| [1] |
Biliary Tract Group, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatolithiasis[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2007, 6(2): 156-161. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2007.02.028. |
| [2] |
CLEMENTE G, de ROSE AM, MURRI R, et al. Liver resection for primary intrahepatic stones: Focus on postoperative infectious complications[J]. World J Surg, 2016, 40(2): 433-439. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-015-3227-x. |
| [3] |
SUZUKI Y, MORI T, YOKOYAMA M, et al. Hepatolithiasis: Analysis of Japanese nationwide surveys over a period of 40 years[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2014, 21(9): 617-622. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.116. |
| [4] |
PENG JX, WANG LZ, DIAO JF, et al. Major hepatectomy for primary hepatolithiasis: A comparative study of laparoscopic versus open treatment[J]. Surg Endosc, 2018, 32(10): 4271-4276. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6176-2. |
| [5] |
PARK JS, JEONG S, LEE DH, et al. Risk factors for long-term outcomes after initial treatment in hepatolithiasis[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2013, 28(11): 1627-1631. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.11.1627. |
| [6] |
YANG Y, RUAN Y, RUAN XM. Analysis on incidence and risk factors of postoperative nosocomial infection in patients with hepatolithiasis[J]. Med & Pharm J Chin PLA, 2021, 33(1): 58-61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2021.01.013. |
| [7] |
GUO P, BIE P. Interpretation of expert consensus on application of choledochoscope in diagnosis and treatment of hepatolithiasis (2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(1): 57-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.012. |
| [8] |
SHANG D, ZHANG GX, ZHANG QK. Minimally invasive integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy for hepatolithiasis based on the SELECT concept[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(1): 31-35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.005. |
| [9] |
TSUI WM, LAM PW, LEE WK, et al. Primary hepatolithiasis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, and oriental cholangiohepatitis: A tale of 3 countries[J]. Adv Anat Pathol, 2011, 18(4): 318-328. DOI: 10.1097/PAP.0b013e318220fb75. |
| [10] |
MAKI T. Pathogenesis of calcium bilirubinate gallstone: Role of E. coli, beta-glucuronidase and coagulation by inorganic ions, polyelectrolytes and agitation[J]. Ann Surg, 1966, 164(1): 90-100. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-196607000-00010. |
| [11] |
TAJEDDIN E, SHERAFAT SJ, MAJIDI MR, et al. Association of diverse bacterial communities in human bile samples with biliary tract disorders: A survey using culture and polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis methods[J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2016, 35(8): 1331-1339. DOI: 10.1007/s10096-016-2669-x. |
| [12] |
JIMÉNEZ E, SÁNCHEZ B, FARINA A, et al. Characterization of the bile and gall bladder microbiota of healthy pigs[J]. Microbiologyopen, 2014, 3(6): 937-949. DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.218. |
| [13] |
MOLINERO N, RUIZ L, MILANI C, et al. The human gallbladder microbiome is related to the physiological state and the biliary metabolic profile[J]. Microbiome, 2019, 7(1): 100. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-019-0712-8. |
| [14] |
TABATA M, NAKAYAMA F. Bacteriology of hepatolithiasis[J]. Prog Clin Biol Res, 1984, 152: 163-174.
|
| [15] |
TURNBAUGH PJ, GORDON JI. An invitation to the marriage of metagenomics and metabolomics[J]. Cell, 2008, 134(5): 708-713. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.025. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
SHEEN-CHEN S, CHEN W, ENG H, et al. Bacteriology and antimicrobial choice in hepatolithiasis[J]. Am J Infect Control, 2000, 28(4): 298-301. DOI: 10.1067/mic.2000.107071. |
| [19] |
CHANG WT, LEE KT, WANG SR, et al. Bacteriology and antimicrobial susceptibility in biliary tract disease: An audit of 10-year's experience[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2002, 18(5): 221-228.
|
| [20] |
WU SD, YU H, SUN JM. Bacteriological and electron microscopic examination of primary intrahepatic stones[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2006, 5(2): 228-231.
|
| [21] |
LI SQ, LIANG LJ, HUA YP, et al. Bacterial spectrum of bile in patients with intrahepatic stone and its clinical significance[J/CD]. Chin Arch Gen Surg (Electronic Edition), 2009, 3(4): 313-316. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0793.2009.04.014. |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
CHEN AN, WANG H, ZHOU YN, et al. Supervision of the main pathogenic bacteria resistance rates and rationality analysis of antibacterial drugs usage in hepatolithiasis with biliary tract infection[J]. Acad J Guangdong Pharm Coll, 2017, 33(3): 388-392. DOI: 10.16809/j.cnki.2096-3653.2017011204. |
| [24] |
WU ZQ. The relationship between bile bacterial spectrum and postoperative infection in patients with intrahepatic bile duct stones[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2017.
吴樟强. 肝内胆管结石患者胆汁细菌谱与术后感染的关系[D]. 福州: 福建医科大学, 2017.
|
| [25] |
BAO WZ. The relationship between Helicobacter pylori and primary intrahepatic bile duct stones[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2006.
包文中. 幽门螺杆菌与原发性肝内胆管结石之间的关系[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2006.
|
| [26] |
BELZER C, KUSTERS JG, KUIPERS EJ, et al. Urease induced calcium precipitation by Helicobacter species may initiate gallstone formation[J]. Gut, 2006, 55(11): 1678-1679. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.098319. |
| [27] |
WU T. The relationship between the diversity of intestinal flora and biliary tract flora and gallstone disease[D]. Kunming: Kunming Medical University, 2014.
吴韬. 肠道菌群和胆道菌群多样性与胆石病的相关性研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2014.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
DOS SANTOS JS, JÚNIOR WS, MÓDENA JL, et al. Effect of preoperative endoscopic decompression on malignant biliary obstruction and postoperative infection[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2005, 52(61): 45-47.
|
| [30] |
KOSE SH, GRICE K, ORSI WD, et al. Metagenomics of pigmented and cholesterol gallstones: The putative role of bacteria[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 11218. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-29571-8. |
| [31] |
KIM B, PARK JS, BAE J, et al. Bile microbiota in patients with pigment common bile duct stones[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2021, 36(15): e94. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e94. |
| [32] |
XIAO Z, HUANG Z, GAO J, et al. The imbalance of biliary microflora in hepatolithiasis[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 157: 104966. DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104966. |
| [33] |
HUANG ZQ, YANG KZ, MENG XJ, et al. The significance of bile β-glucuronidase activity[J]. Chin J Surg, 1982, 20(1): 49-52.
黄志强, 杨可桢, 孟宪钧, 等. 胆汁β-葡萄糖醛酸酶活性的意义[J]. 中华外科杂志, 1982, 20(1): 49-52.
|
| [34] |
FAN HJ, TIAN DG, WEI XP. Advances in etiological mechanism and surgical treatment of recurrent intrahepatic bile duct stones[J]. Chin J New Clin Med, 2019, 12(9): 1029-1034. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3806.2019.09.27. |
| [35] |
YANG L, JUNMIN S, HONG Y, et al. PGE(2) induces MUC2 and MUC5AC expression in human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells via EP4/p38MAPK activation[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2013, 12(3): 479-486. DOI: 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31012-9 |
| [36] |
SHODA J, KANO M, ASANO T, et al. Secretory low-molecular-weight phospholipases A2 and their specific receptor in bile ducts of patients with intrahepatic calculi: Factors of chronic proliferative cholangitis[J]. Hepatology, 1999, 29(4): 1026-1036. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510290440. |
| [37] |
LI FY, CHENG NS, MAO H, et al. Significance of controlling chronic proliferative cholangitis in the treatment of hepatolithiasis[J]. World J Surg, 2009, 33(10): 2155-2160. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-009-0154-8. |
| [38] |
ZHANG Z. Detection of Hp infection and its related proteins and β-glucuronidase in gallbladder bile and mucosa in patients with gallbladder stones and its significance[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2007.
张震. 胆囊结石患者胆囊胆汁、粘膜中Hp感染与其相关蛋白和β-葡萄糖醛酸酶检测及其意义[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2007.
|
| [39] |
HAN J, WU S, FAN Y, et al. Biliary microbiota in choledocholithiasis and correlation with duodenal microbiota[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 625589. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.625589. |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
ZENG Y, XIAO LJ, YAO HH, et al. A study of the immune in formation of calcium bilirubinate gallstones in different rabbit models-The changes of the immunoglobulins in serum and bile and the immunoglobulins forming cells in the gallbladder mucoderm[J]. J West China Univ Med Sci, 2000, 31(2): 155-158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-173X.2000.02.009. |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
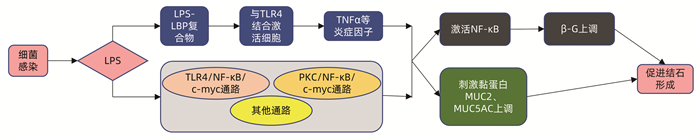
YAO CH. The role of LINC00311 in LPS-induced human intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells to activate the TLR4/NF-κB/c-myc signaling pathway to up-regulate the expression of endogenous β-glucuronidase[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2019.
姚晨辉. LINC00311在LPS诱导人肝内胆管上皮细胞激活TLR4/NF-κB/c-myc信号通路从而上调内源性β-葡萄糖醛酸酶表达过程中的作用[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2019.
|
| [45] |
YAO D, DONG Q, TIAN Y, et al. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates endogenous β-glucuronidase via PKC/NF-κB/c-myc signaling cascade: A possible factor in hepatolithiasis formation[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2018, 444(1-2): 93-102. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-017-3234-3. |
| [46] |
MANNE A, ESNAKULA A, ABUSHAHIN L, et al. Understanding the clinical impact of MUC5AC expression on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(12): 3059. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13123059. |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
SHEN Y, CHEN Z, WANG Y, et al. Aquaporin 5 expression inhibited by LPS via p38/JNK signaling pathways in SPC-A1 cells[J]. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2010, 171(3): 212-217. DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.03.021. |
| [49] |
LI M, TIAN Y, WU S, et al. LPS stimulates MUC5AC expression in human biliary epithelial cells: Whether there exists a possible pathway of PKC/NADPH/ROS?[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014, 385(1-2): 87-93. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-013-1817-1. |
| [50] |
WANG P, MA X, HE Y, et al. Effect of p38 mitogen-activate protein kinase on MUC5AC protein expression of bile duct epithelial cells in hepatolithiasis patients[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(10): 13753-13758.
|
| [51] |
KHARE A, GAUR S. Cholesterol-lowering effects of lactobacillus species[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2020, 77(4): 638-644. DOI: 10.1007/s00284-020-01903-w. |
| [52] |
RUIZ L, MARGOLLES A, SÁNCHEZ B. Bile resistance mechanisms in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium[J]. Front Microbiol, 2013, 4: 396. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00396. |
| [53] |
YE FQ. Metagenomics study of the biliary tract of patients with common bile duct stones and the intestines of Alzheimer's mice[D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Medical Sciences, 2016.
叶福强. 胆总管结石患者胆道和阿尔茨海默症小鼠肠道的宏基因组学研究[D]. 北京: 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院, 2016.
|
| [54] |
VÍTEK L, CAREY MC. New pathophysiological concepts underlying pathogenesis of pigment gallstones[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2012, 36(2): 122-129. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2011.08.010. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: