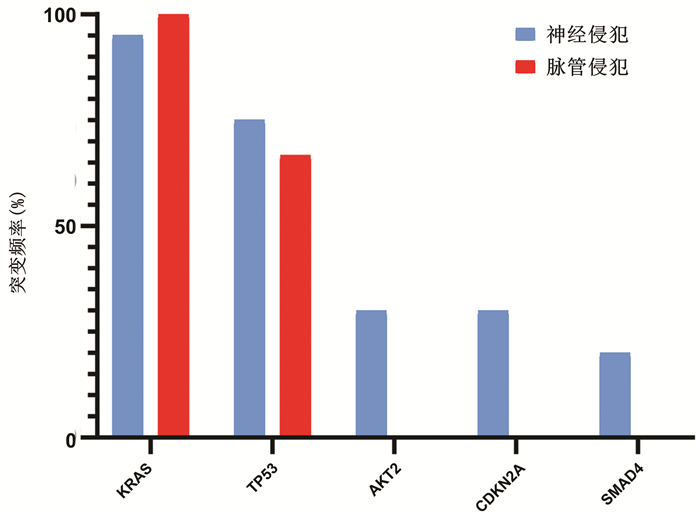
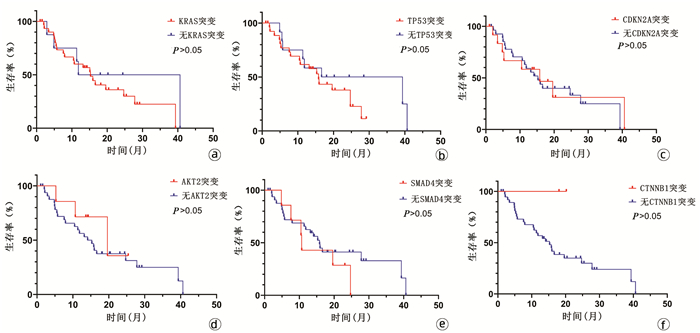
| [1] |
SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(1): 7-34. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21551. |
| [2] |
STEUER CE, RAMALINGAM SS. Tumor mutation burden: Leading immunotherapy to the era of precision medicine?[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(7): 631-632. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.8770. |
| [3] |
von HOFF DD, ERVIN T, ARENA FP, et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 369(18): 1691-1703. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1304369. |
| [4] |
CONROY T, PAILLOT B, FRANÇOIS E, et al. Irinotecan plus oxaliplatin and leucovorin-modulated fluorouracil in advanced pancreatic cancer—a Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of the Federation Nationale des Centres de Lutte Contre le Cancer study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2005, 23(6): 1228-1236. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2005.06.050. |
| [5] |
FRANCO J, WITKIEWICZ AK, KNUDSEN ES. CDK4/6 inhibitors have potent activity in combination with pathway selective therapeutic agents in models of pancreatic cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2014, 5(15): 6512-6525. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2270. |
| [6] |
OSHIMA M, OKANO K, MURAKI S, et al. Immunohistochemically detected expression of 3 major genes (CDKN2A/p16, TP53, and SMAD4/DPC4) strongly predicts survival in patients with resectable pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2013, 258(2): 336-346. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182827a65. |
| [7] |
BIANKIN AV, WADDELL N, KASSAHN KS, et al. Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes[J]. Nature, 2012, 491(7424): 399-405. DOI: 10.1038/nature11547. |
| [8] |
KAWAGUCHI K, IGARASHI K, MIYAKE K, et al. MEK inhibitor trametinib in combination with gemcitabine regresses a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) pancreatic cancer nude mouse model[J]. Tissue Cell, 2018, 52: 124-128. DOI: 10.1016/j.tice.2018.05.003. |
| [9] |
BOURNET B, BUSCAIL C, MUSCARI F, et al. Targeting KRAS for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of pancreatic cancer: Hopes and realities[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2016, 54: 75-83. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.11.012. |
| [10] |
MORTON JP, TIMPSON P, KARIM SA, et al. Mutant p53 drives metastasis and overcomes growth arrest/senescence in pancreatic cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107(1): 246-251. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908428107. |
| [11] |
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2017, 32(2): 185-203. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.07.007. |
| [12] |
WADDELL N, PAJIC M, PATCH AM, et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 495-501. DOI: 10.1038/nature14169. |
| [13] |
ORMANNS S, HAAS M, REMOLD A, et al. The impact of SMAD4 loss on outcome in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer treated with systemic chemotherapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(5): 1094. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18051094. |
| [14] |
XIA X, WU W, HUANG C, et al. SMAD4 and its role in pancreatic cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(1): 111-119. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-2883-z. |
| [15] |
CRANE CH, VARADHACHARY GR, YORDY JS, et al. Phase Ⅱ trial of cetuximab, gemcitabine, and oxaliplatin followed by chemoradiation with cetuximab for locally advanced (T4) pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Correlation of Smad4(Dpc4) immunostaining with pattern of disease progression[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(22): 3037-3043. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.8038. |
| [16] |
OTTENHOF NA, MORSINK FH, TEN KATE F, et al. Multivariate analysis of immunohistochemical evaluation of protein expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals prognostic significance for persistent Smad4 expression only[J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2012, 35(2): 119-126. DOI: 10.1007/s13402-012-0072-x. |
| [17] |
SHIN SH, KIM HJ, HWANG DW, et al. The DPC4/SMAD4 genetic status determines recurrence patterns and treatment outcomes in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A prospective cohort study[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(11): 17945-17959. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14901. |
| [18] |
CHENG JQ, RUGGERI B, KLEIN WM, et al. Amplification of AKT2 in human pancreatic cells and inhibition of AKT2 expression and tumorigenicity by antisense RNA[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1996, 93(8): 3636-3641. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3636. |
| [19] |
RUGGERI BA, HUANG L, WOOD M, et al. Amplification and overexpression of the AKT2 oncogene in a subset of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas[J]. Mol Carcinog, 1998, 21(2): 81-86.
|
| [20] |
CUI Y, WANG Q, WANG J, et al. Knockdown of AKT2 expression by RNA interference inhibits proliferation, enhances apoptosis, and increases chemosensitivity to the anticancer drug VM-26 in U87 glioma cells[J]. Brain Res, 2012, 1469: 1-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.06.043. |
| [21] |
NITULESCU GM, MARGINA D, JUZENAS P, et al. Akt inhibitors in cancer treatment: The long journey from drug discovery to clinical use (Review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2016, 48(3): 869-885. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3306. |
| [22] |
CHEN D, NIU M, JIAO X, et al. Inhibition of AKT2 enhances sensitivity to gemcitabine via regulating PUMA and NF-κB signaling pathway in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13(1): 1186-1208. DOI: 10.3390/ijms13011186. |
| [23] |
LIU Q, TURNER KM, ALFRED YUNG WK, et al. Role of AKT signaling in DNA repair and clinical response to cancer therapy[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2014, 16(10): 1313-1323. DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nou058. |
| [24] |
KORINEK V, BARKER N, MORIN PJ, et al. Constitutive transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin-Tcf complex in APC -/- colon carcinoma[J]. Science, 1997, 275(5307): 1784-1787. DOI: 10.1126/science.275.5307.1784. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
CLEVERS H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease[J]. Cell, 2006, 127(3): 469-480. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.018. |
| [27] |
SINGHI AD, GEORGE B, GREENBOWE JR, et al. Real-time targeted genome profile analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas identifies genetic alterations that might be targeted with existing drugs or used as biomarkers[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(8): 2242-2253. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.037. |
| [28] |
WEISS GJ, BLAYDORN L, BECK J, et al. Phase Ib/Ⅱ study of gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel, and pembrolizumab in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2018, 36(1): 96-102. DOI: 10.1007/s10637-017-0525-1. |

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: